|
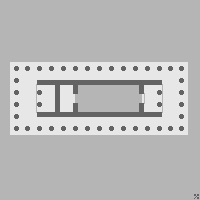
Hephaisteion
The Temple of Hephaestus or Hephaisteion (also "Hephesteum" or "Hephaesteum"; , , and formerly called in error the Theseion or "Theseum"; , ), is a well-preserved Greek temple dedicated to Hephaestus; it remains standing largely intact today. It is a Doric peripteral temple, and is located at the north-west side of the Agora of Athens, on top of the Agoraios Kolonos hill. From the 7th century until 1834, it served as the Greek Orthodox church of Saint George Akamates. The building's condition has been maintained due to its history of varied use. Name Hephaestus is the patron god of metal working, craftsmanship, and fire. There were numerous potters' workshops and metal-working shops in the vicinity of the temple, as befits the temple's honoree. Archaeological evidence suggests that there was no earlier building on the site except for a small sanctuary that was burned during the Second Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BCE. The name ''Theseion'' or Temple of Theseus was attri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthodomos
An opisthodomos (ὀπισθόδομος, 'back room') is either the rear room of an ancient Greek temple or to the inner shrine, also called the adyton ('not to be entered'). The confusion arises from the lack of agreement in ancient inscriptions. In modern scholarship, it usually refers to the rear porch of a temple. On the Athenian Acropolis especially, the opisthodomos came to be a treasury, where the revenues and precious dedications of the temple were kept. Its use in antiquity was not standardised. In part because of the ritual secrecy of such inner spaces, it is not known exactly what took place within opisthodomoi; it can safely be assumed that practice varied widely by place, date and particular temple. Architecturally, the opisthodomos (as a back room) balances the pronaos or porch of a temple, creating a plan with diaxial symmetry. The upper portion of its outer wall could be decorated with a frieze, as on the Hephaisteion and the Parthenon. Opisthodomoi are pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Temple
Greek temples (, semantically distinct from Latin , " temple") were structures built to house deity statues within Greek sanctuaries in ancient Greek religion. The temple interiors did not serve as meeting places, since the sacrifices and rituals dedicated to the deity took place outside them, within the wider precinct of the sanctuary, which might be large. Temples were frequently used to store votive offerings. They are the most important and most widespread surviving building type in Greek architecture. In the Hellenistic kingdoms of Southwest Asia and of North Africa, buildings erected to fulfill the functions of a temple often continued to follow the local traditions. Even where a Greek influence is visible, such structures are not normally considered as Greek temples. This applies, for example, to the Graeco-Parthian and Bactrian temples, or to the Ptolemaic examples, which follow Egyptian tradition. Most Greek temples were oriented astronomically. Between the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southernmost capital on the European mainland. With its urban area's population numbering over 3.6 million, it is the List of urban areas in the European Union, eighth-largest urban area in the European Union (EU). The Municipality of Athens (also City of Athens), which constitutes a small administrative unit of the entire urban area, had a population of 643,452 (2021) within its official limits, and a land area of . Athens is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years, and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BCE. According to Greek mythology the city was named after Athena, the ancient Greek goddess of wisdom, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Architecture
Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greeks, or Hellenes, whose Ancient Greece, culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Asia Minor, Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC. Ancient Greek architecture is best known for its Ancient Greek temple, temples, many of which are found throughout the region, with the Parthenon regarded, now as in ancient times, as the prime example. Most remains are very incomplete ruins, but a number survive substantially intact, mostly outside modern Greece. The second important type of building that survives all over the Hellenic world is the Theatre of Ancient Greece#Characteristics of the buildings, open-air theatre, with the earliest dating from around 525–480 BC. Other architectural forms that are still in evidence are the processional gateway (''propylon''), the public square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthenon
The Parthenon (; ; ) is a former Ancient Greek temple, temple on the Acropolis of Athens, Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the Greek gods, goddess Athena. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of classical Art in Ancient Greece, Greek art, and the Parthenon is considered an enduring symbol of Ancient Greece, democracy, and western culture, Western civilization. The Parthenon was built in the 5th century BC in thanksgiving for the Greek victory over the Achaemenid Empire, Persian invaders during the Greco-Persian Wars. Like most Greek temples, the Parthenon also served as the city treasury. Construction started in 447 BC when the Delian League was at the peak of its power. It was completed in 438 BC; work on the artwork and decorations continued until 432 BC. For a time, it served as the treasury of the Delian League, which later became the Athenian Empire. In the final decade of the 6th century AD, the Parthenon was converted into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peristyle
In ancient Ancient Greek architecture, Greek and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture, a peristyle (; ) is a continuous porch formed by a row of columns surrounding the perimeter of a building or a courtyard. ''Tetrastoön'' () is a rarely used archaic term for this feature. The peristyle in a Greek temple is a ''peristasis (architecture), peristasis'' (). In the Christian Church architecture, ecclesiastical architecture that developed from the Roman basilica, a courtyard peristyle and its garden came to be known as a cloister. Etymology The Greek word περίστυλον ''perístylon'' is composed of περί ''peri'', "around" or "surrounded", and στῦλος ''stylos'', "column" or "pillar", together meaning "surrounded by columns/pillars". It was Latinised into synonyms ''peristylum'' and ''peristylium''. In Greek architecture A peristyle was mostly used as a courtyard in Ancient Greece, but in the homes of people who were in the upper class or if they owned s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cella
In Classical architecture, a or naos () is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings: of a hermit's or monk's cell, and (since the 17th century) of a biological cell in plants or animals. Greek and Roman temples In ancient Greek and Roman temples, the ''cella'' was a room at the center of the building, usually containing a cult image or statue representing the particular deity venerated in the temple. In addition, the ''cella'' might contain a table to receive supplementary votive offerings, such as votive statues of associated deities, precious and semi-precious stones, helmets, spear and arrow heads, swords, and war trophies. No gatherings or sacrifices took place in the ''cella'', as the altar for sacrifices was always located outside the building along the axis and temporary altars for other deities were built next to it. The accumulated offerings made Greek and Roman temples virtual treasuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the '' cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as the ''cella''. The word ''pronaos'' () is Greek for "before a temple". In Latin, a pronaos is also referred to as an ''anticum'' or ''prodomus''. The pronaos of a Greek a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Hephaestus (South), Athens - 20070711
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in English, while those of other religions are not, even though they fulfill very similar functions. The religions for which the terms are used include the great majority of ancient religions that are now extinct, such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. Among religions still active: Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir or Kovil), Buddhism (whose temples are called Vihar), Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baháʼí Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baháʼí House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are often called Jinja), Confucia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parian Marble
Parian marble is a fine-grained, semi translucent, and pure-white marble quarried during the classical antiquity, classical era on the Greece, Greek List of islands of Greece, island of Paros in the Aegean Sea. A subtype, referred to as Parian ''lychnites'', was particularly notable in antiquity by ancient Greeks as a material for making sculptures. Some of the greatest masterpieces of ancient Greek sculpture were carved from Parian marble, including the ''Venus de' Medici, Medici Venus'', the ''Venus de Milo'', and the ''Winged Victory of Samothrace''. Archeological fieldwork on Paros has identified extensive ancient marble Open-pit mining, open-pit quarries, with the most significant sites being found at Chorodaki, Marathi, and Agios Minas. In addition to these open-pit quarries, shaft quarries were also used to mine Parian marble. There were two notable shafts in the valley of Agios Minas, identified as the "Grotto of the Nymphs" and the "Grotto of Pan" because of the relief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crepidoma
In classical Greek architecture, crepidoma () is the foundation of one or more steps on which the superstructure of a building is erected. Usually the crepidoma has three levels, especially in Doric temples. However, exceptions are common: For example, the Heraion at Olympia features only two steps, and the Olympeion at Agrigento, Sicily has four. Each level of crepidoma typically decreases in size incrementally going upwards, forming a series of steps along all or some sides of the building. The crepidoma rests on the euthynteria () or foundation, which historically was constructed of locally available stone for the sake of economy. The topmost level of the crepidoma is called the stylobate () and it is the platform for the columns ( - ). The lower levels of the crepidoma are called the stereobates. The step-like arrangement of the crepidoma may extend around all four sides of a structure like a temple, for example, on the Parthenon The Parthenon (; ; ) is a form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penteli
Penteli () is a village and a municipality in the North Athens regional unit, Attica, Greece. Belonging to the Athens rural area, it takes its name from Mount Pentelicus. Municipality The municipality Penteli was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 3 former municipalities, that became municipal units: * Melissia * Nea Penteli *Penteli Geography Penteli is situated on the southern slopes of the limestone Penteli mountains. The municipality has an area of 36.064 km2, the municipal unit Penteli 28.878 km2. It is 14 km northeast of central Athens. Some of the neighbourhoods of Penteli are Agia Triada, Agios Dimitrios, Daou and Kallithea. History The bones of prehistoric animals - mastodons, rhinoceros, antelope, and giraffe, along with giant turtles, hyenas and other animals no longer extant in the area - have been found among the limestone crags of the mountain that looms over the present suburb of Athens. The Penteli mountains were reno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |