|
Henry D. Coffinberry
Henry Darling Coffinberry (October 12, 1841 – January 17, 1912) was an American industrialist from Cleveland, Ohio. Along with his partner, Robert Wallace, H. D. Coffinberry is considered one of the founding fathers of modern Great Lakes shipping. Following a memorable Civil War career on the ironclad gunboat ''USS Louisville (1862), Louisville'', Coffinberry returned to civilian life in Cleveland, Ohio. There he met Robert Wallace and together they built the first iron- and steel-hulled freighters to be used on the Great Lakes. Coffinberry and Wallace were partners in both a foundry (Globe Iron Works) and a wooden shipbuilding firm, (Cleveland Dry Dock Company). Coffinberry became president of the Globe Ship Building Company in the early 1880s, which launched the first iron-hulled (''SS Onoko, Onoko'', 1882) and steel-hulled (''Spokane'', 1886) Great Lakes freighters. After selling their share to Marcus Alonzo Hanna, M. A. Hanna, Coffinberry and several partners left Globe in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maumee, Ohio
Maumee ( ) is a city in Lucas County, Ohio, United States. Located along the Maumee River, it is a suburb about southwest of Toledo, Ohio, Toledo. The population was 13,896 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Maumee was declared an All-America City by the National Civic League in June 2006. History In pre-colonial times, Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans (notably the Ottawa (tribe), Ottawa) began using the rich resources at the present site of Maumee, Ohio, in the Maumee River valley. Throughout much of the eighteenth century, French, British and American forces struggled for control of the lower Maumee River as a major transportation artery linking East and West through Lake Erie. Following the American Revolutionary War, Native Americans of the region, including the Odawa, Ojibwe and Potawatomie, and Shawnee, made alliances in what became called the Northwest Territory by the United States, which claimed it from the British after gaining indepen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
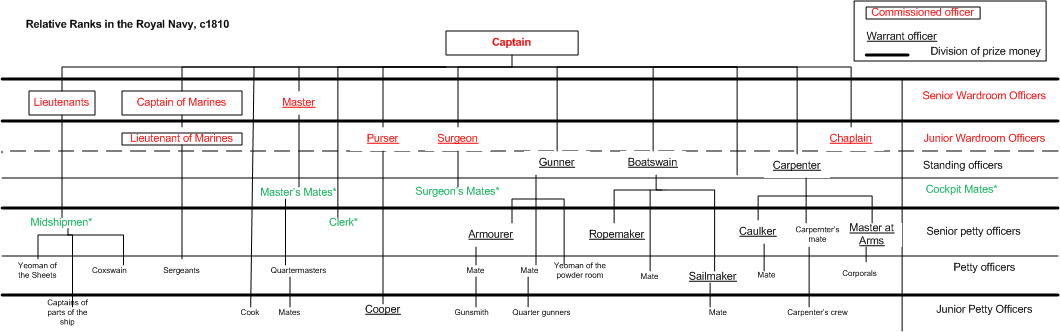
Master's Mate
Master's mate is an obsolete rating which was used by the British Royal Navy, Royal Navy, United States Navy and merchant services in both countries for a senior petty officer who assisted the sailing master, master. Master's mates evolved into the modern rank of sub-lieutenant in the Royal Navy, while in the merchant service they evolved into the numbered mates or officers. Royal Navy Originally, a master's mate was an experienced petty officer who assisted the sailing master, master but was not in line for promotion to lieutenant. By the mid-eighteenth century, he was far more likely to be a senior midshipman, still waiting to pass his examination for lieutenant or to receive his Commissioned officer#Commissioned officers, commission, but taking rather more responsibility aboard ship. Six master's mates were allowed on a First-rate, first rate, three on a Third-rate, third rate, and two on most frigates. Duties Master's mates were experienced seamen, and were usually selected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
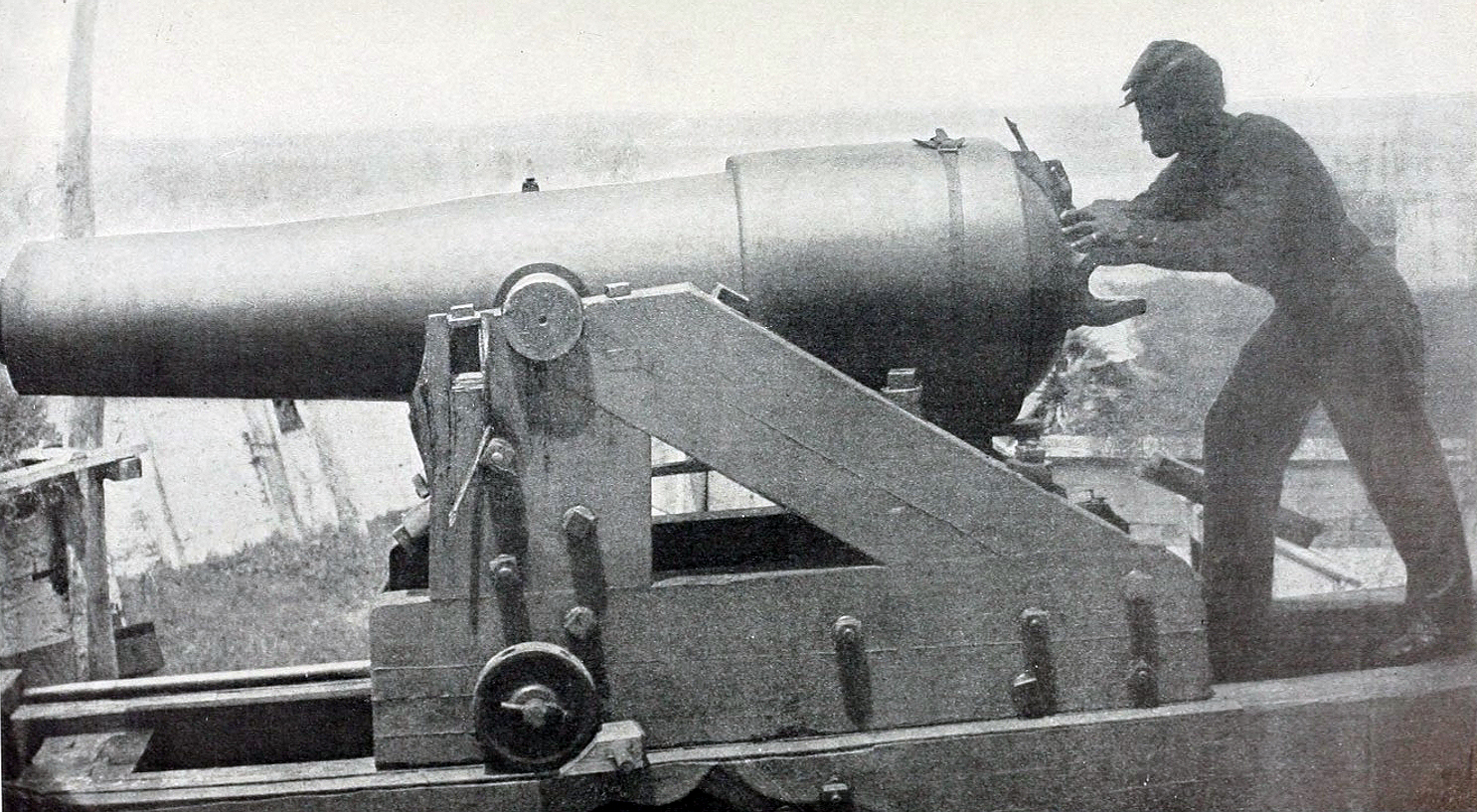
Dahlgren Gun
Dahlgren guns were muzzle-loading naval guns designed by a United States Navy Rear Admiral John A. Dahlgren (November 13, 1809 – July 12, 1870), mostly used in the American Civil War. Dahlgren's design philosophy evolved from an accidental explosion in 1849 of a gun being tested for accuracy, killing a gunner. He believed a safer, more powerful naval cannon could be designed using more scientific design criteria. Dahlgren guns were designed with a smooth curved shape, equalizing strain and concentrating more weight of metal in the gun breech where the greatest pressure of expanding propellant gases needed to be met to keep the gun from bursting. Because of their rounded contours, Dahlgren guns were nicknamed "soda bottles", a shape which became their most identifiable characteristic. Dahlgren boat howitzers During the Mexican–American War, the U.S. found itself lacking in light guns that could be fired from ships' boats and landed to be used as light artillery in suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parrott Rifle
The Parrott rifle was a type of muzzle-loading rifled artillery weapon used extensively in the American Civil War. Parrott rifle The gun was invented by Captain Robert Parker Parrott, a West Point graduate. He was an American soldier and inventor of military ordnance. He resigned from the service in 1836 and became the superintendent of the West Point Foundry in Cold Spring, New York. He created the first Parrott rifle (and corresponding projectile) in 1860 and patented it in 1861.. Daniel Treadwell, who developed a method for making built-up guns in the early 1840s, tried to claim that his patent infringed on an earlier one, but in 1866 United States District Court court dismissed it, deciding that Treadwell's claim was invalidated by a 1843 British patent to John Frith. Parrotts were manufactured with a combination of cast and wrought iron. The cast iron made for an accurate gun, but was brittle enough to suffer fractures. Hence, a large wrought iron reinforcing band was o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathaniel Prentice Banks
Nathaniel Prentice (or Prentiss) Banks (January 30, 1816 – September 1, 1894) was an American politician from Massachusetts and a Union general during the Civil War. A millworker, Banks became prominent in local debating societies and entered politics as a young adult. Initially a member of the Democratic Party, Banks's abolitionist views drew him to the nascent Republican Party, through which he won election to the United States House of Representatives and as Governor of Massachusetts in the 1850s. At the start of the 34th Congress, he was elected Speaker of the House in an election that spanned a record 133 ballots taken over the course of two months. At the outbreak of the Civil War, Abraham Lincoln appointed Banks as one of the first political major generals, over the heads of West Point regulars, who initially resented him, but came to acknowledge his influence on the administration of the war. After suffering a series of inglorious setbacks in the Shenandoah River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicksburg Campaign
The Vicksburg campaigns were a series of maneuvers and battles in the Western Theater of the American Civil War directed against Vicksburg, Mississippi, a fortress city that dominated the last Confederate-controlled section of the Mississippi River. The Union Army of the Tennessee under Major General Ulysses S. Grant gained control of the river by capturing this stronghold and defeating Lieutenant General John C. Pemberton's forces stationed there. The campaign consisted of many important naval operations, troop maneuvers, failed initiatives, and eleven distinct battles from December 26, 1862, to July 4, 1863. Military historians divide the campaign into two formal phases: operations against Vicksburg (December 1862 – January 1863) and Grant's operations against Vicksburg (March–July 1863). Grant initially planned a two-pronged approach in which half of his army, under Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman, would advance to the Yazoo River and attempt to reach Vicksburg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Grand Gulf
The Battle of Grand Gulf was fought on April 29, 1863, during the American Civil War. Union Army forces commanded by Major general (United States), Major General Ulysses S. Grant had failed several times to bypass or capture the Confederate States of America, Confederate-held city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, during the Vicksburg campaign. Grant decided to move his army south of Vicksburg, cross the Mississippi River, and then advance on the city. A Confederate States Army, Confederate Army division (military), division under Brigadier General (CSA), Brigadier General John S. Bowen prepared defenses—Forts Wade and Cobun—at Grand Gulf, Mississippi, south of Vicksburg. To clear the way for a Union crossing, seven Union Navy ironclad warships from the Mississippi Squadron commanded by Admiral (United States), Admiral David Dixon Porter bombarded the Confederate defenses at Grand Gulf on April 29. Union fire silenced Fort Wade and killed its commander, but the overall Confedera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Vicksburg
The siege of Vicksburg (May 18 – July 4, 1863) was the final major military action in the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Major General Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Mississippi River and drove the Confederate Army of Mississippi, led by Lieutenant General John C. Pemberton, into the defensive lines surrounding the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, leading to the successful siege and Confederate surrender. Vicksburg was the last major Confederate stronghold on the Mississippi River; therefore, capturing it completed the second part of the Northern strategy, the Anaconda Plan. When two major assaults against the Confederate fortifications, on May 19 and 22, were repulsed with heavy casualties, Grant decided to besiege the city beginning on May 25. After holding out for more than 40 days, with their supplies nearly gone, the garrison surrendered on July 4. The Vicksburg campaign's successfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fort Hindman
The Battle of Arkansas Post, also known as the Battle of Fort Hindman, was fought from January 9 to 11, 1863, along the Arkansas River at Arkansas Post, Arkansas, as part of the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. Confederate forces constructed Fort Hindman near Arkansas Post in late 1862. Also in late 1862, Major General John A. McClernand of the Union Army (as the United States Army was known during the war) was authorized to recruit troops in the Midwest in preparation for an expedition down the Mississippi River against Vicksburg, Mississippi. Union Major General Ulysses S. Grant began an overland campaign against Vicksburg along the Mississippi Central Railroad in November. Grant and Union General-in-Chief Henry Halleck did not trust McClernand, and through machinations placed the start of the riverine movement against Vicksburg under the command of Major General William T. Sherman before McClernand could arrive. Sherman's movement was defeated at the Battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Dixon Porter
David Dixon Porter (June 8, 1813 – February 13, 1891) was a United States Navy admiral (United States), admiral and a member of one of the most distinguished families in the history of the U.S. Navy. Promoted as the second U.S. Navy officer ever to attain the rank of admiral, after his adoptive brother David G. Farragut, Porter helped improve the Navy as the List of Superintendents of the United States Naval Academy, Superintendent of the United States Naval Academy, U.S. Naval Academy after significant service in the American Civil War. Porter began naval service as a midshipman at the age of 10 years under his father, Commodore David Porter (naval officer), David Porter, on the frigate . For the remainder of his life, he was associated with the sea. Porter served in the Mexican War in the attack on the fort at the City of Vera Cruz. At the outbreak of the Civil War, he was part of a plan to hold Fort Pickens, near Pensacola, Florida, for the Union; its execution disrupted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haines Bluff
Haines may refer to: *Haines (surname), ''includes partial list of people with the surname'' * Haines (character), a character in James Joyce's ''Ulysses'' Places Antarctica * Haines Glacier, Antarctica * Haines Mountains, mountain range in Antarctica Australia * Haines, South Australia, a locality on Kangaroo Island * Hundred of Haines, a cadastral unit in South Australia Canada * Haines Junction, Yukon, town in Yukon Territory, Canada :* Haines Junction Airport United States * Haines, Alaska, city in Haines Borough, Alaska, US :* Haines Airport, an airport in Haines, Alaska, US :* Haines Seaplane Base, a seaplane base in Haines, Alaska, US * Haines Borough, Alaska, US * Haines, Oregon, town in Baker County, Oregon, US * Haines City, Florida, city in Polk County, Florida, US * Haines Mission, an alternative name for Fort William H. Seward, Alaska, US * Haines Falls, New York, town in Greene County, New York, US * Haines Township, Pennsylvania, town in Centre County, Pennsylv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |