|
Henriques Street
The Whitechapel murders were committed in or near the impoverished Whitechapel district in the East End of London between 3 April 1888 and 13 February 1891. At various points some or all of these eleven unsolved murders of women have been ascribed to the notorious unidentified serial killer known as Jack the Ripper. Most, if not all, of the eleven victims—Emma Elizabeth Smith, Martha Tabram, Mary Ann "Polly" Nichols, Annie Chapman, Elizabeth Stride, Catherine Eddowes, Mary Jane Kelly, Rose Mylett, Alice McKenzie, Frances Coles, and an unidentified woman—were engaged in prostitution. Smith was sexually assaulted and robbed by a gang. Tabram was stabbed 39 times. Nichols, Chapman, Stride, Eddowes, Kelly, McKenzie and Coles had their throats cut. Eddowes and Stride were murdered on the same night, within approximately an hour and less than a mile apart; their murders are known as the "double event", after a phrase in a postcard sent to the press by someone claiming to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dismembered
Dismemberment is the act of completely disconnecting and/or removing the limbs, skin, and/or organs from a living or dead being. It has been practiced upon human beings as a form of capital punishment, especially in connection with regicide, but can occur as a result of a traumatic accident, or in connection with murder, suicide, or cannibalism. As opposed to surgical amputation of limbs, dismemberment is often fatal. In criminology, a distinction is made between offensive dismemberment, in which dismemberment is the primary objective of the dismemberer, and defensive dismemberment, in which the motivation is to destroy evidence. In 2019, American psychiatrists and medical professionals Michael H. Stone, Gary Brucato, and Ann Burgess proposed formal criteria by which "dismemberment" might be systematically distinguished from the act of mutilation, as these terms are commonly used interchangeably. They suggested that dismemberment involves "the entire removal, by any m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourpence (British Coin)
The British fourpence coin, sometimes known as a groat, "joey" or fourpenny bit, is a silver coin worth of one pound or of one shilling. It is a continuation of the English groat series struck intermittently from the late 13th century until the Acts of Union in 1707. The British groat was struck throughout the 18th century, though by 1800 it had come mostly to be coined to be given as ceremonial alms at the Royal Maundy service. It was resurrected as a circulating coin in 1836, as the Royal Mint sought to fill the gap between the penny and sixpence. The fourpence was chosen at the urging of the politician Joseph Hume, who noted that fourpence was the cab fare for short journeys. The new coin did not endear him to hackney drivers, who previously often received sixpence without a request for change, and they gave it the nickname "joey". There was also confusion between the groat and the sixpence. In 1845, the Royal Mint began to strike the threepenny bit for circulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Lodging-house
"Common lodging-house" is a Victorian era term for a form of cheap accommodation in which the inhabitants (who are not members of one family) are all lodged together in the same room or rooms, whether for eating or sleeping. The slang terms ''dosshouse'' (British English) and ''flophouse'' (North American English) designate roughly the equivalent of common lodging-houses. The nearest modern equivalent is a hostel. Great Britain There was no statutory definition of the class of houses in England intended to be included in the expression common lodging-house, but the definition used above was adopted to include those houses which, under the Public Health Act 1875 (38 & 39 Vict. c. 55) and other legislation, must be registered and inspected. The provisions of the Public Health Act were that every urban and rural district council must keep registers showing the names and residences of the keepers of all common lodging-houses in their districts, the location of every such house, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a British daily broadsheet conservative newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed in the United Kingdom and internationally. It was founded by Arthur B. Sleigh in 1855 as ''The Daily Telegraph and Courier''. ''The Telegraph'' is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. The paper's motto, "Was, is, and will be", was included in its emblem which was used for over a century starting in 1858. In 2013, ''The Daily Telegraph'' and ''The Sunday Telegraph'', which started in 1961, were merged, although the latter retains its own editor. It is politically conservative and supports the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party. It was moderately Liberalism, liberal politically before the late 1870s.Dictionary of Nineteenth Century Journalismp 159 ''The Telegraph'' has had a number of news scoops, including the outbreak of World War II by rookie reporter Clare Hollingworth, desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol Dependency
Alcohol dependence is a previous (DSM-IV and ICD-10) psychiatric diagnosis in which an individual is physically or psychologically dependent upon alcohol (also chemically known as ethanol). In 2013, it was reclassified as alcohol use disorder in DSM-5, which combined alcohol dependence and alcohol abuse into this diagnosis. Definition Diagnosis DSM: Alcohol dependence According to the DSM-IV criteria for alcohol dependence, at least three out of seven of the following criteria must be manifest during a 12-month period: * Tolerance * Withdrawal symptoms or clinically defined alcohol withdrawal syndrome * Use in larger amounts or for longer periods than intended * Persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to cut down on alcohol use * Time is spent obtaining alcohol or recovering from effects * Social, occupational and recreational pursuits are given up or reduced because of alcohol use * Use is continued despite knowledge of alcohol-related harm (physical or psychologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Anderson (police Official)
Sir Robert Anderson (29 May 1841 – 15 November 1918) was the second Assistant Commissioner (Crime) of the London Metropolitan Police, from 1888 to 1901. He was also an intelligence officer, theologian and writer. Early life and education Anderson was born in Mountjoy Square in Dublin, Ireland. His father, Matthew Anderson, was Crown Solicitor, a distinguished elder in the Presbyterian Church of Ireland, and of Ulster Scots descent. Matthew married Mary, daughter of Samuel Lee of Derry. Robert described himself as "an anglicised Irishman of Scottish extraction". His elder brother Samuel Lee Anderson was a successful barrister who invariably acted for the Crown, and like his brother also acted as an intelligence officer. Their sister Annie married Sir Walter Boyd, 1st Baronet, a dominant figure among the Irish judiciary in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, and a staunch upholder of British rule in Ireland. Annie played a key role in her brother's religious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
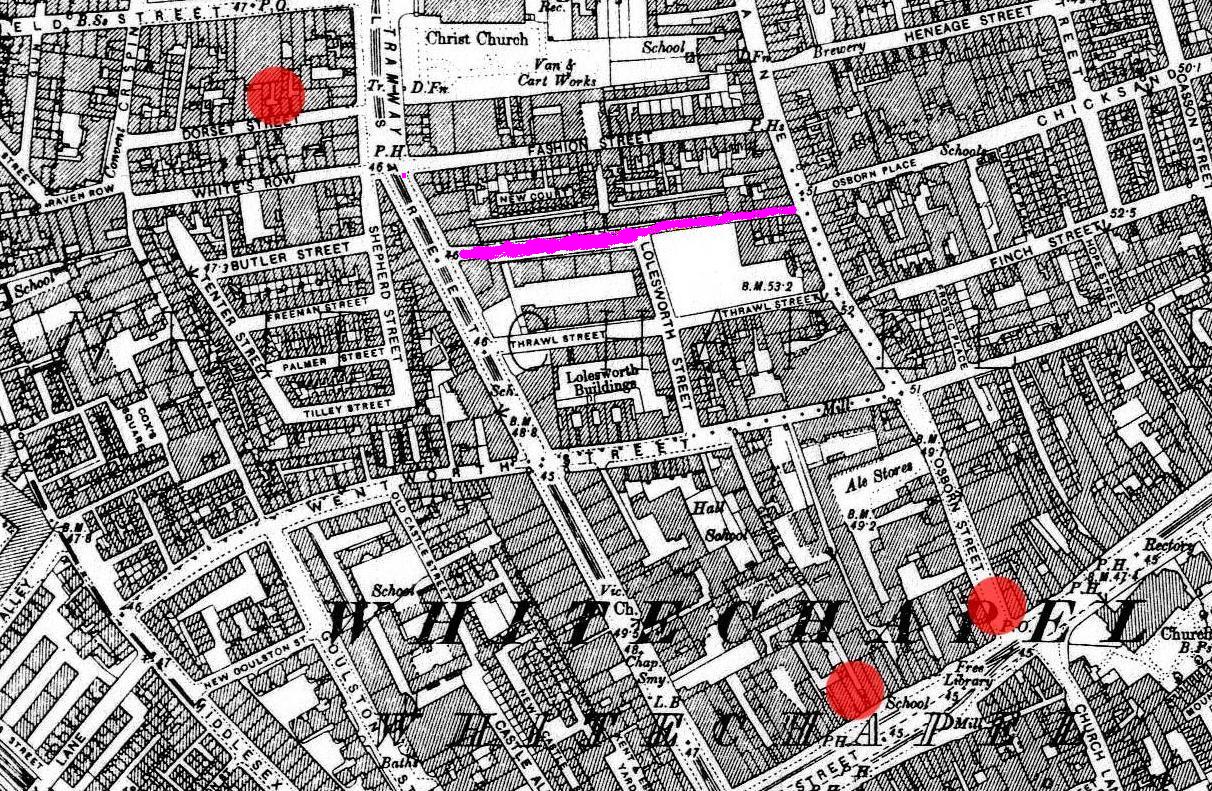
Dorset Street (Spitalfields)
Dorset Street, originally known as Datchet Street, was a street in Spitalfields, East London, once situated at the heart of the area's rookery. By repute it was "the worst street in London", and it was the scene of the brutal murder of Mary Jane Kelly by Jack the Ripper on 9 November 1888. The murder was committed at Kelly's lodgings which were situated at No. 13, Miller's Court, entered from a passageway between 26 and 27, Dorset Street. The road was renamed Duval Street in 1904, before having its north side demolished in 1928 during the rebuilding of Old Spitalfields Market, and the buildings on the south side replaced by a car park in the 1960s. The site was built over during redevelopment of the Fruit and Wool Exchange in the 2010s. History Laid out in 1674 and originally known as "Datchet Street" (probably from William Wheler of Datchet, who owned land in the area), it was given the name Dorset Street soon after. Locally, it was sometimes known as "Dosset Street" or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flower And Dean Street
Flower and Dean Street was a road at the heart of the Spitalfields rookery in the East End of London. It was one of the most notorious slums of the Victorian era, being described in 1883 as "perhaps the foulest and most dangerous street in the whole metropolis", and was closely associated with the victims of Jack the Ripper. Land was acquired by the Fossan brothers in the mid 17th century. At that time it consisted of the southern part of Lolesworth Field, a tenterground to its south and a spinning and twisting ground with gardens to the south of that. The brothers built a street through the field which was named after them, which became Fashion Street. They split the tenterground into two long parcels and employed two bricklayers, John Flower and Gowan Dean, to build houses along its length. By the nineteenth century the back gardens of the original tenements had been built on for narrow courts and alleys and the area had become a slum. The poverty and deprivation of the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rookery (slum)
A rookery, in the colloquial English of the 18th and 19th centuries, was a city slum occupied by poor people and frequently also by criminals and prostitutes. Such areas were overcrowded, with low-quality housing and little or no sanitation. Local industry such as coal plants and gasholders polluted the rookery air. Poorly constructed dwellings, built with multiple stories and often crammed into any area of open ground, created densely-populated areas of gloomy, narrow streets and alleyways. By many, these parts of the city were sometimes deemed "uninhabitable". Etymology The term rookery originated because of the perceived similarities between a city slum and the nesting habits of the rook, a bird in the crow family. Rooks nest in large, noisy colonies consisting of multiple nests, often untidily crammed into a close group of treetops called a rookery. The word might also be linked to the slang expression ''to rook'' (meaning to cheat or steal), a verb well established in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed the Georgian era and preceded the Edwardian era, and its later half overlaps with the first part of the ''Belle Époque'' era of continental Europe. Various liberalising political reforms took place in the UK, including expanding the electoral franchise. The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine caused mass death in Ireland early in the period. The British Empire had relatively peaceful relations with the other great powers. It participated in various military conflicts mainly against minor powers. The British Empire expanded during this period and was the predominant power in the world. Victorian society valued a high standard of personal conduct across all sections of society. The Victorian morality, emphasis on morality gave impetus to soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |