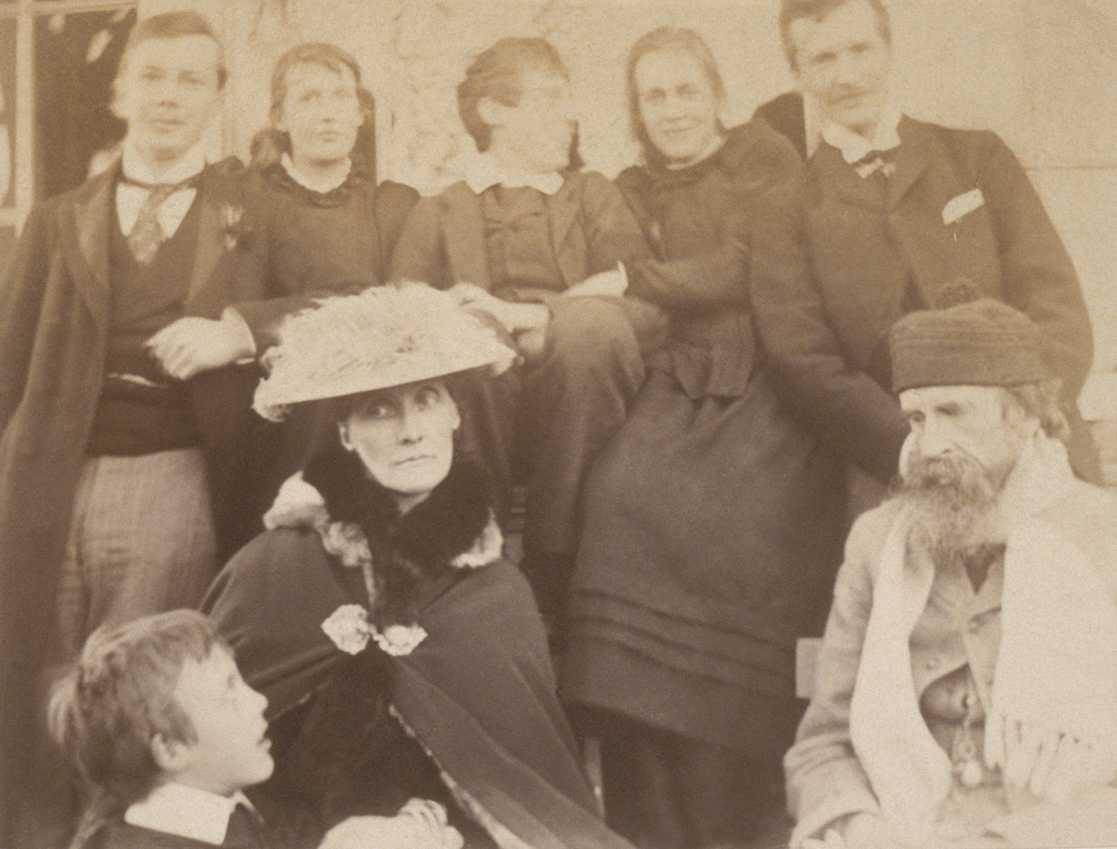|
Henrietta Bingham
Henrietta Bingham (January 3, 1901 – June 17, 1968) was a wealthy American journalist, newspaper executive and horse breeder. When she was twelve, she was present when her mother was killed in a road accident which traumatized the whole family. She subsequently developed a very close relationship with her father, who took a long time to recognize her lesbianism although eventually he became reconciled to her sexuality. In the 1920s she became an anglophile flapper and she associated with the Bloomsbury Group. In 1935 she purchased and ran a Kentucky estate for breeding thoroughbred racehorses. Her 1954 marriage, after a succession of partners, men and women, was unsuccessful. Early life Henrietta Worth Bingham was born in Louisville, Kentucky, on January 3, 1901, to Robert Worth Bingham (1871–1937), a lawyer who was an aspiring politician, and Eleanor "Babes" Miller (1870–1913) who had married in 1896. Her father's family had become prosperous in textiles and her mother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
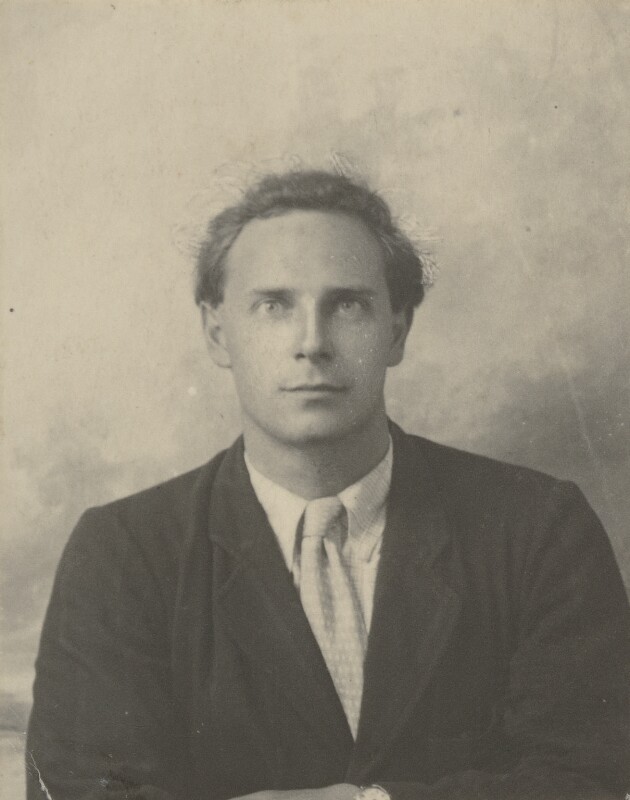
Stephen Tomlin
Stephen Tomlin (2 March 1901 – 5 January 1937) was a British artist associated with the Bloomsbury Group, Bloomsbury Set. He was the youngest son of the judge and law lord Thomas, Thomas Tomlin, Baron Tomlin, Lord Tomlin of Ash. Life Tomlin studied classics at New College, Oxford from January 1919. However, he suffered a nervous breakdown following the death of a fellow student and left after two terms. He then became a pupil of Frank Dobson (sculptor), Frank Dobson and later established a career as a portrait sculptor. Tomlin's circle of friends, and sitters for portraits, included many members of the Bloomsbury Group, particularly second generation members like Francis Birrell and David Garnett. Tomlin was bisexual and had affairs with a number of members of the Bloomsbury set including Henrietta Bingham and Dora Carrington. In 1927 he married Julia Strachey, niece of Lytton Strachey. His relationships with men are less well attested, probably due to the necessity of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Louisville Times
''The Louisville Times'' was a newspaper that was published in Louisville, Kentucky. It was founded in 1884 by Walter N. Haldeman, as the afternoon counterpart to ''The Courier-Journal'', the dominant morning newspaper in Louisville and the commonwealth of Kentucky for many years. The two newspapers published a combined edition (as the ''Courier-Journal & Times'') on Sundays. Both newspapers were later owned and operated by the Bingham family, headed for much of the 20th century by patriarch Barry Bingham, Sr. The ''Times'', which operated in the shadows of "The C-J" during most of its existence, nevertheless was a testing ground for many new ideas, usually involving design and typography. Another experiment under publisher Barry Bingham, Jr. was the idea of signed editorials. But like many other afternoon newspapers in America, circulation dwindled over the years as readers' lifestyles changed and television newscasts became more popular. In May 1986, the ''Times'' and the ''Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia Woolf
Adeline Virginia Woolf (; ; 25 January 1882 28 March 1941) was an English writer and one of the most influential 20th-century modernist authors. She helped to pioneer the use of stream of consciousness narration as a literary device. Virginia Woolf was born in South Kensington, London, into an affluent and intellectual family as the seventh child of Julia Prinsep Jackson and Leslie Stephen. She grew up in a blended household of eight children, including her sister, the painter Vanessa Bell. Educated at home in English classics and Victorian literature, Woolf later attended King’s College London, where she studied classics and history and encountered early advocates for women’s rights and education. After the death of her father in 1904, Woolf and her family moved to the bohemian Bloomsbury district, where she became a founding member of the influential Bloomsbury Group. She married Leonard Woolf in 1912, and together they established the Hogarth Press in 1917 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Partridge
Reginald Sherring Partridge, (1894 – 30 November 1960), generally known as Ralph Partridge, was a member of the Bloomsbury Group. He worked for Leonard Woolf and Virginia Woolf, married Dora Carrington and then Frances Marshall, and was the unrequited love of Lytton Strachey. Biography Partridge was born in 1894, the son of (William) Reginald Partridge, magistrate and collector of the North-Western Provinces and Oudh for the Indian Civil Service, and Jessie (née Sherring). His father was the son of a Devon solicitor while, on his mother's side, the Sherring family were clerics and Christian missionaries working in India at Varanasi. In his childhood Partridge had been known as 'Rex'.Frances Partridge: The Biography, Anne Chisholm, Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 2009 He was educated at Westminster School where he was Head Boy. Partridge won a scholarship to read Classics at Christ Church, Oxford, and rowed for Oxford University. He was commissioned during World War I, joining the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lytton Strachey
Giles Lytton Strachey (; 1 March 1880 – 21 January 1932) was an English writer and critic. A founding member of the Bloomsbury Group and author of ''Eminent Victorians'', he established a new form of biography in which psychology, psychological insight and sympathy are combined with irreverence and wit. His biography ''Queen Victoria'' (1921) was awarded the James Tait Black Memorial Prize. Early life and education Youth Strachey was born on 1 March 1880 at Stowey House, Clapham Common, London, the fifth son and 11th child of Lieutenant General Sir Richard Strachey, an officer in the British colonial armed forces, and his second wife, the former Jane Maria Strachey, Jane Grant, who became a leading supporter of the Women's suffrage in the United Kingdom, women's suffrage movement. He was named Giles Lytton after an early 16th-century Gyles Strachey and the Robert Bulwer-Lytton, 1st Earl of Lytton, first Earl of Lytton, who had been a friend of Richard Strachey's when he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Garnett
David Garnett (9 March 1892 – 17 February 1981) was an English writer and publisher. As a child, he had a cloak made of rabbit skin and thus received the nickname "Bunny", by which he was known to friends and intimates all his life. Early life Garnett was born in Brighton, East Sussex, the only child of writer, critic and publisher Edward Garnett and his wife Constance Clara Black, a translator of Russian. His paternal grandfather and great-grandfather both worked at what is now the British Library, then within the British Museum. Encouraged by his father, he gained his first paid work at the age of eleven, drawing a map entitled "NEW SEA and the BEVIS COUNTRY", signed "D. G. fecit", to illustrate a new edition of ''Bevis'', a boy's adventure story by Richard Jefferies. For this he received five shillings from the publisher Gerald Duckworth, for whom his father was a reader. He was then sent as a day boy to a prep school called Westerham, five miles from the Cearne, bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
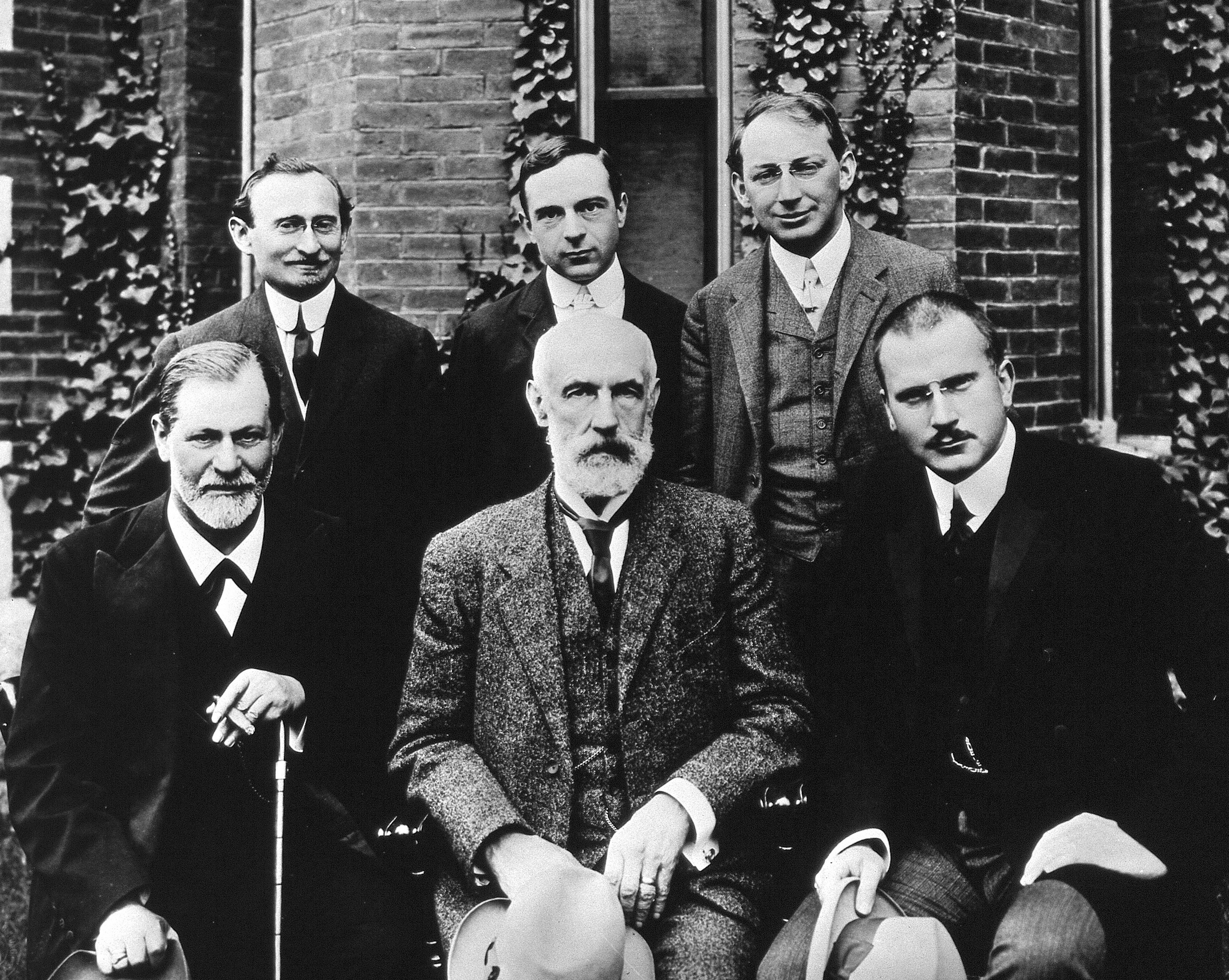
Freudian
Sigmund Freud ( ; ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating pathologies seen as originating from conflicts in the psyche, through dialogue between patient and psychoanalyst, and the distinctive theory of mind and human agency derived from it. Freud was born to Galician Jewish parents in the Moravian town of Freiberg, in the Austrian Empire. He qualified as a doctor of medicine in 1881 at the University of Vienna. Upon completing his habilitation in 1885, he was appointed a docent in neuropathology and became an affiliated professor in 1902. Freud lived and worked in Vienna having set up his clinical practice there in 1886. Following the German annexation of Austria in March 1938, Freud left Austria to escape Nazi persecution. He died in exile in the United Kingdom in 1939. In founding psychoanalysis, Freud developed therapeutic techniques su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Jones
Alfred Ernest Jones (1 January 1879 – 11 February 1958) was a Welsh neurologist and psychoanalyst. A lifelong friend and colleague of Sigmund Freud from their first meeting in 1908, he became his official biographer. Jones was the first English-speaking practitioner of psychoanalysis and became its leading exponent in the English-speaking world. As President of both the International Psychoanalytical Association and the British Psycho-Analytical Society in the 1920s and 1930s, Jones exercised a formative influence in the establishment of their organisations, institutions and publications. Early life and career Ernest Jones was born in Gowerton (formerly Ffosfelin), Wales, an industrial village on the outskirts of Swansea, the first child of Thomas and Ann Jones. His father was a self-taught colliery engineer who went on to establish himself as a successful businessman, becoming accountant and company secretary at the Elba Steelworks in Gowerton. His mother, Mary Ann (né ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcassonne
Carcassonne is a French defensive wall, fortified city in the Departments of France, department of Aude, Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania. It is the prefectures in France, prefecture of the department. Inhabited since the Neolithic Period, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the Aude (river), Aude between historic trade routes, linking the Atlantic to the Mediterranean Sea and the Massif Central to the Pyrénées. Its strategic importance was quickly recognised by the Ancient Rome, Romans, who occupied its hilltop until the demise of the Western Roman Empire. In the fifth century, the region of Septimania was taken over by the Visigoths, who founded the city of Carcassonne in the newly established Visigothic Kingdom. Its citadel, known as the Cité de Carcassonne, is a medieval fortress dating back to the Roman Gaul, Gallo-Roman period and restored by the theorist and architect Eugène Viollet-le-Duc between 1853 and 1879. It was adde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaperone (social)
A chaperone (also spelled chaperon) in its original social usage was a person who for propriety's sake accompanied an unmarried girl in public; usually she was an older married woman, and most commonly the girl's own mother. In modern social usage, a chaperon (frequent in British spelling) or chaperone (usual in American spelling) is a responsible adult who accompanies and supervises young people. By extension, the word chaperone is used in clinical contexts. Origin The word derives figuratively from the French word ''chaperon'' (originally from the Late Latin ''cappa'', meaning "cape"), which referred to a hood that was worn by individuals generally. A chaperone was part of the costume of the Knights of the Garter when they were in full dress and, probably, since the Knights were court attendants, the word ''chaperon'' changed to mean escort. An alternative explanation comes from the sport of falconry, where the word meant the hood placed over the head of a bird of prey t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshman
A freshman, fresher, first year, or colloquially frosh, is a person in the first year at an educational institution, usually a secondary school or at the college and university level, but also in other forms of post-secondary educational institutions. Albania In Albania the freshman/woman is called "fruth", which literally means "measles". The etymology of it is "a person that has not yet passed the social measles", social measles referring to the transformation of social skills that usually takes place in the first year of university. Freshmen/women are regarded as socially inept. Arab world In much of the Arab world, a first-year is called a (; plural , ), which is Arabic for "beginner". Brazil In Brazil, students that pass the vestibulares and begin studying in a college or university are called "calouros" or more informally "bixos" ("bixetes" for girls), an alternate spelling of "bicho", which means "animal" (although commonly used to refer to bugs). Calouros are of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modernist
Modernism was an early 20th-century movement in literature, visual arts, and music that emphasized experimentation, abstraction, and Subjectivity and objectivity (philosophy), subjective experience. Philosophy, politics, architecture, and social issues were all aspects of this movement. Modernism centered around beliefs in a "growing Marx's theory of alienation, alienation" from prevailing "morality, optimism, and Convention (norm), convention" and a desire to change how "social organization, human beings in a society interact and live together". The modernist movement emerged during the late 19th century in response to significant changes in Western culture, including secularization and the growing influence of science. It is characterized by a self-conscious rejection of tradition and the search for newer means of cultural expressions, cultural expression. Modernism was influenced by widespread technological innovation, industrialization, and urbanization, as well as the cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |