|
Hemipristis Serra
''Hemipristis serra'' is an extinct species of weasel shark which existed during the Miocene epoch. It was described by Louis Agassiz in 1843. While today's snaggletooth shark is not very large or dangerous, ''Hemipristis serra'', which lived in the Atlantic Ocean during the Oligocene and Miocene, was considerably larger than its modern-day relative and had much larger teeth. Its total length is estimated to be . Marks made by the teeth of ''H. serra'' are often found on the bones of the dugong ''Metaxytherium'' leading some scientists to hypothesize that ''H. serra'' specialized in preying on these sirenians. In the Gatun Formation of Panama, ''H. serra'' was contemporary with pups of the large lamniform shark ''Otodus megalodon'', and both it and the great hammerhead The great hammerhead (''Sphyrna mokarran'') is the largest species of hammerhead shark, belonging to the family Sphyrnidae, attaining an average length of and reaching a maximum length of . It is found in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Agassiz
Jean Louis Rodolphe Agassiz ( ; ) FRS (For) FRSE (May 28, 1807 – December 14, 1873) was a Swiss-born American biologist and geologist who is recognized as a scholar of Earth's natural history. Spending his early life in Switzerland, he received a PhD at Erlangen and a medical degree in Munich. After studying with Georges Cuvier and Alexander von Humboldt in Paris, Agassiz was appointed professor of natural history at the University of Neuchâtel. He emigrated to the United States in 1847 after visiting Harvard University. He went on to become professor of zoology and geology at Harvard, to head its Lawrence Scientific School, and to found its Museum of Comparative Zoology. Agassiz is known for observational data gathering and analysis. He made institutional and scientific contributions to zoology, geology, and related areas, including multivolume research books running to thousands of pages. He is particularly known for his contributions to ichthyological classification, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemipristis Serra
''Hemipristis serra'' is an extinct species of weasel shark which existed during the Miocene epoch. It was described by Louis Agassiz in 1843. While today's snaggletooth shark is not very large or dangerous, ''Hemipristis serra'', which lived in the Atlantic Ocean during the Oligocene and Miocene, was considerably larger than its modern-day relative and had much larger teeth. Its total length is estimated to be . Marks made by the teeth of ''H. serra'' are often found on the bones of the dugong ''Metaxytherium'' leading some scientists to hypothesize that ''H. serra'' specialized in preying on these sirenians. In the Gatun Formation of Panama, ''H. serra'' was contemporary with pups of the large lamniform shark ''Otodus megalodon'', and both it and the great hammerhead The great hammerhead (''Sphyrna mokarran'') is the largest species of hammerhead shark, belonging to the family Sphyrnidae, attaining an average length of and reaching a maximum length of . It is found in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemipristis Serra Snaggettoth Shark Teeth 007
''Hemipristis'' (from , 'half' and 'saw') is a genus of weasel sharks, family Hemigaleidae. It contains one extant species, the snaggletooth shark (''H. elongata'') and several extinct species. ''Hemipristis'' has two distinct types of teeth in each section of its jaw. The ones on the upper jaw act as knives, cutting through the flesh of the prey, while the pointed ones on the bottom act as forks, spearing the prey and holding it down. Because this shark was poorly studied in the past and its top and bottom jaw teeth differ to such a great degree, its top and lower jaw teeth were assigned to a separate genus in the past. Species * '' Hemipristis elongata'' ( Klunzinger, 1871) * †'' Hemipristis curvatus'' Dames, 1883 * †''Hemipristis serra'' Agassiz, 1835 - An extinct species from the Oligocene-Miocene of Florida, South Carolina, and other areas on the Atlantic coast. * †'' Hemipristis tanakai'' Tomita ''et. al.'', 2023 - Rupelian of Japan See also * List of prehistoric c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemigaleidae
The weasel sharks are a family, the Hemigaleidae, of ground sharks found from the eastern Atlantic Ocean to the continental Indo-Pacific. They are found in shallow coastal waters to a depth of . Most species are small, reaching no more than long, though the snaggletooth shark (''Hemipristis elongatus'') may reach . They have horizontally oval eyes, small spiracles, and precaudal pits. Two dorsal fins occur with the base of the first placed well forward of the pelvic fins. The caudal fin has a strong ventral lobe and undulations on the dorsal lobe margin. They feed on a variety of small bony fishes and invertebrates; at least two species specialize on cephalopods. They are not known to have attacked people. Genera and species The eight known species in this family are placed in four genera. ''Hemipristis'' is placed in the subfamily Hemipristinae, while ''Chaenogaleus'', ''Hemigaleus'', and ''Paragaleus'' are placed in the subfamily Hemigaleinae.Haaramo, M. (2005)Hemigaleidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaxytherium
''Metaxytherium'' is an extinct genus of dugong that lived from the Oligocene until the end of the Pliocene. Fossil remains have been found in Africa, Europe, North America and South America. Generally marine seagrass specialists, they inhabited the warm and shallow waters of the Paratethys, Mediterranean, Caribbean Sea and Pacific coastline. American species of ''Metaxytherium'' are considered to be ancestral to the North Pacific family Hydrodamalinae, which includes the giant Steller's sea cow. Discovery and naming The first remains of ''Metaxytherium'' were described in 1822 by Anselme-Gaëtan Demarest as a species of Hippopotamus, Hippo, ''H. medius'' before the genus name ''Metaxytherium'' was coined in 1840 by De Christol. Although the type species was initially designated to be ''M. cuvieri'', later publications argued that the two species are synonymous and ''M. medium'' thus holds precedence. The grammatical changes of the species name were made to match the rules of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirenian
The Sirenia (), commonly referred to as sea cows or sirenians, are an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit swamps, rivers, estuaries, marine wetlands, and coastal marine waters. The extant Sirenia comprise two distinct families: Dugongidae (the dugong and the now extinct Steller's sea cow) and Trichechidae (manatees, namely the Amazonian manatee, West Indian manatee, and West African manatee) with a total of four species. The Protosirenidae (Eocene sirenians) and Prorastomidae (terrestrial sirenians) families are extinct. Sirenians are classified in the clade Paenungulata, alongside the elephants and the hyraxes, and evolved in the Eocene 50 million years ago (mya). The Dugongidae diverged from the Trichechidae in the late Eocene or early Oligocene (30–35 mya). Sirenians grow to between in length and in weight. The recently extinct Steller's sea cow was the largest known sirenian to have lived, reaching lengths of and weights of . Sirenians have a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
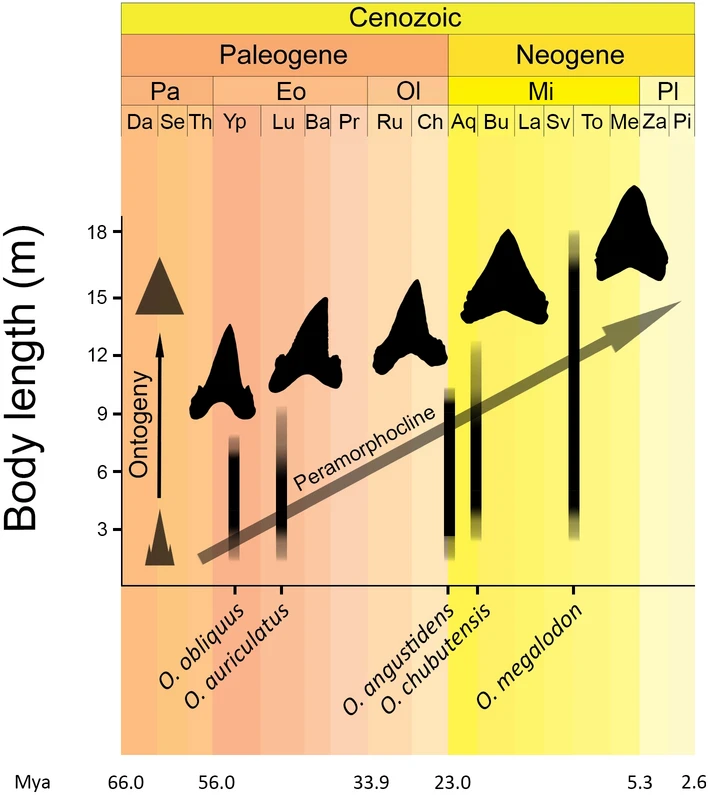
Megalodon
''Otodus megalodon'' ( ; meaning "big tooth"), Common name, commonly known as megalodon, is an extinction, extinct species of giant mackerel shark that lived approximately 23 to 3.6 million years ago (Mya), from the Early Miocene to the Early Pliocene epochs. ''O. megalodon'' was formerly thought to be a member of the family (biology), family Lamnidae and a close relative of the great white shark (''Carcharodon carcharias''), but has been reclassified into the extinct family Otodontidae, which Speciation, diverged from the great white shark during the Early Cretaceous. While regarded as one of the largest and most powerful predators to have ever lived, megalodon is only known from fragmentary remains, and its appearance and maximum size are uncertain. Scientists have argued whether its body form was more stocky or elongated than the modern lamniform sharks. Maximum body length estimates between based on various analyses have been proposed, though the Mode (statistics), modal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Hammerhead
The great hammerhead (''Sphyrna mokarran'') is the largest species of hammerhead shark, belonging to the family Sphyrnidae, attaining an average length of and reaching a maximum length of . It is found in tropical and warm temperate waters worldwide, inhabiting coastal areas and the continental shelf. The great hammerhead can be distinguished from other hammerheads by the shape of its "hammer" (called the "cephalofoil"), which is wide with an almost straight front margin, and by its tall, sickle-shaped first dorsal fin. A solitary, strong-swimming apex predator, the great hammerhead feeds on a wide variety of prey ranging from crustaceans and cephalopods, to bony fish, to smaller sharks. Observations of this species in the wild suggest that the cephalofoil functions to immobilize stingrays, a favored prey. This species has a viviparous mode of reproduction, bearing litters of up to 50 pups every two years. Although potentially dangerous, the great hammerhead rarely shark attack, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Animals Of Indonesia
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its last member. A taxon may become functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to reproduce and recover. As a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of speciation. Species become extinct when they are no longer able to survive in changing conditions or against superio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemipristis
''Hemipristis'' (from , 'half' and 'saw') is a genus of weasel sharks, family Hemigaleidae. It contains one extant species, the snaggletooth shark (''H. elongata'') and several extinct species. ''Hemipristis'' has two distinct types of teeth in each section of its jaw. The ones on the upper jaw act as knives, cutting through the flesh of the prey, while the pointed ones on the bottom act as forks, spearing the prey and holding it down. Because this shark was poorly studied in the past and its top and bottom jaw teeth differ to such a great degree, its top and lower jaw teeth were assigned to a separate genus in the past. Species * '' Hemipristis elongata'' ( Klunzinger, 1871) * †'' Hemipristis curvatus'' Dames, 1883 * †''Hemipristis serra'' Agassiz, 1835 - An extinct species from the Oligocene-Miocene of Florida, South Carolina, and other areas on the Atlantic coast. * †'' Hemipristis tanakai'' Tomita ''et. al.'', 2023 - Rupelian of Japan See also * List of prehistoric c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |