|
Hemagglutination
Hemagglutination, or haemagglutination, is a specific form of agglutination that involves red blood cells (RBCs). It has two common uses in the laboratory: blood typing and the quantification of virus dilutions in a haemagglutination assay. Blood typing Blood type can be determined by using antibodies that bind to the A or B blood group antigens in a sample of blood. For example, if antibodies that bind the A blood group are added and agglutination occurs, the blood is either type A or type AB. To determine between type A or type AB, antibodies that bind the B group are added and if agglutination does not occur, the blood is type A. If agglutination does not occur with either antibodies that bind to type A or type B antigens, then neither antigen is present on the blood cells, which means the blood is type O. In blood grouping, the patient's serum is tested against RBCs of known blood groups and also the patient's RBCs are tested against known serum types. In this way th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemagglutination Assay
The hemagglutination assay or haemagglutination assay (HA) and the hemagglutination inhibition assay (HI or HAI) were developed in 1941–42 by American virologist George Hirst as methods for quantifying the relative concentration of viruses, bacteria, or antibodies. HA and HAI apply the process of hemagglutination, in which sialic acid receptors on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs) bind to the hemagglutinin glycoprotein found on the surface of influenza virus (and several other viruses) and create a network, or lattice structure, of interconnected RBCs and virus particles. The agglutinated lattice maintains the RBCs in a suspended distribution, typically viewed as a diffuse reddish solution. The formation of the lattice depends on the concentrations of the virus and RBCs, and when the relative virus concentration is too low, the RBCs are not constrained by the lattice and settle to the bottom of the well. Hemagglutination is observed in the presence of staphylococci, vibrios, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agglutination (biology)
Agglutination is the clumping of particles. The word ''agglutination'' comes from the Latin '' agglutinare'' (glueing to). Agglutination is a reaction in which particles (as red blood cells or bacteria) suspended in a liquid collect into clumps usually as a response to a specific antibody. This occurs in biology in two main examples: # The clumping of cells such as bacteria or red blood cells in the presence of an antibody or complement. The antibody or other molecule binds multiple particles and joins them, creating a large complex. This increases the efficacy of microbial elimination by phagocytosis as large clumps of bacteria can be eliminated in one pass, versus the elimination of single microbial antigens. # When people are given blood transfusions of the wrong blood group, the antibodies react with the incorrectly transfused blood group and as a result, the erythrocytes clump up and stick together causing them to agglutinate. The coalescing of small particles that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
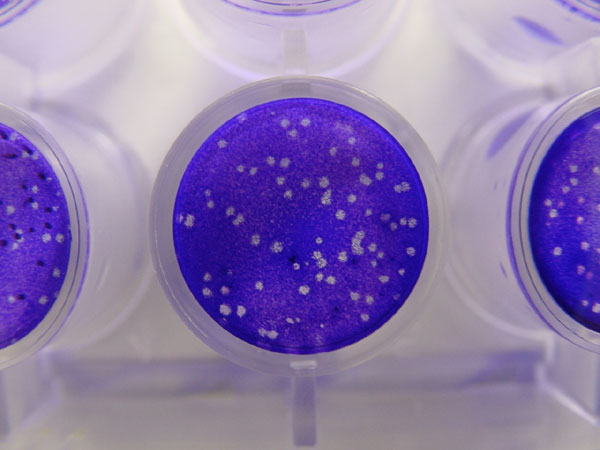
Virus Quantification
Virus quantification is counting or calculating the number of virus particles (virions) in a sample to determine the virus concentration. It is used in both research and development (R&D) in academic and commercial laboratories as well as in production situations where the quantity of virus at various steps is an important variable that must be monitored. For example, the production of virus-based vaccines, recombinant proteins using viral vectors, and viral antigens all require virus quantification to continually monitor and/or modify the process in order to optimize product quality and production yields and to respond to ever changing demands and applications. Other examples of specific instances where viruses need to be quantified include clone screening, multiplicity of infection (MOI) optimization, and adaptation of methods to cell culture. There are many ways to categorize virus quantification methods. Here, the methods are grouped according to what is being measured and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Each individual antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens, and antigens of virtually any size and chemical composition can be recognized. Antigen literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each of the branching chains comprising the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" the antigen (or a microbe or an infected cell bearing such an antigen) for attack by cells of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen () to the body tissue (biology), tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. Erythrocytes take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillary, capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin (Hb), an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiological Cell (biology), cell function such as erythrocyte deformabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABO Blood Group System
The ABO blood group system is used to denote the presence of one, both, or neither of the A and B antigens on erythrocytes (red blood cells). For human blood transfusions, it is the most important of the 47 different blood type (or group) classification systems currently recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusions (ISBT) as of December 2022. A mismatch in this serotype (or in various others) can cause a potentially fatal adverse reaction after a transfusion, or an unwanted immune response to an organ transplant. Such mismatches are rare in modern medicine. The associated anti-A and anti-B antibodies are usually IgM antibodies, produced in the first years of life by sensitization to environmental substances such as food, bacteria, and viruses. The ABO blood types were discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1901; he received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1930 for this discovery. ABO blood types are also present in other primates such as apes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens exist on normal cells, cancer cells, parasites, viruses, fungus, fungi, and bacteria. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, antibodies are ''antigen-specific'', meaning that an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coombs Test
The direct and indirect Coombs tests, also known as antiglobulin test (AGT), are blood tests used in immunohematology. The direct Coombs test detects antibodies that are stuck to the surface of the red blood cells. Since these antibodies sometimes destroy red blood cells they can cause anemia; this test can help clarify the condition. The indirect Coombs test detects antibodies that are floating freely in the blood. These antibodies could act against certain red blood cells; the test can be carried out to diagnose reactions to a blood transfusion. The direct Coombs test is used to test for autoimmune hemolytic anemia, a condition where the immune system breaks down red blood cells, leading to anemia. The direct Coombs test is used to detect antibodies or complement system, complement proteins attached to the surface of red blood cells. To perform the test, a blood sample is taken and the red blood cells are washed (removing the patient's plasma and unbound antibodies from the red b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity of a target entity. The measured entity is often called the analyte, the measurand, or the target of the assay. The analyte can be a drug, biochemical substance, chemical element or compound, or cell in an organism or organic sample. An assay usually aims to measure an analyte's intensive property and express it in the relevant measurement unit (e.g. molarity, density, functional activity in enzyme international units, degree of effect in comparison to a standard, etc.). If the assay involves exogenous reactants (the reagents), then their quantities are kept fixed (or in excess) so that the quantity and quality of the target are the only limiting factors. The difference in the assay outcome is used to deduce the unknown quality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiserum
In immunology, antiserum is a blood serum containing antibodies (either monoclonal or polyclonal) that is used to spread passive immunity to many diseases via blood donation ( plasmapheresis). For example, convalescent serum, or passive antibody transfusion from a previous human survivor, was the only known effective treatment for Ebola infection with a high success rate of 7 out of 8 patients surviving. Antisera are widely used in diagnostic virology laboratories. The most common use of antiserum in humans is as antitoxin or antivenom to treat envenomation. Serum therapy, also known as serotherapy, describes the treatment of infectious diseases using the serum of animals that have been immunized against the specific organism or components of that organism that is causing the infection. History In 1890, Emil von Behring and Kitasato Shibasaburō published their first paper on serum therapy. Behring pioneered the technique, using guinea pigs to produce serum. Based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, sickle cell anemia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |