|
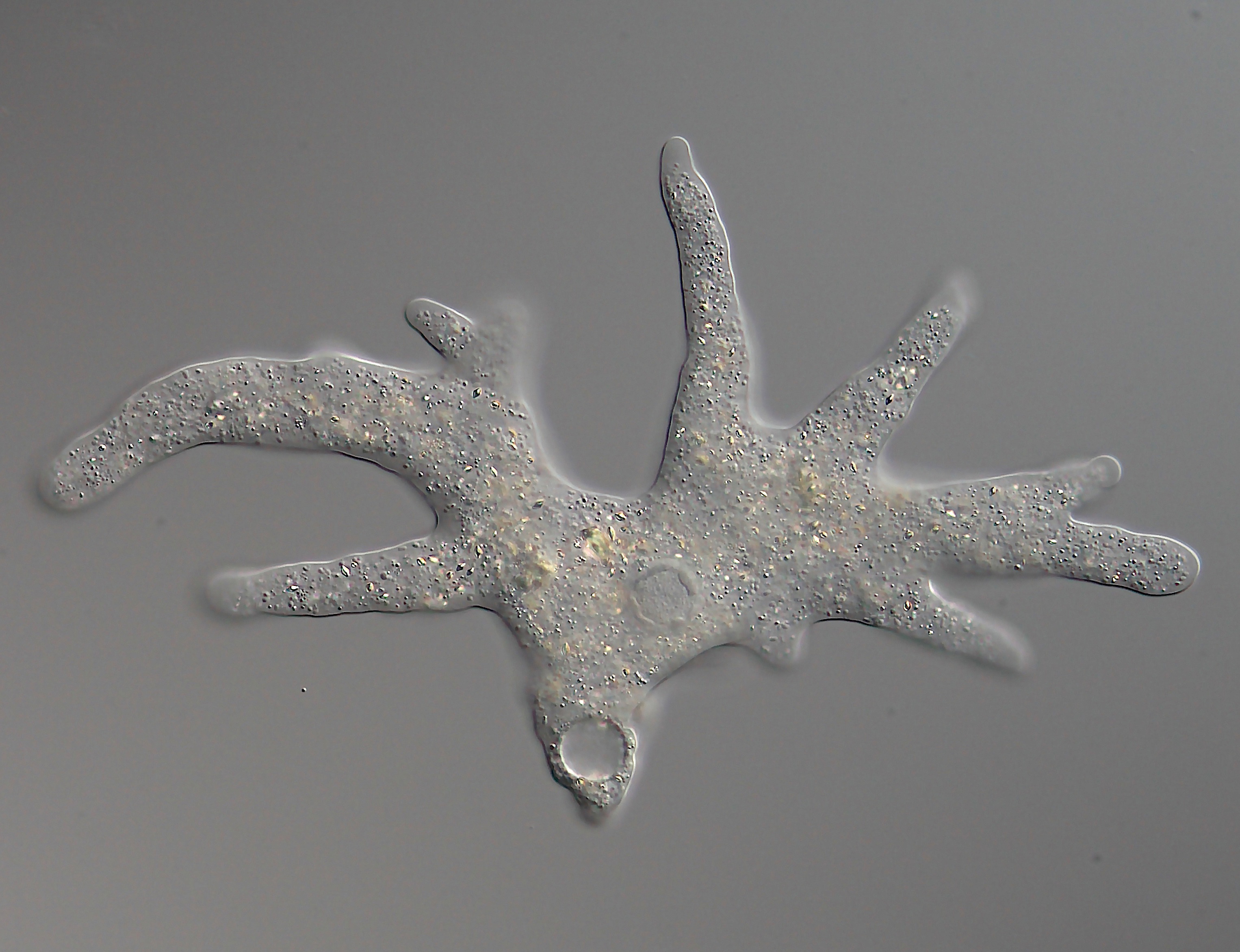
Heliozoan Feeding DSC 1665
Heliozoa, commonly known as sun-animalcules, are microbial eukaryotes (protists) with stiff arms (axopodia) radiating from their spherical bodies, which are responsible for their common name. The axopodia are microtubule-supported projections from the amoeboid cell body, and are variously used for capturing food, sensation, movement, and attachment. They are similar to Radiolaria, but they are distinguished from them by lacking central capsules and other complex skeletal elements, although some produce simple scales and spines. They may be found in both freshwater and marine environments. Classification Originally the heliozoa were treated together as a formal taxon Heliozoa or Heliozoea, with the rank of class or phylum, but it has been realised that they are polyphyletic, as the various orders show notable differences and are no longer believed to be descended from a single common ancestor. Instead, "heliozoa" is regarded as a descriptive term applying to various lines of prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Joblot
Louis Joblot (9 August 1645 – 27 April 1723) was a French naturalist. He was born in Bar-le-Duc and died, aged 57, in Paris Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci .... Publications * Louis Joblot, ''Descriptions et usages de plusiers nouveaux microscopes tant simples que composez ; avec de nouvelles observations faites sur de multitude innombrable d'insectes, & d'autres animaux de diverses especes, qui naissent dans des liqueurs préparées, & dans celles qui ne le sont point'', J. Collombat, printer, Paris, 1718. Sources * Hubert Lechevalier, "Louis Joblot and His Microscopes", ''Bacteriological Reviews'', Vol.40, No.1, March 1976, p. 241-258PDF* P.W. van der Pas ''Complete Dictionary of Scientific Biography'', 2008. References External links ''Observer au X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
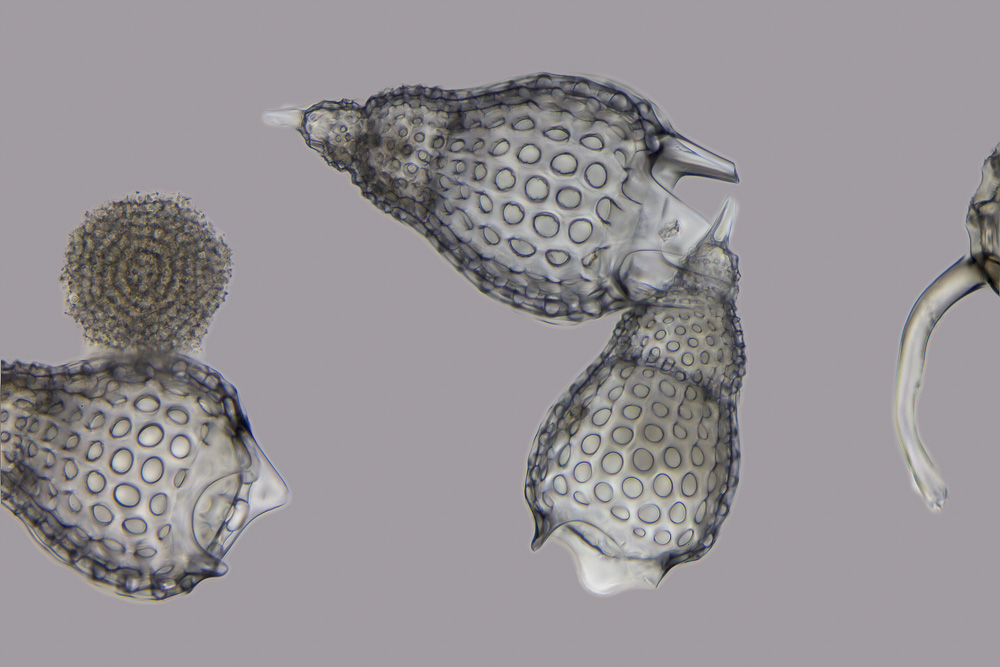
Radiolarian
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are unicellular eukaryotes of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elaborate mineral skeleton is usually made of silica. They are found as zooplankton throughout the global ocean. As zooplankton, radiolarians are primarily heterotrophic, but many have photosynthetic endosymbionts and are, therefore, considered mixotrophs. The skeletal remains of some types of radiolarians make up a large part of the cover of the ocean floor as siliceous ooze. Due to their rapid change as species and intricate skeletons, radiolarians represent an important diagnostic fossil found from the Cambrian onwards. Description Radiolarians have many needle-like pseudopods supported by bundles of microtubules, which aid in the radiolarian's buoyancy. The cell nucleus and most other organelles are in the endoplasm, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axopodia
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and may also contain microtubules and intermediate filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility and ingestion. They are often found in amoebas. Different types of pseudopodia can be classified by their distinct appearances. Lamellipodia are broad and thin. Filopodia are slender, thread-like, and are supported largely by microfilaments. Lobopodia are bulbous and amoebic. Reticulopodia are complex structures bearing individual pseudopodia which form irregular nets. #Axopodia, Axopodia are the phagocytosis type with long, thin pseudopods supported by complex microtubule arrays enveloped with cytoplasm; they respond rapidly to physical contact. Generally, several pseudopodia arise from the surface of the body, (''polypodial'', for example, ''Amoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliozoan Feeding DSC 1665
Heliozoa, commonly known as sun-animalcules, are microbial eukaryotes (protists) with stiff arms (axopodia) radiating from their spherical bodies, which are responsible for their common name. The axopodia are microtubule-supported projections from the amoeboid cell body, and are variously used for capturing food, sensation, movement, and attachment. They are similar to Radiolaria, but they are distinguished from them by lacking central capsules and other complex skeletal elements, although some produce simple scales and spines. They may be found in both freshwater and marine environments. Classification Originally the heliozoa were treated together as a formal taxon Heliozoa or Heliozoea, with the rank of class or phylum, but it has been realised that they are polyphyletic, as the various orders show notable differences and are no longer believed to be descended from a single common ancestor. Instead, "heliozoa" is regarded as a descriptive term applying to various lines of prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleariid
The nucleariids, or nucleariid amoebae, are a group of amoebae that compose the sister clade of the fungi. Together, they form the clade Holomycota. They are aquatic organisms found in freshwater and marine habitats, as well as in faeces. They are free-living phagotrophic predators that mostly consume algae and bacteria. Nucleariids are characterized by simple, spherical or flattened single-celled bodies with filopodia (fine, thread-like pseudopods), covered by a mucous coat. They lack flagella and microtubules. Inside the cytoplasm of some species are endosymbiotic proteobacteria. Some species are naked, with only the mucous coat as cover, while others (known as 'scaled' nucleariids) have silica-based or exogenous particles of various shapes. An exceptional nucleariid, '' Fonticula alba'', develops multicellular fruting bodies (sorocarps) for spore dispersal. It is one of several cases of independently evolved multicellularity within Opisthokonta, the clade that houses both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleariida
The nucleariids, or nucleariid amoebae, are a group of amoebae that compose the sister clade of the fungi. Together, they form the clade Holomycota. They are aquatic organisms found in freshwater and marine habitats, as well as in faeces. They are free-living phagotrophic predators that mostly consume algae and bacteria. Nucleariids are characterized by simple, spherical or flattened single-celled bodies with filopodia (fine, thread-like pseudopods), covered by a mucous coat. They lack flagella and microtubules. Inside the cytoplasm of some species are endosymbiotic proteobacteria. Some species are naked, with only the mucous coat as cover, while others (known as 'scaled' nucleariids) have silica-based or exogenous particles of various shapes. An exceptional nucleariid, ''Fonticula alba'', develops multicellular fruting bodies (sorocarps) for spore dispersal. It is one of several cases of independently evolved multicellularity within Opisthokonta, the clade that houses both Holo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotosphaerida
The nucleariids, or nucleariid amoebae, are a group of amoebae that compose the sister clade of the fungi. Together, they form the clade Holomycota. They are aquatic organisms found in freshwater and marine habitats, as well as in faeces. They are free-living phagotrophic predators that mostly consume algae and bacteria. Nucleariids are characterized by simple, spherical or flattened single-celled bodies with filopodia (fine, thread-like pseudopods), covered by a mucous coat. They lack flagella and microtubules. Inside the cytoplasm of some species are endosymbiotic proteobacteria. Some species are naked, with only the mucous coat as cover, while others (known as 'scaled' nucleariids) have silica-based or exogenous particles of various shapes. An exceptional nucleariid, ''Fonticula alba'', develops multicellular fruting bodies (sorocarps) for spore dispersal. It is one of several cases of independently evolved multicellularity within Opisthokonta, the clade that houses both Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sticholonche
''Sticholonche'' is a genus of radiolarians with a single species, ''Sticholonche zanclea'', found in open oceans at depths of 99–510 metres. It is generally considered a heliozoan, placed in its own order, called the Taxopodida. However it has also been classified as an unusual radiolarian, and this has gained support from genetic studies, which place it near the Acantharea The Acantharia are a group of radiolarian protozoa, distinguished mainly by their strontium sulfate skeletons. Acantharians are heterotrophic marine Plankton, microplankton that range in size from about 200 microns in diameter up to several milli .... ''Sticholonche'' are usually around 200 μm, though this varies considerably, and have a bilaterally symmetric shape, somewhat flattened and widened at the front. The axopods are arranged into distinct rows, six of which lie in a dorsal groove and are rigid, and the rest of which are mobile. These are used primarily for buoyancy, rather than feeding. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
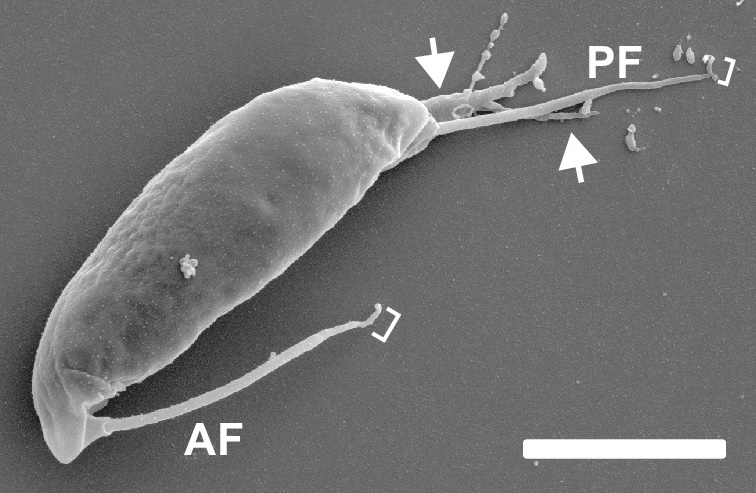
Cercozoa
Cercozoa (now synonymised with Filosa) is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead united by phylogeny, molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or Ubiquitin#Polyubiquitin chains, polyubiquitin. They were the first major eukaryotic group to be recognized mainly through phylogeny, molecular phylogenies. They are the natural predators of many species of bacteria. They are closely related to the phylum Retaria, comprising amoeboids that usually have complex shells, and together form a supergroup called Rhizaria. Characteristics The group includes most amoeboids and flagellates that feed by means of filose pseudopods. These may be restricted to part of the cell surface, but there is never a true cytostome or mouth as found in many other protozoa. They show a variety of forms and have proven difficult to define in terms of structural characteristics, although their unity is strongly supported b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |