|
Heliospheric Current Sheet
The heliospheric current sheet, or interplanetary current sheet, is a surface separating regions of the heliosphere where the interplanetary magnetic field points toward and away from the Sun. A small electrical current with a current density of about 10−10 A/m2 flows within this surface, forming a current sheet confined to this surface.Israelevich, P. L., ''et al.'',MHD simulation of the three-dimensional structure of the heliospheric current sheet" (2001) ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'', v.376, p.288–291 The shape of the current sheet results from the influence of the Sun's rotating magnetic field on the plasma in the interplanetary medium. The thickness of the current sheet is about near the orbit of the Earth. Characteristics Ballerina's skirt shape As the Sun rotates, its magnetic field twists into an Archimedean spiral, as it extends through the Solar System. This phenomenon is often called the Parker spiral, after Eugene Parker's workParker, E. N.,Dynamics of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic Spiral
The Archimedean spiral (also known as Archimedes' spiral, the arithmetic spiral) is a spiral named after the 3rd-century BC Greek mathematician Archimedes. The term ''Archimedean spiral'' is sometimes used to refer to the more general class of spirals of this type (see below), in contrast to ''Archimedes' spiral'' (the specific arithmetic spiral of Archimedes). It is the locus corresponding to the locations over time of a point moving away from a fixed point with a constant speed along a line that rotates with constant angular velocity. Equivalently, in polar coordinates it can be described by the equation r = b\cdot\theta with real number . Changing the parameter controls the distance between loops. From the above equation, it can thus be stated: position of the particle from point of start is proportional to angle as time elapses. Archimedes described such a spiral in his book ''On Spirals''. Conon of Samos was a friend of his and Pappus states that this spiral was discove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
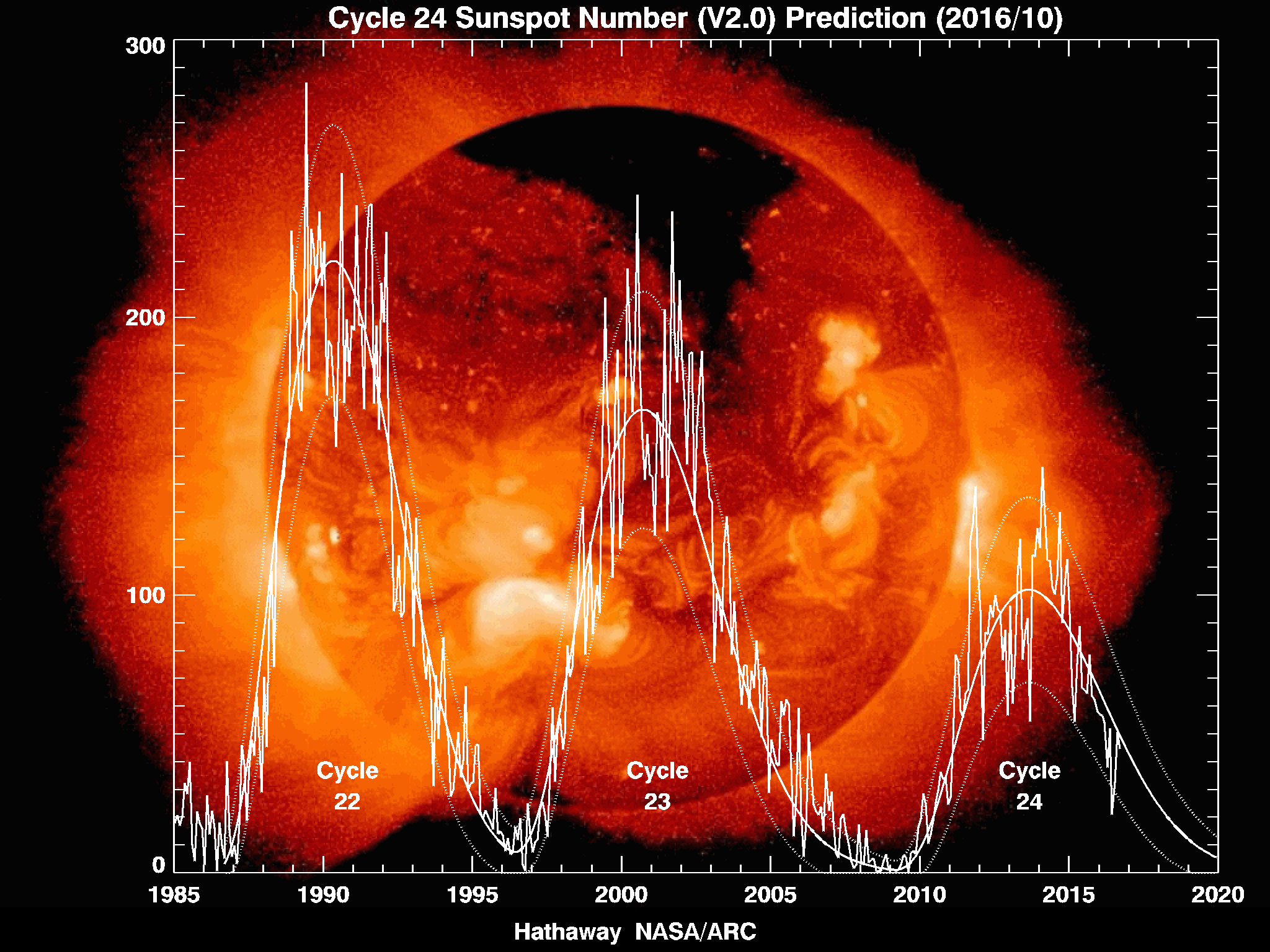
Solar Cycle
The Solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of Modern Maximum, variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surface. Over the period of a solar cycle, levels of solar radiation and ejection of solar material, the number and size of sunspots, solar flares, and coronal loops all exhibit a synchronized fluctuation from a Solar minimum, period of minimum activity to a Solar maximum, period of a maximum activity back to a period of minimum activity. The magnetic field of the Sun flips during each solar cycle, with the flip occurring when the solar cycle is near its maximum. After two solar cycles, the Sun's magnetic field returns to its original state, completing what is known as a Hale cycle. This cycle has been observed for centuries by changes in the Sun's appearance and by terrestrial phenomena such as aurora but was not clearly identified un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Maximum
Solar maximum is the regular period of greatest solar activity during the Sun's 11-year solar cycle. During solar maximum, large numbers of sunspots appear, and the solar irradiance output grows by about 0.07%. On average, the solar cycle takes about 11 years to go from one solar maximum to the next, with duration observed varying from 9 to 14 years. Large solar storms often occur during solar maximum. For example, the Carrington Event, which took place a few months before the solar maximum of solar cycle 10, was the most intense geomagnetic storm in recorded history and widely considered to have been caused by an equally large solar storm. Predictions Predictions of a future maximum's timing and strength are very difficult; predictions vary widely. There was a solar maximum in 2000. In 2006, NASA initially expected a solar maximum in 2010 or 2011, and thought that it could be the strongest since 1958. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Tension Force
In physics, magnetic tension is a restoring force with units of force density that acts to straighten bent magnetic field lines. In SI units, the force density \mathbf_T exerted perpendicular to a magnetic field \mathbf can be expressed as :\mathbf_T = \frac where \mu_0 is the vacuum permeability. Magnetic tension forces also rely on vector current densities and their interaction with the magnetic field. Plotting magnetic tension along adjacent field lines can give a picture as to their divergence and convergence with respect to each other as well as current densities. Magnetic tension is analogous to the restoring force of rubber bands. Mathematical statement In ideal magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) the magnetic tension force in an electrically conducting fluid with a bulk plasma velocity field \mathbf, current density \mathbf, mass density \rho, magnetic field \mathbf, and plasma pressure p can be derived from the Cauchy momentum equation: : \rho\left(\frac + \mathbf \cdot \nab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to: Mathematics and Direction * Vector (geometric), a line * Radius, adjective form of * Radial distance (geometry), a directional coordinate in a polar coordinate system * Radial set * A bearing from a waypoint, such as a VHF omnidirectional range Biology * Radial artery, the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm * Radial nerve, supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb * Radial symmetry, one of the types of distribution of body parts or shapes in biology * Radius (bone), a bone of the forearm Technology * Radial (radio), lines which radiate from a radio antenna * Radial axle, on a locomotive or carriage * Radial compressor * Radial delayed blowback * Radial engine * Radial tire A radial tire (more properly, a radial-ply tire) is a particular design of vehicular tire. In this design, the cord plies are arranged at 90 degrees to the direction of travel, or radially (from the center of the tire). Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poloidal
The terms toroidal and poloidal refer to directions relative to a torus of reference. They describe a three-dimensional coordinate system in which the poloidal direction follows a small circular ring around the surface, while the toroidal direction follows a large circular ring around the torus, encircling the central void. The earliest use of these terms cited by the Oxford English Dictionary is by Walter M. Elsasser (1946) in the context of the generation of the Earth's magnetic field by currents in the core, with "toroidal" being parallel to lines of constant latitude and "poloidal" being in the direction of the magnetic field (i.e. towards the poles). The OED also records the later usage of these terms in the context of toroidally confined plasmas, as encountered in magnetic confinement fusion. In the plasma context, the toroidal direction is the long way around the torus, the corresponding coordinate being denoted by in the slab approximation or or in magnetic coordinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroid (geometry)
In mathematics, a toroid is a surface of revolution with a hole in the middle. The axis of revolution passes through the hole and so does not intersect the surface. For example, when a rectangle is rotated around an axis parallel to one of its edges, then a hollow rectangle-section ring is produced. If the revolved figure is a circle, then the object is called a torus. The term ''toroid'' is also used to describe a toroidal polyhedron. In this context a toroid need not be circular and may have any number of holes. A ''g''-holed ''toroid'' can be seen as approximating the surface of a torus having a topological genus, ''g'', of 1 or greater. The Euler characteristic χ of a ''g'' holed toroid is 2(1−''g''). The torus is an example of a toroid, which is the surface of a doughnut. Doughnuts are an example of a solid torus created by rotating a disk, and are not toroids. Toroidal structures occur in both natural and synthetic materials. Equations A toroid is specified b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Units
The astronomical unit (symbol: au or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to . Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its modern redefinition in 2012. The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars. It is also a fundamental component in the definition of another unit of astronomical length, the parsec. One au is approximately equivalent to 499 light-seconds. History of symbol usage A variety of unit symbols and abbreviations have been in use for the astronomical unit. In a 1976 resolution, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) had used the symbol ''A'' to denote a length equal to the astronomical unit. In the astronomical literature, the symbol AU is common. In 2006, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) had recommended ua as the symbol for the unit, from the French "uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, forming the Sun and a protoplanetary disc. The Sun is a typical star that maintains a balanced equilibrium by the fusion of hydrogen into helium at its core, releasing this energy from its outer photosphere. Astronomers classify it as a G-type main-sequence star. The largest objects that orbit the Sun are the eight planets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetohydrodynamics
In physics and engineering, magnetohydrodynamics (MHD; also called magneto-fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is a model of electrically conducting fluids that treats all interpenetrating particle species together as a single Continuum mechanics, continuous medium. It is primarily concerned with the low-frequency, large-scale, magnetic behavior in Plasma (physics), plasmas and liquid metals and has applications in multiple fields including space physics, geophysics, astrophysics, and engineering. The word ''magnetohydrodynamics'' is derived from ' meaning magnetic field, ' meaning water, and ' meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970. History The MHD description of electrically conducting fluids was first developed by Hannes Alfvén in a 1942 paper published in Nature (journal), ''Nature'' titled "Existence of Electromagnetic–Hydrodynamic Waves" which outlined his discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, electric currents, and electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function (mathematics), function assigning a Euclidean vector, vector to each point of space, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |