|
Heiligenbeil Cauldron
The Heiligenbeil Pocket or Heiligenbeil Cauldron () was the site of a major encirclement battle on the Eastern Front during the closing weeks of World War II, in which the Wehrmacht's 4th Army was almost entirely destroyed during the Soviet Braunsberg Offensive Operation (13–22 March 1945). The pocket was located near Heiligenbeil in East Prussia in eastern Germany (now Mamonovo, Kaliningrad Oblast), and the battle, part of a broader Soviet offensive into the region of East Prussia, lasted from 26 January until 29 March 1945. Attack on East Prussia The Red Army's East Prussian Operation commenced on 13 January 1945, with the objective of rolling up the substantial German defences in East Prussia and cutting off the provincial capital of Königsberg. The Soviet forces were opposed by the German Army Group Centre, including the Fourth Army, under the command of General Friedrich Hossbach. While the 3rd Belorussian Front initially met strong resistance, the outnumbered Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
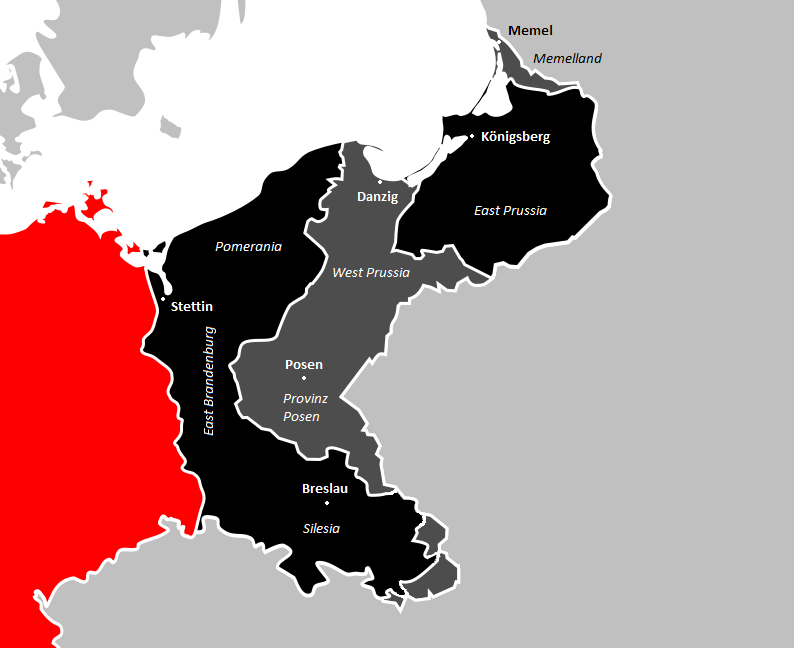
Historical Eastern Germany
In present-day Germany, the former eastern territories of Germany () refer to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany, i.e. the Oder–Neisse line, which historically had been considered German and which were annexed by Poland and the Soviet Union after World War II. In contrast to the lands awarded to the restored Polish state by the Treaty of Versailles after World War I, the German territories lost with the post-World War II Potsdam Agreement were either almost exclusively inhabited by Germans before 1945 (the bulk of East Prussia, Lower Silesia, Farther Pomerania, and parts of Western Pomerania, Lusatia, and Neumark), mixed German– Polish with a German majority (the Posen–West Prussia Border March, Lauenburg and Bütow Land, the southern and western rim of East Prussia, Ermland, Western Upper Silesia, and the part of Lower Silesia east of the Oder), or mixed German– Czech with a German majority ( Glatz). Virtually the entire German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th Panzer Division (Wehrmacht)
The 7th Panzer Division was an Panzer, armored formation of the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army in World War II. It participated in the Battle of France, the invasion of the Soviet Union, the occupation of Vichy France, and on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front until the end of the war. The 7th Panzer Division is also known by its nickname, Ghost Division. The division met with great success in France in 1940 and then again in the Soviet Union in 1941. In May 1942, the division was withdrawn from the Soviet Union and sent back to France to replace losses and refit. It returned to Southern Russia following the defeat at Stalingrad, and helped to check a general collapse of the front in a series of defensive battles as part of Army Group Don, and participated in General Erich von Manstein's counterattack at Third Battle of Kharkov, Kharkov. The division fought in the unsuccessful offensive at Battle of Kursk, Kursk in the summer of 1943, suffering heavy losses in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German 28th Jäger Division
German(s) may refer to: * Germany, the country of the Germans and German things **Germania (Roman era) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizenship in Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman era) *German diaspora * German language * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (disambiguati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
48th Army (Soviet Union)
The 48th Army was a field army of the Soviet Red Army, active from 1941 to 1945. The army was first formed in August 1941 and fought in the Leningrad Strategic Defensive Operation. The army suffered heavy losses and was disbanded in early September. Its remnants were moved to the 54th Army. Reformed in April 1942 on the Bryansk Front, the army fought in the Maloarkhangelsk Offensive in the winter of 1943. It was sent to the Central Front in March and defended the northern face of the Kursk Bulge. During the summer, it fought in Operation Kutuzov and the Chernigov-Pripyat Offensive. From November, the army fought in the Gomel-Rechitsa Offensive. The army fought in Operation Bagration from June 1944. During the offensive, the army captured Zhlobin and Bobruisk and was on the Narew by early September. During early 1945, the army fought in the East Prussian Offensive and ended the war in East Prussia during May. The army was transferred to Poland in July 1945 and its headquarters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Army (Wehrmacht)
The 2nd Army () was a field army of the German Army during World War II. History 1939–1941 The 2nd Army headquarters was briefly established in Berlin from Group Command 1 on 26 August 1939 and at the beginning of the Invasion of Poland it was renamed Army Group North on 2 September. The 2nd Army was reestablished on 20 October 1939, with '' Generaloberst'' Maximilian von Weichs in command, by renaming the 8th Army, which had been moved from Poland to the west. After the beginning of the Battle of France the army was assigned to Army Group A in June 1940, when it fought across the Aisne and around Reims. In April 1941, the army was involved in the invasion of the Balkans, capturing Belgrade in a rapid offensive. 1941–1945 From 1941 until the end of the war the army was deployed in the Eastern Front, starting with the Operation Barbarossa as part of Army Group Centre. It advanced from Białystok to Mogilev, Gomel, Chernigov, Bryansk successively and defended ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbląg
Elbląg (; ; ) is a city in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland, located in the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 127,390 inhabitants, as of December 2021. It is the capital of Elbląg County. Elbląg is one of the oldest cities in the province. Its history dates back to 1237, when the Teutonic Order constructed their fortified stronghold on the banks of a nearby river. The castle subsequently served as the official seat of the Teutonic Order Masters. Elbląg became part of the Hanseatic League, which contributed much to the city's wealth. Through the Hanseatic League, the city was linked to other major ports like Gdańsk, Lübeck and Amsterdam. Elbląg joined Poland in 1454 and after the defeat of the Teutonic Knights in the Thirteen Years’ War was recognized as part of Poland in 1466. It then flourished and turned into a significant trading point, but its growth was eventually hindered by the Second Northern War and the Swedish Deluge. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Guards Tank Army
The 5th Guards Tank Army (Russian: 5-я гварде́йская та́нковая а́рмия) was a Soviet Guards armored formation which fought in many notable actions during World War II. The army was formed in February 1943. Until the aftermath of the Vilnius Offensive in July 1944, it was commanded by Pavel Rotmistrov. Its organisation varied throughout its history, but in general included two or more Guards Tank Corps and one or more Guards Mechanised Corps. It was considered an elite formation. Under Red Army doctrine of deep operations, Tank Armies were primarily to be used for large-scale exploitation of major offensives. Once a breach in enemy lines had been made by other units (typically Shock Armies or combined-arms armies), the tank army would be inserted into the gap to drive deep into enemy territory, attacking rear areas and seizing major communications centers to disrupt the enemy reactions. Tank armies were expected to penetrate up to several hundred kilom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giżycko
Giżycko (former or ''Łuczany''; ) is a town in northeastern Poland with 28,597 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is situated between Lake Kisajno and Lake Niegocin in the region of Masuria, within the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. It is the seat of Giżycko County. Giżycko is a popular summer tourist destination due to its location within the Masurian Lake District and possesses numerous historical monuments, including a 14th-century Teutonic castle. History Antiquity and Middle Ages The first known settlements in the area of today's Giżycko were recorded in Roman times by Tacitus in his Germania and are connected to Amber Road in vicinity of which Giżycko was located. A defensive settlement of the Baltic Prussians was known to exist in the area, and in IX was recorded as being ruled by king known as Izegup or Jesegup. After his failed attempt in 997 AD Bolesław I the Brave sent another expedition in 1008 to conquer/Christianize the Old Prussians. Just like S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg-Hans Reinhardt
Georg-Hans Reinhardt (1 March 1887 – 23 November 1963) was a German general of the ''Wehrmacht'' during World War II, who was subsequently convicted of war crimes. He commanded the 3rd Panzer Army from 1941 to 1944, and Army Group Centre in 1944 and 1945, reaching the rank of colonel general (Generaloberst). Following the war, Reinhardt was tried in the High Command Trial, as part of the Subsequent Nuremberg Trials. He was found guilty of war crimes and crimes against humanity and sentenced to 15 years. He was released in 1952. World War II Born in 1887, Reinhardt fought during World War I. He commanded the 4th Panzer Division (Wehrmacht), 4th Panzer Division during the Invasion of Poland in September 1939. In the 1940 Battle of France, Reinhardt commanded the XXXXI Panzer Corps (Germany), XXXXI Panzer Corps. Operation Barbarossa In 1941, Reinhardt and XLI Panzer Corps were deployed on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front for Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Centre
Army Group Centre () was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created during the planning of Operation Barbarossa, Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union, as one of the three German Army formations assigned to the invasion. After Army Group North was trapped in the Courland Pocket in mid-1944, it was renamed to Army Group Courland and the first Army Group Centre was renamed "Army Group North". The second iteration of Army Group Centre was formed by the redesignation of Army Group A as the replacement for the first Army Group Centre. Formation and Command The army group was officially created by Adolf Hitler when he issued Führer Directive 21 on 18 December 1940, ordering German forces to prepare for an attack on Soviet Russia in 1941. The first commanding officer of Army Group Centre was Field Marshal Fedor von Bock, who would lead it until he was relieved on 18 December 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, Baltic Crusades. It was named in honour of King Ottokar II of Bohemia, who led a campaign against the pagan Old Prussians, a Baltic tribe. A Baltic Sea, Baltic port city, it successively became the capital of the State of the Teutonic Order, the Duchy of Prussia and the provinces of East Prussia and Province of Prussia, Prussia. Königsberg remained the coronation city of the Prussian monarchy from 1701 onwards, though the capital was Berlin. From the thirteenth to the twentieth centuries on, the inhabitants spoke predominantly German language, German, although the city also had a profound influence upon the Lithuanian and Polish cultures. It was a publishing center of Lutheranism, Lutheran literatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |