|
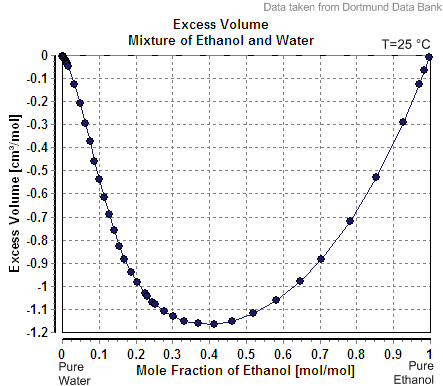
Heat Of Mixing
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of mixing (also heat of mixing and excess enthalpy) is the enthalpy liberated or absorbed from a Chemical substance, substance upon Mixing (process engineering), mixing. When a substance or Chemical compound, compound is combined with any other substance or compound, the enthalpy of mixing is the consequence of the new interactions between the two substances or compounds. This enthalpy, if released Exothermic process, exothermically, can in an extreme case cause an explosion. Enthalpy of mixing can often be ignored in calculations for mixtures where other heat terms exist, or in cases where the Ideal solution, mixture is ideal. The sign convention is the same as for enthalpy of reaction: when the enthalpy of mixing is positive, mixing is endothermic, while negative enthalpy of mixing signifies exothermic mixing. In ideal mixtures, the enthalpy of mixing is null. In non-ideal mixtures, the thermodynamic activity of each component is different from its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
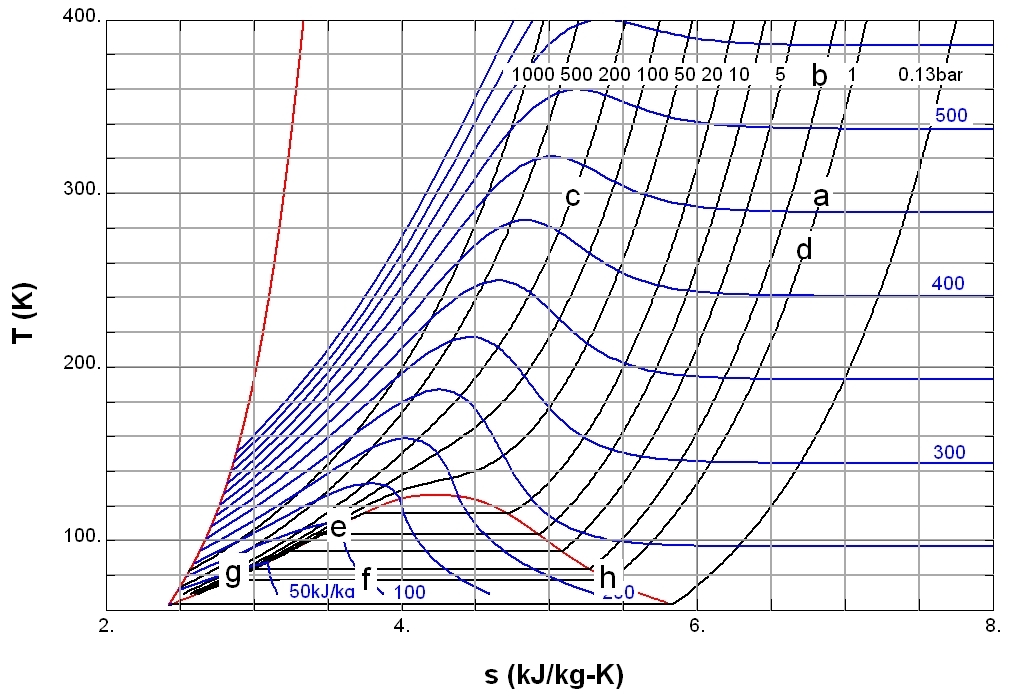
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, Work (thermodynamics), work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of thermodynamics, which convey a quantitative description using measurable macroscopic physical quantity, physical quantities but may be explained in terms of microscopic constituents by statistical mechanics. Thermodynamics applies to various topics in science and engineering, especially physical chemistry, biochemistry, chemical engineering, and mechanical engineering, as well as other complex fields such as meteorology. Historically, thermodynamics developed out of a desire to increase the thermodynamic efficiency, efficiency of early steam engines, particularly through the work of French physicist Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot, Sadi Carnot (1824) who believed that engine efficiency was the key that could help France win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy Of Mixing
In thermodynamics, the entropy of mixing is the increase in the total entropy when several initially separate systems of different composition, each in a thermodynamic state of internal equilibrium, are mixed without chemical reaction by the thermodynamic operation of removal of impermeable partition(s) between them, followed by a time for establishment of a new thermodynamic state of internal equilibrium in the new unpartitioned closed system. In general, the mixing may be constrained to occur under various prescribed conditions. In the customarily prescribed conditions, the materials are each initially at a common temperature and pressure, and the new system may change its volume, while being maintained at that same constant temperature, pressure, and chemical component masses. The volume available for each material to explore is increased, from that of its initially separate compartment, to the total common final volume. The final volume need not be the sum of the initially se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy Change Of Solution
In thermochemistry, the enthalpy of solution (heat of solution or enthalpy of solvation) is the enthalpy change associated with the dissolution of a substance in a solvent at constant pressure resulting in infinite dilution. The enthalpy of solution is most often expressed in kJ/ mol at constant temperature. The energy change can be regarded as being made up of three parts: the endothermic breaking of bonds within the solute and within the solvent, and the formation of attractions between the solute and the solvent. An ideal solution has a null enthalpy of mixing. For a non-ideal solution, it is an excess molar quantity. Energetics Dissolution by most gases is exothermic. That is, when a gas dissolves in a liquid solvent, energy is released as heat, warming both the system (i.e. the solution) and the surroundings. The temperature of the solution eventually decreases to match that of the surroundings. The equilibrium, between the gas as a separate phase and the gas in solutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy
Enthalpy () is the sum of a thermodynamic system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function in thermodynamics used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant external pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure–volume term expresses the work (physics), work W that was done against constant external pressure P_\text to establish the system's physical dimensions from V_\text=0 to some final volume V_\text (as W=P_\text\Delta V), i.e. to make room for it by displacing its surroundings. The pressure-volume term is very small for solids and liquids at common conditions, and fairly small for gases. Therefore, enthalpy is a stand-in for energy in chemical systems; Bond energy, bond, Lattice energy, lattice, solvation, and other chemical "energies" are actually enthalpy differences. As a state function, enthalpy depends only on the final configuration of internal e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Molar Property
In thermodynamics, an apparent molar property of a solution component in a mixture or solution is a quantity defined with the purpose of isolating the contribution of each component to the non-ideality of the mixture. It shows the change in the corresponding solution property (for example, volume) per mole of that component added, when all of that component is added to the solution. It is described as ''apparent'' because it appears to represent the molar property of that component ''in solution'', provided that the properties of the other solution components are assumed to remain constant during the addition. However this assumption is often not justified, since the values of apparent molar properties of a component may be quite different from its molar properties in the pure state. For instance, the volume of a solution containing two components identified as solvent and solute is given by : V=V_0 + ^\phi_1 \ =\tilde_ n_ + ^\phi\tilde_1 n_1 \, where is the volume of the pure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipole-Dipole Forces
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways: * An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system is a pair of charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign separated by some typically small distance. (A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.) * A magnetic dipole is the closed circulation of an electric current system. A simple example is a single loop of wire with constant current through it. A bar magnet is an example of a magnet with a permanent magnetic dipole moment. Dipoles, whether electric or magnetic, can be characterized by their dipole moment, a vector quantity. For the simple electric dipole, the electric dipole moment points from the negative charge towards the positive charge, and has a magnitude equal to the strength of each charge times the separation between the charges. (To be precise: for the definition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Dipole Interaction
In molecular physics and chemistry, the van der Waals force (sometimes van der Waals' force) is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and therefore more susceptible to disturbance. The van der Waals force quickly vanishes at longer distances between interacting molecules. Named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, the van der Waals force plays a fundamental role in fields as diverse as supramolecular chemistry, structural biology, polymer science, nanotechnology, surface science, and condensed matter physics. It also underlies many properties of organic compounds and molecular solids, including their solubility in polar and non-polar media. If no other force is present, the distance between atoms at which the force becomes repulsive rather than attractive as the atoms approach one another is called the van der W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently bonded to a more Electronegativity, electronegative donor atom or group (Dn), interacts with another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Unlike simple Dipole–dipole attraction, dipole–dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding arises from charge transfer (nB → σ*AH), Atomic orbital, orbital interactions, and quantum mechanical Delocalized electron, delocalization, making it a resonance-assisted interaction rather than a mere electrostatic attraction. The general notation for hydrogen bonding is Dn−H···Ac, where the solid line represents a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are nitrogen (N), oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermolecular Force
An intermolecular force (IMF; also secondary force) is the force that mediates interaction between molecules, including the electromagnetic forces of attraction or repulsion which act between atoms and other types of neighbouring particles (e.g. atoms or ions). Intermolecular forces are weak relative to intramolecular forces – the forces which hold a molecule together. For example, the covalent bond, involving sharing electron pairs between atoms, is much stronger than the forces present between neighboring molecules. Both sets of forces are essential parts of force fields frequently used in molecular mechanics. The first reference to the nature of microscopic forces is found in Alexis Clairaut's work ''Théorie de la figure de la Terre,'' published in Paris in 1743. Other scientists who have contributed to the investigation of microscopic forces include: Laplace, Gauss, Maxwell, Boltzmann and Pauling. Attractive intermolecular forces are categorized into the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Solution
In chemistry, a regular solution is a solution whose entropy of mixing is equal to that of an ideal solution with the same composition, but is non-ideal due to a nonzero enthalpy of mixing.P. Atkins and J. de Paula, ''Atkins' Physical Chemistry'' (8th ed. W.H. Freeman 2006) p.149P.A. Rock, ''Chemical Thermodynamics. Principles and Applications'' (Macmillan 1969) p.263 Such a solution is formed by random mixing of components of similar molar volume and without strong specific interactions, and its behavior diverges from that of an ideal solution by showing phase separation at intermediate compositions and temperatures (a miscibility gap). Its entropy of mixing is equal to that of an ideal solution with the same composition, due to random mixing without strong specific interactions. For two components :\Delta S_ = -nR(x_1\ln x_1 + x_2\ln x_2)\, where R\, is the gas constant, n\, the total number of mole (unit), moles, and x_i\, the mole fraction of each component. Only the enthalpy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
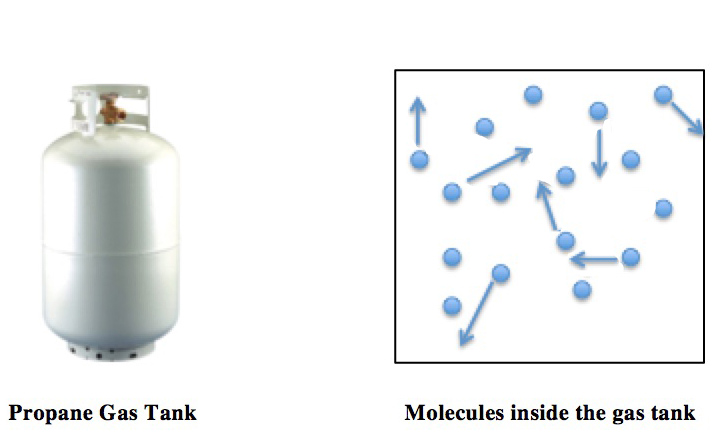
Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and Thermodynamic temperature, temperature respectively; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory of gases, kinetic theory, as was achieved (independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state function, state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |