|
Healthy Development Measurement Tool
The Healthy Development Measurement Tool (HDMT), developed by the San Francisco Department of Public Health, provides an approach for evaluating land-use planning and urban development with regards to the achievement of human health needs. The HDMT provides a set of baseline data on community health metrics for San Francisco and development targets to assess the extent to which urban development projects and plans can improve community health. The HDMT also provides a range of policy and design strategies that can advance health conditions and resources via the development process. Background In the San Francisco Bay Area, between the mid- and late- 1990s, the bustling information economy brought multitudes of young people to the Bay Area and Silicon Valley’s technology-inspired new economy.San Francisco Department of Public Health"Eastern Neighborhoods Community Health Impact Assessment (ENCHIA)." Housing was notoriously difficult to find, with vacancy rates at less than 2%. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Healthy Development Measurement Tool (diagram)
The Healthy Development Measurement Tool (HDMT), developed by the San Francisco Department of Public Health, provides an approach for evaluating land-use planning and urban development with regards to the achievement of human health needs. The HDMT provides a set of baseline data on community health metrics for San Francisco and development targets to assess the extent to which urban development projects and plans can improve community health. The HDMT also provides a range of policy and design strategies that can advance health conditions and resources via the development process. Background In the San Francisco Bay Area, between the mid- and late- 1990s, the bustling information economy brought multitudes of young people to the Bay Area and Silicon Valley’s technology-inspired new economy.San Francisco Department of Public Health"Eastern Neighborhoods Community Health Impact Assessment (ENCHIA)." Housing was notoriously difficult to find, with vacancy rates at less than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Health In The United States
The United States Public Health Service (USPHS or PHS) is a collection of agencies of the Department of Health and Human Services concerned with public health, containing nine out of the department's twelve operating divisions. The Assistant Secretary for Health oversees the PHS. The Public Health Service Commissioned Corps (PHSCC) is the federal uniformed service of the PHS, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. PHS had its origins in the system of marine hospitals that originated in 1798. In 1871 these were consolidated into the Marine Hospital Service, and shortly afterwards the position of Surgeon General and the PHSCC were established. As the system's scope grew to include quarantine authority and research, it was renamed the Public Health Service in 1912. A series of reorganizations in 1966–1973 began a shift where PHS' divisions were promoted into departmental operating agencies. PHS was established as a thin layer of hierarchy above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information System
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system to also include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations. The uncounted plural, ''geographic information systems'', also abbreviated GIS, is the most common term for the industry and profession concerned with these systems. It is roughly synonymous with geoinformatics and part of the broader geospatial field, which also includes GPS, remote sensing, etc. Geographic information science, the academic discipline that studies these systems and their underlying geographic principles, may also be abbreviated as GIS, but the unambiguous GIScience is more common. GIScience is often considered a subdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and planning. Gentrification often increases the economic value of a neighborhood, but the resulting demographic displacement may itself become a major social issue. Gentrification often sees a shift in a neighborhood's racial or ethnic composition and average household income as housing and businesses become more expensive and resources that had not been previously accessible are extended and improved. The gentrification process is typically the result of increasing attraction to an area by people with higher incomes spilling over from neighboring cities, towns, or neighborhoods. Further steps are increased investments in a community and the related infrastructure by real estate development businesses, local government, or community activists and resulting economic development, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affordable Housing
Affordable housing is housing which is deemed affordable to those with a household income at or below the median as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. Most of the literature on affordable housing refers to mortgages and a number of forms that exist along a continuum – from emergency homeless shelters, to transitional housing, to non-market rental (also known as social or subsidized housing), to formal and informal rental, indigenous housing, and ending with affordable home ownership. Housing choice is a response to an extremely complex set of economic, social, and psychological impulses. For example, some households may choose to spend more on housing because they feel they can afford to, while others may not have a choice. Definition and measurement There are several means of defining and measuring affordable housing. The definition and measurement may change in different nations, cities, or for specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
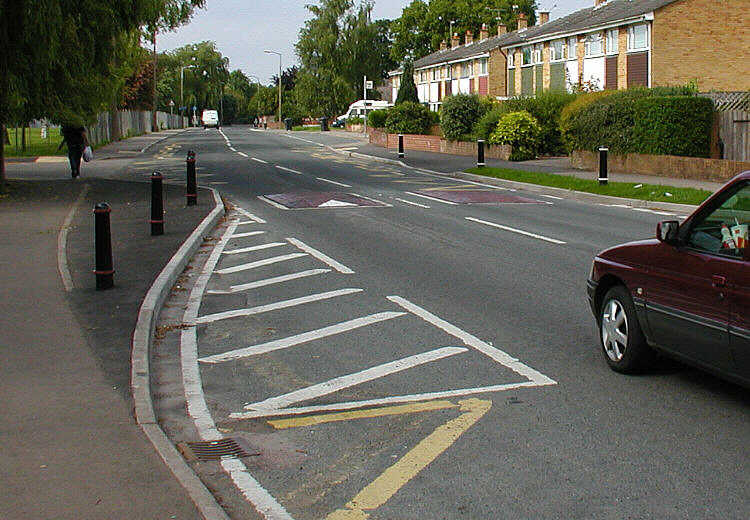
Traffic Calming
Traffic calming uses physical design and other measures to improve safety for motorists, pedestrians and cyclists. It has become a tool to combat speeding and other unsafe behaviours of drivers in the neighbourhoods. It aims to encourage safer, more responsible driving and potentially reduce traffic flow. Urban planners and traffic engineers have many strategies for traffic calming, including narrowed roads and speed humps. Such measures are common in Australia and Europe (especially Northern Europe), but less so in North America. Traffic calming is a calque (literal translation) of the German word ''Verkehrsberuhigung'' – the term's first published use in English was in 1985 by Carmen Hass-Klau. History In its early development in the UK in the 1930s, traffic calming was based on the idea that residential areas should be protected from through-traffic. Subsequently, it became valued for its ability to improve pedestrian safety and reduce noise and air pollution from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
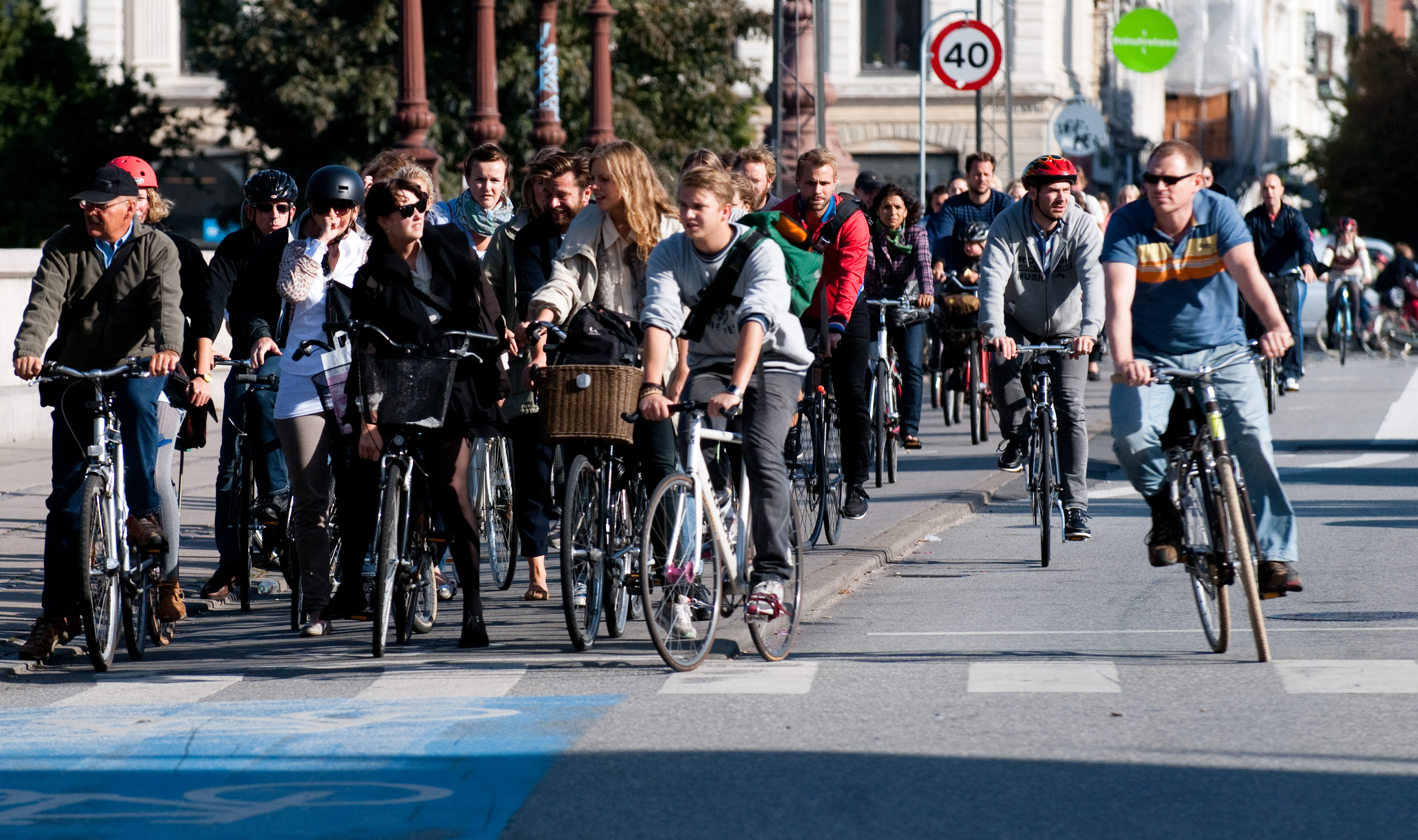
Pedestrian-friendly
Walkability is a term for planning concepts best understood by the mixed-use of amenities in high-density neighborhoods where people can access said amenities by foot. It is based on the idea that urban spaces should be more than just transport corridors designed for maximum vehicle throughput. Instead, it should be relatively complete livable spaces that serve a variety of uses, users, and transportation modes and reduce the need for cars for travel. The term 'walkability' was primarily invented in the 1960s due to Jane Jacobs' revolution in urban studies. In recent years, walkability has become popular because of its health, economic, and environmental benefits. It is an essential concept of sustainable urban design. Factors influencing walkability include the presence or absence and quality of footpaths, sidewalks or other pedestrian rights-of-way, traffic and road conditions, land use patterns, building accessibility, and safety, among others. Factors One proposed defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity And The Environment
Obesity and the environment aims to look at the different environmental factors that researchers worldwide have determined cause and perpetuate obesity. Obesity is a condition in which a person's weight is higher than what is considered healthy for their height, and is the leading cause of preventable death worldwide. Obesity can result from several factors such as poor nutritional choices, overeating, genetics, culture, and metabolism. Many diseases and health complications are associated with obesity (e.g., Type-II diabetes, heart disease, cancer, stroke). Worldwide, the rates of obesity have nearly tripled since 1975, leading health professionals to label the condition as a modern epidemic in most parts of the world. Current (as of 2022) worldwide population estimates of obese adults near 13%; overweight adults total approximately 39%. Environmental obesogens Studies have shown that obesity has become increasingly prevalent in both people and animals (pets and laboratory ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
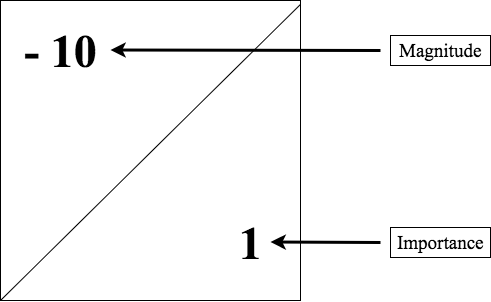
Leopold Matrix
The Leopold matrix is a qualitative environmental impact assessment method developed in 1971 by Luna Leopold and collaborators for the USGS. It is used to identify and assign numerical weightings to potential environmental impacts of proposed projects on the environment. It came as a response to the National Environmental Policy Act of 1969 which was criticized for lacking adequate guidance for government agencies on how to properly predict potential environmental impacts and consequently prepare impact reports. The system consists of a grid of 100 rows representing the possible project activities on the horizontal axis and 88 columns representing environmental factors on the vertical axis, for a total of 8800 possible interactions. In practice, only a select few (25-50) of these interactions are likely to be of sufficient importance to be thoroughly considered. Where an impact is expected, the appropriate cell of the matrix is split diagonally from the top right corner to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Health
Environmental health is the branch of public health concerned with all aspects of the natural and built environment affecting human health. In order to effectively control factors that may affect health, the requirements that must be met in order to create a healthy environment must be determined. Environmental health focuses on the natural and built environments for the benefit of human health. The major sub-disciplines of environmental health are environmental science, toxicology, environmental epidemiology, and environmental and occupational medicine. Definitions WHO definitions Environmental health was defined in a 1989 document by the World Health Organization (WHO) as: Those aspects of human health and disease that are determined by factors in the environment. It is also referred to as the theory and practice of accessing and controlling factors in the environment that can potentially affect health. A 1990 WHO document states that environmental health, as used b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Built Environment
The term built environment refers to human-made conditions and is often used in architecture, landscape architecture, urban planning, public health, sociology, and anthropology, among others. These curated spaces provide the setting for human activity and were created to fulfill human desires and needs. The term can refer to a plethora of components including the traditionally associated buildings, cities, public infrastructure, transportation, open space, as well as more conceptual components like farmlands, damned rivers, wildlife management, and even domesticated animals. The built environment is made up of physical features. However, when studied, the built environment often highlights the connection between physical space and social consequences. It impacts the environment and how society physically maneuvers and functions, as well as less tangible aspects of society such as socioeconomic inequity and health. Various aspects of the built environment contribute to scholars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |