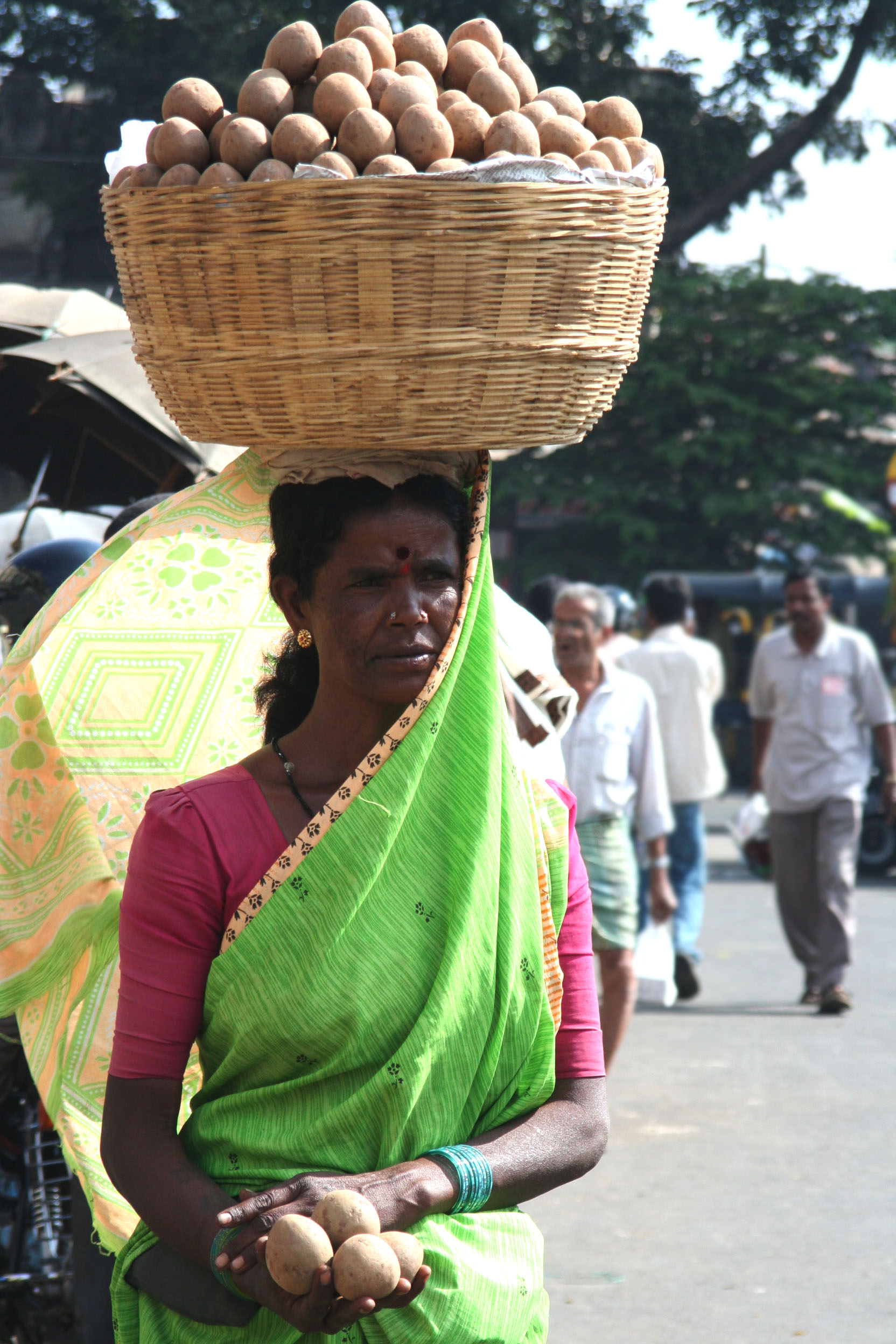|
Head-carrying
Carrying on the head is a common practice in many parts of the world as an alternative to carrying a burden on the back, shoulders and so on. People have carried burdens balanced on top of the head since ancient times, usually to do daily work, but sometimes in religious ceremonies or as a feat of skill, such as in certain dances. Working Carrying on the head is common in many parts of the developing world, as only a simple length of cloth shaped into a ring or ball is needed to carry loads approaching the person's own weight. The practice is efficient, in a place or at a time when there are no vehicles or beasts of burden available for transporting the objects. Today, women and men carry burdens on their heads where there is no less expensive, or more efficient, way of transporting workloads. In India, women carry baskets of bricks to workmen on construction sites. It is also used by the lowest caste to carry away human waste scooped out of pit latrines, the practice of manual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kayayei
Kayayei or Kaya Yei is a Ghanaian term for a female Porter (carrier), porter or bearer. Many of these women have migrated from a rural community to any of Ghana's urban cities in search of work. They generally Head-carrying, carry their burdens on their heads. Etymology The term ''kayayei'' (singular, ''kaya yoo'') is a compound word, compound formed from two languages of Ghana, languages spoken in Ghana. ''Kaya'' means "load, luggage, goods or burden" in the Hausa language, and ''yei'' means "women or females" in the Ga language,. People in Kumasi refer to the porters as ''paa o paa''. Role ''Kaya'' have always been manual labourers. They transport goods to and from markets, particularly agricultural goods. Typically, ''Kaya'' carry their loads in a large pan placed on their heads, using a moistened coil of cloth as a buffer, see Head-carrying. Conditions ''Kaya Yei'' still toil away in markets in Ghana today, often in poor conditions and with minimal income. Occasionally, ''K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matki (earthen Pot)
A ''matki'' or ''matka'' (Hindi and Urdu: ''maṭkī'', ''maṭkā'') in South Asia is an earthen pot used as a home "water storage cooler". It has been in use since ancient times and can be found in houses of every social class. Production They are made by the combination of two types of clay: the first is taken from the surface of the earth and the second after digging more than 10 feet deeper into the earth. Making a matka is a long process of at least 8 days. The clay is mixed with water, shaped, finished, polished, dried and fired in a kiln for 5 days. Modern designs are fitted with taps. Cooling process The cooling process works through evaporative cooling. Capillary action causes water to evaporate from the mini-pores in the pot, taking the heat from the water inside, thus making the water inside cooler than the outside temperature. Hence it is used only during summer and not in winter. Gallery Pani ka matka.jpg, A matka (big earthen pot) on roadside at Chinawal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumpline
A tumpline () is a strap attached at both ends to a sack, backpack, or other luggage and used to carry the object by placing the strap over the top of the head. This utilizes the spine rather than the shoulders as standard backpack straps do. Tumplines are not intended to be worn over the forehead, but rather over the top of the head just back from the hairline, pulling straight down in alignment with the spine. The bearer then leans forward, allowing the back to help support the load. The indigenous natives in Mexico (and other Latin American countries) traditionally have used the tumpline for carrying heavy loads, such as firewood, baskets (including baskets loaded with construction materials and dirt for building), bird cages, and furniture. In Mexico a common name for ''tumpline'' is "mecapal". Modern highland Mayans of southern Mexico use tumplines for various pedestrian transport. During World War Two, the Canadian Army developed special supply-packs with tumplines for m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set De Flo'
Set de flo' (Set the floor) was a type of dance competition held among African Americans during the 19th century. Overview Set de flo' dancing involves drawing a circle on the ground (usually on a dirt floor); dancers are required to not step outside the bounds of the circle, and if they did, they will be disqualified. A caller, usually a fiddler, would call out increasingly complicated dance steps, which the dancers would have to perform without a misstep. Competitors could dance solo, or as couples. The expression "set de flo'" apparently refers not to the drawing of the circle on the ground, but to a particular dance step where the dancer would stomp on the floor when they began dancing, a move that appeared to set the floor in place for the dancer. When couples competed, the man and woman would bow to one another at the start of the dance. The woman would place her hands on her hips, then her male partner would grin and roll his eyes, then they would begin dancing, it was some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
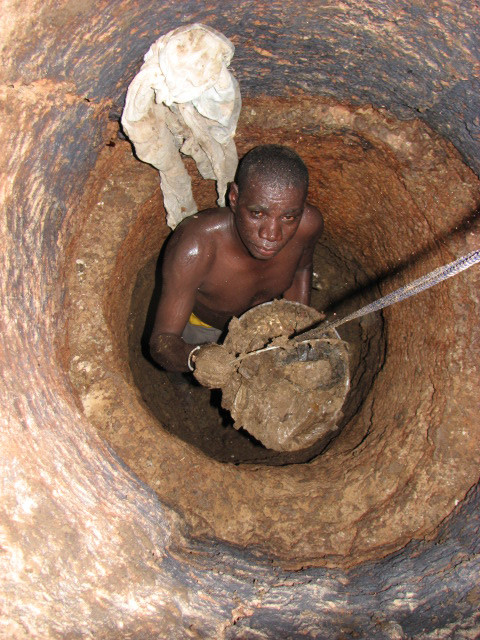
Manual Scavenging
Manual scavenging is a term used mainly in India for "manually cleaning, carrying, disposing of, or otherwise handling, human excreta in an insanitary latrine or in an open drain or sewer or in a septic tank or a pit". Manual scavengers usually use hand tools such as buckets, brooms and shovels. The workers have to move the excreta, using brooms and tin plates, into baskets, which they carry to disposal locations sometimes several kilometers away. The practice of employing human labour for cleaning of sewers and septic tanks is also prevalent in Bangladesh and Pakistan. These sanitation workers, called "manual scavengers", rarely have any personal protective equipment. The work is regarded as a dehumanizing practice. The occupation of sanitation work is intrinsically linked with caste in India. All kinds of cleaning are considered lowly and are assigned to people from the lowest rung of the social hierarchy. In the caste-based society, it is mainly the Dalits who work as sanitati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Slave Trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage. Europeans established a coastal slave trade in the 15th century and trade to the Americas began in the 16th century, lasting through the 19th century. The vast majority of those who were transported in the transatlantic slave trade were from Central Africa and West Africa and had been sold by West African slave traders to European slave traders, while others had been captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids. European slave traders gathered and imprisoned the enslaved at slave fort, forts on the African coast and then brought them to the Americas. Some Portuguese and Europeans participated in slave raids. As the National Museums Liverpool explains: "European traders captured some Africans in raids along the coast, but bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finishing School
A finishing school focuses on teaching young women social graces and upper-class cultural rites as a preparation for entry into society. The name reflects the fact that it follows ordinary school and is intended to complete a young woman's education by providing classes primarily on deportment, etiquette, and other non-academic subjects. The school may offer an intensive course, or a one-year programme. In the United States, a finishing school is sometimes called a charm school. Graeme Donald claims that the educational ladies' salons of the late 19th century led to the formal finishing institutions common in Switzerland around that time. At the schools' peak, thousands of wealthy young women were sent to one of the dozens of finishing schools available, starting at age 16. The primary goals of such institutions were to teach students the skills necessary to attract a good husband, and to become interesting socialites and wives. The 1960s marked the decline of the finishin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comportment
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate physical environment. It is the computed response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary. While some behavior is produced in response to an organism's environment (extrinsic motivation), behavior can also be the product of intrinsic motivation, also referred to as "agency" or "free will". Taking a behavior informatics perspective, a behavior consists of actor, operation, interactions, and their properties. This can be represented as a behavior vector. Models Biology Definition Behavior may be defined as "the internally coordinated responses (actions or inactions) of whole living organisms (individuals or groups) to int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prospective Study
A prospective cohort study is a longitudinal cohort study that follows over time a group of similar individuals ( cohorts) who differ with respect to certain factors under study to determine how these factors affect rates of a certain outcome. For example, one might follow a cohort of middle-aged truck drivers who vary in terms of smoking habits to test the hypothesis that the 20-year incidence rate of lung cancer will be highest among heavy smokers, followed by moderate smokers, and then non–smokers. The prospective study is important for research on the etiology of diseases and disorders. The distinguishing feature of a prospective cohort study is that at the time the investigators begin enrolling subjects and collecting baseline exposure information, none of the subjects have developed any of the outcomes of interest. After baseline information is collected, subjects in a prospective cohort study are then followed "longitudinally," i.e., over a period of time, usually for y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a medical condition typically brought on by the aging process in which there are anatomic changes and possibly a loss of function of one or more intervertebral discs of the vertebral column, spine. DDD can take place with or without symptoms, but is typically identified once symptoms arise. The root cause is thought to be loss of soluble proteins within the fluid contained in the disc with resultant reduction of the oncotic pressure, which in turn causes loss of fluid volume. Normal downward forces cause the affected disc to lose height, and the distance between vertebrae is reduced. The Intervertebral disc, anulus fibrosus, the tough outer layers of a disc, also weakens. This loss of height causes laxity of the longitudinal ligaments, which may allow anterior, posterior, or lateral shifting of the vertebral bodies, causing facet joint malalignment and arthritis; scoliosis; Cervical vertebrae, cervical hyperlordosis; thoracic hyperkyphosis; lumbar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Case–control Study
A case–control study (also known as case–referent study) is a type of observational study in which two existing groups differing in outcome are identified and compared on the basis of some supposed causal attribute. Case–control studies are often used to identify factors that may contribute to a medical condition by comparing subjects who have the condition with patients who do not have the condition but are otherwise similar. They require fewer resources but provide less evidence for causal inference than a randomized controlled trial. A case–control study is often used to produce an odds ratio. Some statistical methods make it possible to use a case–control study to also estimate relative risk, risk differences, and other quantities. Definition Porta's ''Dictionary of Epidemiology'' defines the case–control study as: "an observational epidemiological study of persons with the disease (or another outcome variable) of interest and a suitable control group of persons wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egbado
The Ẹgbado (Morphology: Ẹgba l'odo), now Yewa, are a subgroup of the Yoruba people and mostly inhabit Ogun West Senatorial District, Ogun State, in south-west Nigeria, Africa. In 1995, the group's name was changed to Yewa after the Yewa River, the river (odo) they foraged towards. The name of this river is derived from the Yoruba goddess Yewa. Yewa/Ẹgbado mainly occupy four Local Government Areas in Ogun State, Yewa South, Yewa North, Imeko-Afon, and Ipokia, while the Ado-Odo/Ota LGA forms the fifth Awori part of the senatorial district. Other Yewa/Ẹgbado are located in Lagos West, Lagos East, Oyo North, and Oyo South senatorial zones. Before the creation of the Southern Nigeria Protectorate, Egba territory and people is bordered by the Ketu (Benin) in the West, the Lagos Colony in south, Ijebu in the east, and Oyo, Ibadan and Isoya near Ile Ife in the north. The people are directly connected to the Ogun River, but detached from the swampy coast of Lagos. Throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |