|
Haystack Observatory
Haystack Observatory is a multidisciplinary radio science center, ionospheric observatory, and astronomical microwave observatory owned by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). It is in Westford, Massachusetts, in the United States, about northwest of Boston. The observatory was built by MIT's Lincoln Laboratory for the United States Air Force and was called the Haystack Microwave Research Facility. Construction began in 1960, and the antenna began operating in 1964. In 1970 the facility was transferred to MIT, which then formed the Northeast Radio Observatory Corporation (NEROC) with other universities to operate the site as the Haystack Observatory. , a total of nine institutions participated in NEROC. The Haystack Observatory site is also the location of the Millstone Hill Geospace Facility, an atmospheric-sciences research center. Lincoln Laboratory continues to use the site, which it calls the Lincoln Space Surveillance Complex (LSSC). The George R. Wallace Ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westford, Massachusetts
Westford is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was at 24,643 at the time of the 2020 United States census, 2020 Census. History Westford began as 'West Chelmsford,' a village in the town of Chelmsford, Massachusetts, Chelmsford. The village of West Chelmsford grew large enough to sustain its own governance in 1729, and was officially incorporated as Westford that year on September 23. In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, Westford primarily produced granite, apples, and worsted yarn. The Abbot Worsted Company was said to be the first company in the nation to use camel hair for worsted yarns. Paul Revere's son attended Westford Academy and a bell cast by Revere graces its lobby today. A weather vane made by Paul Revere sits atop the Abbot Elementary school. By the end of the American Civil War, as roads and transportation improved, Westford began to serve as a residential suburb for the factories of Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
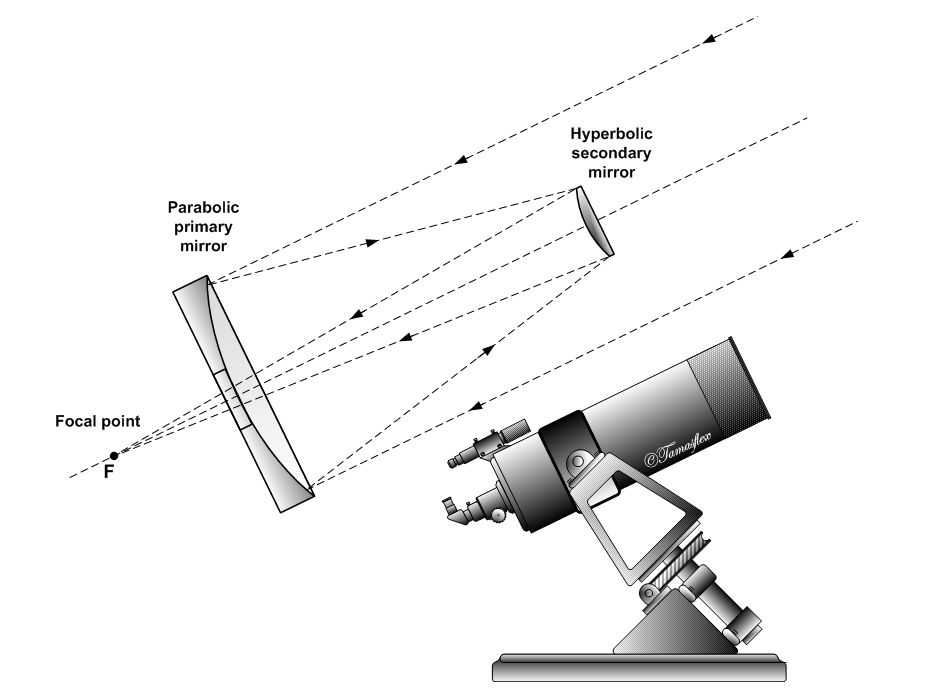
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and Antenna (radio), radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the Focus (optics), focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a Telephoto lens, telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesy
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional space, 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical body, astronomical bodies, such as planets or Natural satellite, circumplanetary systems. Geodynamics, Geodynamical phenomena, including crust (geology), crustal motion, tides, and polar motion, can be studied by designing global and national Geodetic control network, control networks, applying space geodesy and terrestrial geodetic techniques, and relying on Geodetic datum, datums and coordinate systems. Geodetic job titles include geodesist and geodetic surveyor. History Geodesy began in pre-scientific Classical antiquity, antiquity, so the very word geodesy comes from the Ancient Greek word or ''geodaisia'' (literally, "division of Earth"). Early ideas about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project West Ford
Project West Ford (also known as Westford Needles and Project Needles) was a test carried out by Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Lincoln Laboratory on behalf of the United States military in 1961 and 1963 to create an artificial ionosphere above the Earth. This was done to solve a major weakness that had been identified in military communications. History At the height of the Cold War, all international communications were either sent through submarine communications cables or bounced off the natural ionosphere. The United States military was concerned that the Soviets might cut those cables, forcing the unpredictable ionosphere to be the only means of communication with overseas forces. To mitigate the potential threat, Walter E. Morrow started Project Needles at the MIT Lincoln Laboratory in 1958. The goal of the project was to place a ring of 480,000,000 (Abstract) copper dipole antennas in orbit to facilitate global radio communication. The dipoles collectively prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, space garbage, or cosmic debris) are defunct human-made objects in spaceprincipally in Earth orbitwhich no longer serve a useful function. These include derelict spacecraft (nonfunctional spacecraft and abandoned launch vehicle stages), mission-related debris, and particularly numerous in-Earth orbit, fragmentation debris from the breakup of derelict rocket bodies and spacecraft. In addition to derelict human-made objects left in orbit, space debris includes fragments from disintegration, erosion, or collisions; solidified liquids expelled from spacecraft; unburned particles from solid rocket motors; and even paint flecks. Space debris represents a risk to spacecraft. Space debris is typically a negative externality. It creates an external cost on others from the initial action to launch or use a spacecraft in near-Earth orbit, a cost that is typically not taken into account nor fully accoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dish Antenna
A parabolic antenna is an antenna that uses a parabolic reflector, a curved surface with the cross-sectional shape of a parabola, to direct the radio waves. The most common form is shaped like a dish and is popularly called a dish antenna or parabolic dish. The main advantage of a parabolic antenna is that it has high directivity. It functions similarly to a searchlight or flashlight reflector to direct radio waves in a narrow beam, or receive radio waves from one particular direction only. Parabolic antennas have some of the highest gains, meaning that they can produce the narrowest beamwidths, of any antenna type. In order to achieve narrow beamwidths, the parabolic reflector must be much larger than the wavelength of the radio waves used, so parabolic antennas are used in the high frequency part of the radio spectrum, at UHF and microwave ( SHF) frequencies, at which the wavelengths are small enough that conveniently sized reflectors can be used. Parabolic antennas ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ku-band
The Ku band () is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in the microwave range of frequencies from 12 to 18 gigahertz (GHz). The symbol is short for "K-under" (originally ), because it is the lower part of the original NATO K band, which was split into three bands (Ku, K, and Ka) because of the presence of the atmospheric water vapor resonance peak at 22.24 GHz, (1.35 cm) which made the center unusable for long range transmission. In radar applications, it ranges from 12 to 18 GHz according to the formal definition of radar frequency band nomenclature in IEEE Standard 521–2002. Ku band is primarily used for satellite communications, most notably the downlink used by direct broadcast satellites to broadcast satellite television, and for specific applications such as NASA's Tracking Data Relay Satellite used for International Space Station (ISS) communications and SpaceX Starlink satellites. Ku band satellites are also used for backhauls and pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Space Surveillance Network
The United States Space Surveillance Network (SSN) detects, tracks, catalogs and identifies artificial objects orbiting Earth, e.g. active/inactive satellites, spent rocket bodies, or fragmentation debris. The system is the responsibility of United States Space Command and operated by the United States Space Force and its functions are: * Predict when and where a decaying space object will re-enter the Earth's atmosphere; * Prevent a returning space object, which to radar looks like a missile, from triggering a false alarm in missile-attack warning sensors of the U.S. and other countries; * Chart the present position of space objects and plot their anticipated orbital paths; * Detect new artificial objects in space; * Correctly map objects traveling in Earth orbit; * Produce a running catalog of artificial space objects; * Determine ownership of a re-entering space object; * The Space Surveillance Network includes dedicated, collateral, and contributing electro-optical, pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
W Band
The W band of the microwave part of the electromagnetic spectrum ranges from 75 to 110 GHz, wavelength ≈2.7–4 mm. It sits above the U.S. IEEE-designated V band (40–75 GHz) in frequency, and overlaps the NATO designated M band (60–100 GHz). The W band is used for satellite communications, millimeter-wave radar research, military radar targeting and tracking applications, and some non-military applications. Radar A number of passive millimeter-wave cameras for concealed weapons detection operate at 94 GHz. A frequency around 77 GHz is used for automotive cruise control radar. The atmospheric radio window at 94 GHz is used for imaging millimeter-wave radar applications in astronomy, defense, and security applications. Heat ray Less-than-lethal weaponry exists that uses millimeter waves to heat a thin layer of human skin to an intolerable temperature so as to make the targeted person move away. A two-second burst of the 95 GHz focuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Band
The X band is the designation for a band of frequencies in the microwave radio region of the electromagnetic spectrum. In some cases, such as in communication engineering, the frequency range of the X band is set at approximately 7.0–11.2 GHz. In radar engineering, the frequency range is specified by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as 8.0–12.0 GHz. The X band is used for radar, satellite communication, and wireless computer networks. Radar X band is used in radar applications, including continuous-wave, pulsed, single- polarization, dual-polarization, synthetic aperture radar, and phased arrays. X-band radar frequency sub-bands are used in civil, military, and government institutions for weather monitoring, air traffic control, maritime vessel traffic control, defense tracking, and vehicle speed detection for law enforcement. X band is often used in modern radars. The shorter wavelengths of the X band provide higher-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geostationary Orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular orbit, circular geosynchronous orbit in altitude above Earth's equator, in radius from Earth's center, and following the retrograde and prograde motion, direction of Earth's rotation. An object in such an orbit has an orbital period equal to Earth's rotational period, one sidereal time, sidereal day, and so to ground observers it appears motionless, in a fixed position in the sky. The concept of a geostationary orbit was popularised by the science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke in the 1940s as a way to revolutionise telecommunications, and the first satellite to be placed in this kind of orbit was launched in 1963. Communications satellites are often placed in a geostationary orbit so that Earth-based satellite dish, satellite antennas do not have to rotate to track t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientific research, and Earth observation. Additional military uses are reconnaissance, early warning, signals intelligence and, potentially, weapon delivery. Other satellites include the final rocket stages that place satellites in orbit and formerly useful satellites that later become defunct. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which are small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as groups, forming constellatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |