|
Harvesting
Harvesting is the process of collecting plants, animals, or fish (as well as fungi) as food, especially the process of gathering mature crops, and "the harvest" also refers to the collected crops. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulses for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper. On smaller farms with minimal mechanization, harvesting is the most labor-intensive activity of the growing season. On large mechanized farms, harvesting uses farm machinery, such as the combine harvester. Automation has increased the efficiency of both the seeding and harvesting processes. Specialized harvesting equipment, using conveyor belts for gentle gripping and mass transport, replaces the manual task of removing each seedling by hand. The term "harvesting" in general usage may include immediate postharvest handling, including cleaning, sorting, packing, and cooling. The completion of harvesting marks the end of the growing season, or the growing cycle for a particular c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
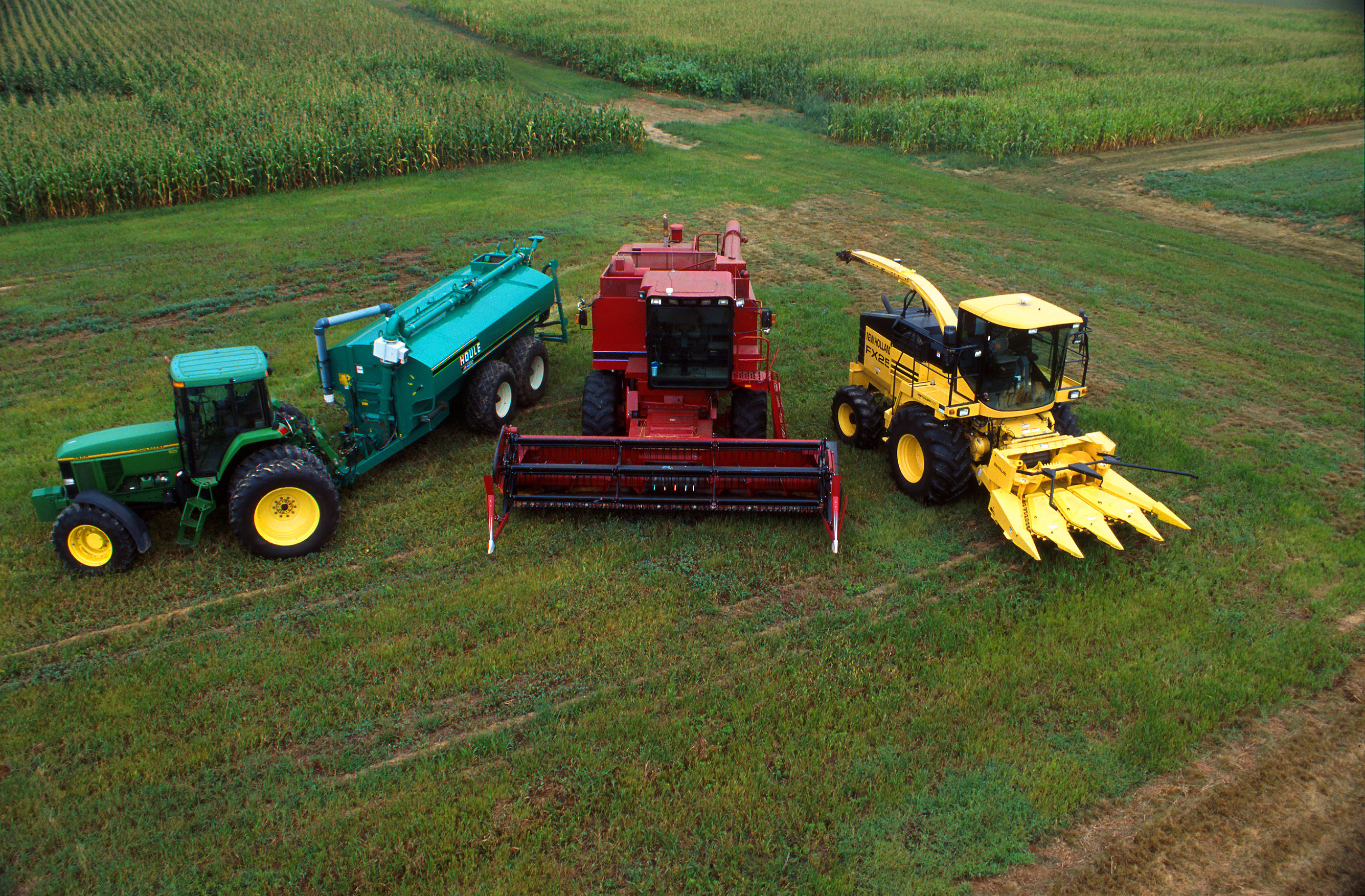
Combine Harvester
The modern combine harvester, also called a combine, is a machine designed to harvest a variety of cultivated seeds. Combine harvesters are one of the most economically important labour-saving inventions, significantly reducing the fraction of the population engaged in agriculture. Among the crops harvested with a combine are wheat, rice, oats, rye, barley, Maize, corn (maize), sorghum, millet, soybeans, flax (linseed), sunflowers and rapeseed (canola). The separated straw (consisting of stems and any remaining leaves with limited nutrients left in it) is then either chopped onto the field and ploughed back in, or laid out in rows, ready to be Baler, baled and used for bedding and cattle feed. The name of the machine is derived from the fact that the harvester combined multiple separate harvesting operations – Reaper, reaping, threshing or winnowing and gathering – into a single process around the start of the 20th century. A combine harvester still performs its functions ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
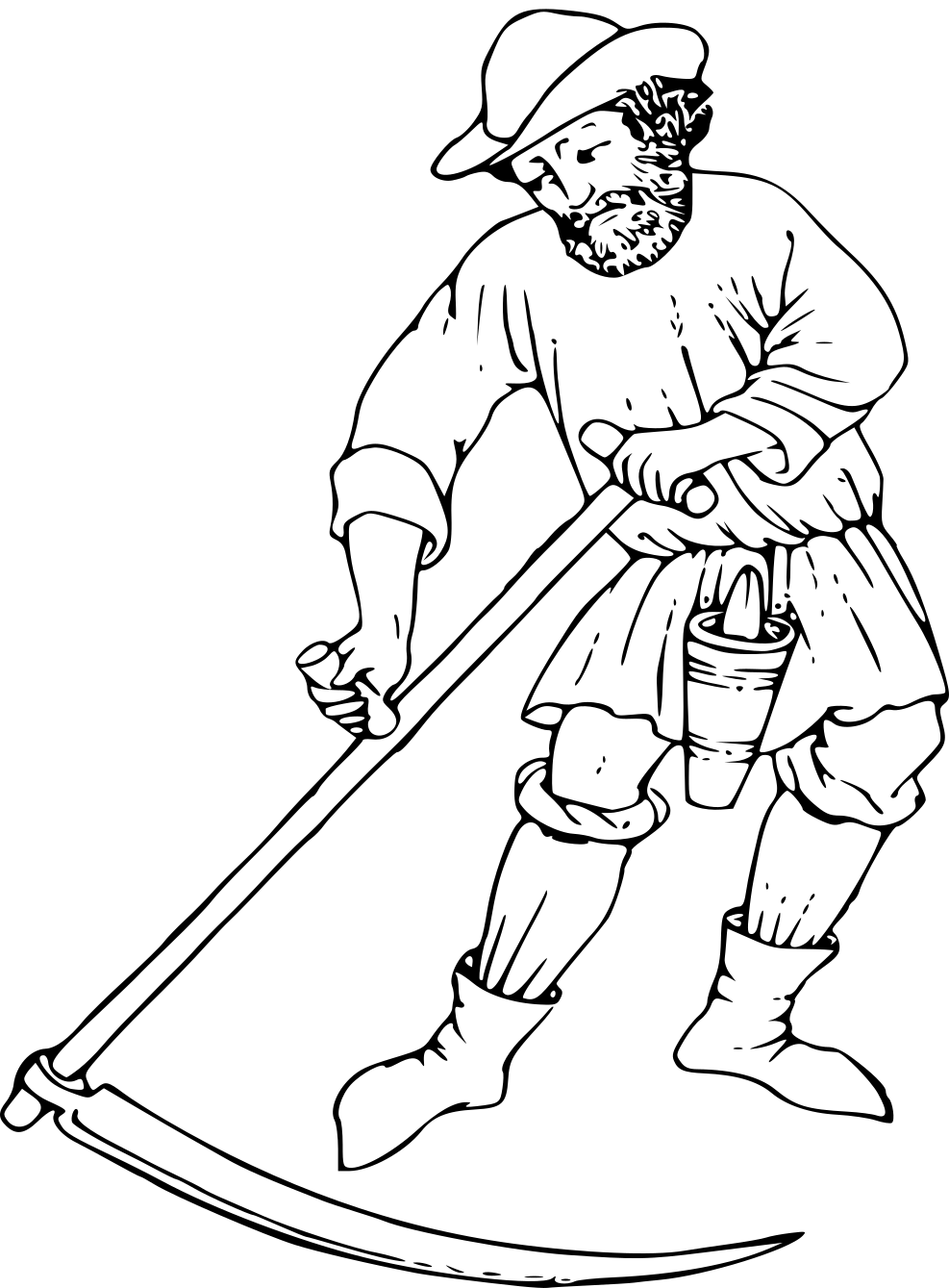
Sickle
A sickle, bagging hook, reaping-hook or grasshook is a single-handed agricultural tool designed with variously curved blades and typically used for harvesting or reaping grain crops, or cutting Succulent plant, succulent forage chiefly for feeding livestock. Falx was a synonym, but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge. Since the beginning of the Iron Age hundreds of region-specific variants of the sickle have evolved, initially of iron and later steel. This great diversity of sickle types across many cultures can be divided into smooth or serrated blades, both of which can be used for cutting either green grass or mature cereals using slightly different techniques. The serrated blade that originated in prehistoric sickles still dominates in the reaping of grain and is even found in modern grain-harvesting machines and in some kitchen knives. History Pre-Neolithic The development of the sickle in Mesopota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farm Machinery
Agricultural machinery relates to the machine (mechanical), mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are list of agricultural machinery, many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractors and the farm implements that they tow or operate. Machinery is used in both organic farming, organic and nonorganic farming. Especially since the advent of mechanised agriculture, agricultural machinery is an indispensable part of how the world is fed. Agricultural machinery can be regarded as part of wider agricultural automation technologies, which includes the more advanced digital equipment and agricultural robotics. While robots have the potential to automate the three key steps involved in any agricultural operation (diagnosis, decision-making and performing), conventional motorized machinery is used principally to automate only the performing step where diagnosis and decision-making are conducted by humans based on observations an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021Water Cycle Changes. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often has large impacts on the ecosystems and agriculture of affected regions, and causes harm to the local economy. Annua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postharvest
In agriculture, postharvest handling is the stage of crop production immediately following harvest, including cooling, cleaning, sorting and packing. The instant a crop is removed from the ground, or separated from its parent plant, it begins to deteriorate. Postharvest treatment largely determines final quality, whether a crop is sold for fresh consumption, or used as an ingredient in a processed food product. Goals The most important goals of post-harvest handling are to keep the product cool and safe, to avoid moisture loss and slow down undesirable chemical changes, and avoiding physical damage such as bruising, to delay spoilage. Sanitation is also an important factor, to reduce the possibility of pathogens that could be carried by fresh produce, for example, as residue from contaminated washing water. After the field, post-harvest processing is usually continued in a packing house. This can be a simple shed, providing shade and running water, or a large-scale, sophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture In Volgograd Oblast 002
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domestication, domesticated species created food economic surplus, surpluses that enabled people to live in the cities. While humans started gathering grains at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers only began planting them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs, and cattle were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. In the 20th century, industrial agriculture based on large-scale monocultures came to dominate agricultural output. , smallholding, small farms produce about one-third of the world's food, but large farms are prevalent. The largest 1% of farms in the world are greater than and operate more than 70% of the world's farmland. Nearly 40% of agricultural land is found on fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaper
A reaper is a farm implement that reaps (cuts and often also gathers) crops at harvest when they are ripe. Usually the crop involved is a cereal grass, especially wheat. The first documented reaping machines were Gallic reapers that were used in Roman times in what would become modern-day France. The Gallic reaper involved a comb which collected the heads, with an operator knocking the grain into a box for later threshing. Most modern mechanical reapers cut grass; most also gather it, either by windrowing or picking it up. Modern machines that not only cut and gather the grass but also thresh its seeds (the grain), winnow the grain, and deliver it to a truck or wagon, are called combine harvesters or simply combines, and are the engineering descendants of earlier reapers. Hay is harvested somewhat differently from grain; in modern haymaking, the machine that cuts the grass is called a hay mower or, if integrated with a conditioner, a mower-conditioner. As a manual tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythe
A scythe (, rhyming with ''writhe'') is an agriculture, agricultural hand-tool for mowing grass or Harvest, harvesting Crop, crops. It was historically used to cut down or reaping, reap edible grain, grains before they underwent the process of threshing. Horse-drawn and then tractor machinery largely replaced the scythe, but it is still used in some areas of Europe and Asia. Reapers are bladed machines that automate the cutting action of the scythe, and sometimes include subsequent steps in preparing the grain or the straw or hay. The word "scythe" derives from Old English ''siðe''. In Middle English and later, it was usually spelled ''sithe'' or ''sythe''. However, in the 15th century some writers began to use the ''sc-'' spelling as they thought (wrongly) that the word was related to the Latin (meaning "to cut"). Nevertheless, the ''sithe'' spelling lingered, and notably appears in Noah Webster's dictionaries. A scythe consists of a shaft about long called a ''snaith'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanization
Mechanization (or mechanisation) is the process of changing from working largely or exclusively by hand or with animals to doing that work with machinery. In an early engineering text, a machine is defined as follows: In every fields, mechanization includes the use of hand tools. In modern usage, such as in engineering or economics, mechanization implies machinery more complex than hand tools and would not include simple devices such as an ungeared horse or donkey mill. Devices that cause speed changes or changes to or from reciprocating to rotary motion, using means such as gears, pulleys or line shaft, sheaves and belts, drive shaft, shafts, Cam (mechanism), cams and Crank (mechanism), cranks, usually are considered machines. After electrification, when most small machinery was no longer hand powered, mechanization was synonymous with motorized machines. Extension of mechanization of the production process is termed as automation and it is controlled by a Feedback, closed l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse (legume)
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, but also as livestock forage and silage, and as soil-enhancing green manure. Legumes produce a botanically unique type of fruit – a simple dry fruit that develops from a simple carpel and usually dehisces (opens along a seam) on two sides. Most legumes have symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria, Rhizobia, in structures called root nodules. Some of the fixed nitrogen becomes available to later crops, so legumes play a key role in crop rotation. Terminology The term ''pulse'', as used by the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), is reserved for legume crops harvested solely for the dry seed. This excludes green beans and green peas, which are considered vegetable crops. Also excluded are seeds that are main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |