|
Harrisburg Intermodal Yard
Harrisburg Intermodal Yard is a large rail yard located in Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. The yard originally was operated by the Pennsylvania Railroad and was known as the Lucknow Yard, later to be operated by Conrail, and since 1999, has been operated by the Norfolk Southern Railway. The Harrisburg Yard, the Enola Yard and the Rutherford Yard are the three major rail facilities located in the Harrisburg area. See also * Buffalo Line * Harrisburg Line The Harrisburg Line is a railroad, rail line owned and operated by the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS) in the United States, U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The line runs from Philadelphia (HP 5.2) west to Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, Harrisburg (HP 112 ... References External links Norfolk Southern Railway facilities {{Coord, 40.295, -76.891, type:landmark_region:US-PA_dim:5000, display=title Conrail Norfolk Southern Railway Rail yards in Pennsylvania Transportation buildings and structures in Dauphin County, Pennsylvania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Yard
A rail yard, railway yard, railroad yard (US) or simply yard, is a series of Track (rail transport), tracks in a rail network for storing, sorting, or loading and unloading rail vehicles and locomotives. Yards have many tracks in parallel for keeping rolling stock or unused locomotives stored off the main line (rail), main line, so that they do not obstruct the flow of traffic. Cars or wagons are moved around by specially designed yard switcher locomotives (US) or shunter locomotives (UK), a type of locomotive. Cars or wagons in a yard may be sorted by numerous categories, including railway company, loaded or unloaded, destination, car type, or whether they need repairs. Yards are normally built where there is a need to store rail vehicles while they are not being loaded or unloaded, or are waiting to be assembled into trains. Large yards may have a Centralized traffic control, tower to control operations. Many yards are located at strategic points on a Main line (railway), main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harrisburg, Pennsylvania
Harrisburg ( ; ) is the capital city of the U.S. commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the seat of Dauphin County. With a population of 50,099 as of 2020, Harrisburg is the ninth-most populous city in Pennsylvania. It is the larger of the two principal cities of the Harrisburg–Carlisle metropolitan statistical area, also known as the Susquehanna Valley, which had a population of 591,712 in 2020 and is the fourth-most populous metro area in Pennsylvania. Harrisburg is situated on the east bank of the Susquehanna River, southwest of Allentown and northwest of Philadelphia. Harrisburg played a role in American history during the Westward Migration, the American Civil War, and the Industrial Revolution. During part of the 19th century, the building of the Pennsylvania Canal and later the Pennsylvania Railroad allowed Harrisburg to develop into one of the most industrialized cities in the Northeastern United States. In the mid- to late 20th century, the city's economic fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
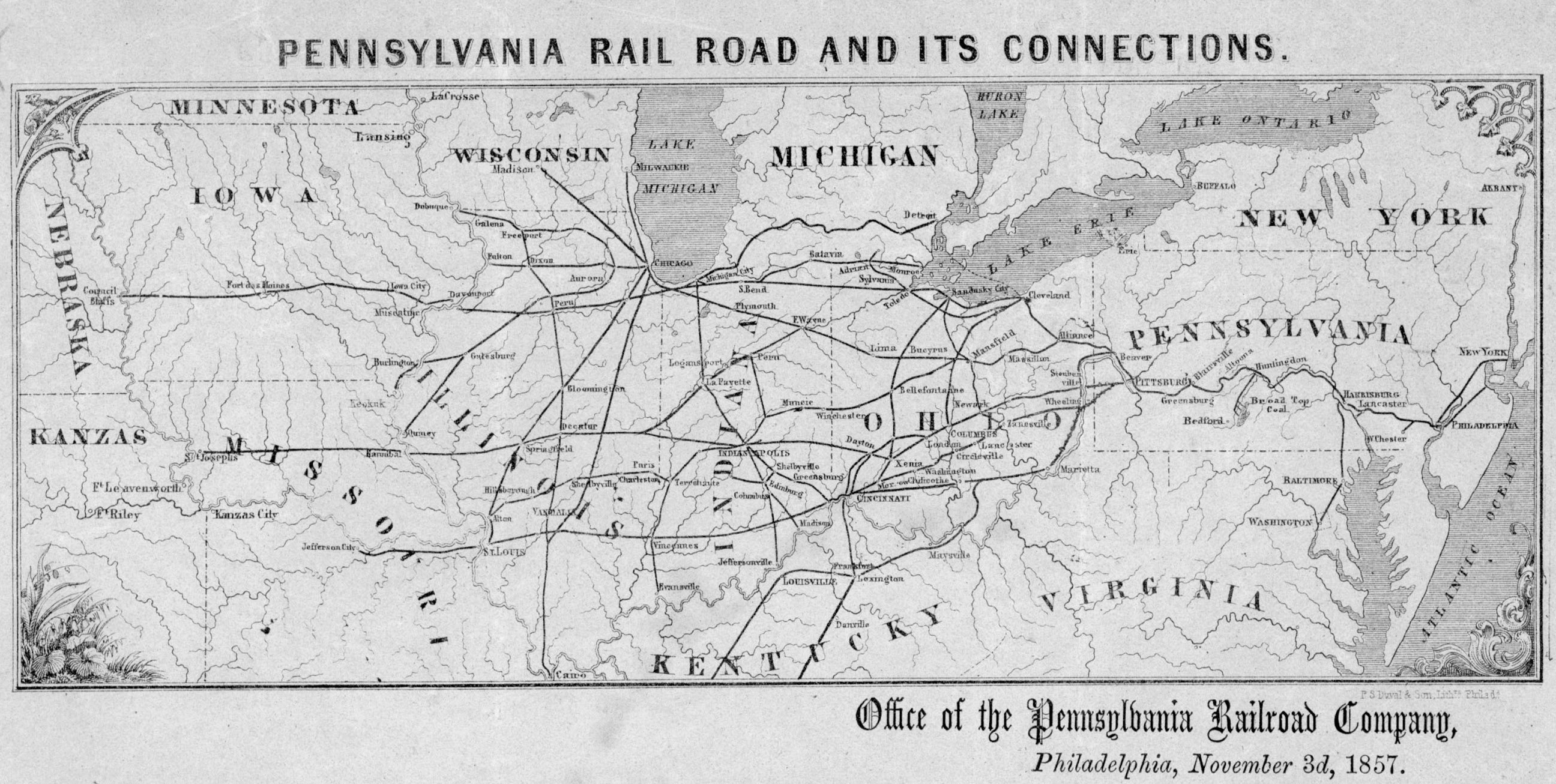
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its peak in 1882, the Pennsylvania Railroad was the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Over its existence, Pennsylvania Railroad acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe railroads. Its only formidable rival was the New York Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conrail
Conrail , formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name. It continues to do business as an asset management and network services provider in three Shared Assets Areas that were excluded from the division of its operations during its acquisition by CSX Corporation and the Norfolk Southern Railway. The federal government created Conrail to take over the potentially profitable lines of multiple bankrupt carriers, including the Penn Central Transportation Company and Erie Lackawanna Railway. After railroad regulations were lifted by the 4R Act and the Staggers Act, Conrail began to turn a profit in the 1980s and was privatized in 1987. The two remaining Class I railroads in the East, CSX Transportation and the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS), agreed in 1997 to acquire the system and split it into two roughly-equal parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk Southern Railway
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States. Headquartered in Atlanta, the company was formed in 1982 with the merger of the Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. The company operates in 22 eastern states, the District of Columbia, and has rights in Canada over the Albany to Montreal route of the Canadian Pacific Kansas City. Norfolk Southern Railway is the leading subsidiary of the Norfolk Southern Corporation. Norfolk Southern maintains 28,400 miles of track, with the rest managed by other parties through trackage rights. Intermodal containers and trailers are the most common commodity type carried by NS, which have grown as the coal business has declined throughout the 21st century; coal was formerly the largest traffic source. The railway offers the largest intermodal rail network in eastern North America. NS was also the pioneer of Roadrailer service. Norfolk Southern and its chief competitor, CSX ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enola Yard
Enola Yard is a large rail yard located in East Pennsboro Township, Pennsylvania, along the western shore of the Susquehanna River in Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. Built in 1905 and expanded through the 1930s, Enola yard was the world's largest freight train, freight yard in 1956. It remains in operation today, though it has long since been eclipsed in size and traffic, first by Conway Yard outside Pittsburgh, PA and later by Bailey Yard in North Platte, Nebraska. History The Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) built the yard in 1905 with two Classification yard#Hump yard, hump classification yards. Initially, the yard processed 7,000 Railroad car#Freight cars, cars per day. The westbound complex had a 20-track receiving yard and 25 classification tracks; the eastbound, a 21-track receiving yard and 17 classification tracks. There were no separate departure yards. By the late 1920s, Enola encompassed 316 acres and had a capacity of 9,692 cars. Service buildings included a 43-stall Railway r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutherford Intermodal Yard
Rutherford Intermodal Yard is a large rail yard located in Swatara Township, Dauphin County, just east of Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. History The yard was formerly operated by the Reading Railroad and later Conrail. Ownership was transferred from Conrail to the Norfolk Southern Railway in 1999. In the summer of 2000, Norfolk Southern retrofitted the yard for $31 million, its first major investment in the Harrisburg area. Large cargo containers are transferred at the yard from flatbed truck trailers to flatbed rail cars, or vice versa.Harrisburg's historic Enola Yard is railroad hub Brotherhood of Locomotive Engineers and Trainmen, press release. Retrieved February 25, 2010. The Rutherford facility has 10 classification tracks, two loading/unloading tracks, two overhead cranes, and parking space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harrisburg Metropolitan Area
Harrisburg ( ; ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), U.S. commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat, seat of Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Dauphin County. With a population of 50,099 as of 2020 United States census, 2020, Harrisburg is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, ninth-most populous city in Pennsylvania. It is the larger of the two principal cities of the Harrisburg–Carlisle metropolitan statistical area, also known as the Susquehanna Valley, which had a population of 591,712 in 2020 and is the Pennsylvania metropolitan areas, fourth-most populous metro area in Pennsylvania. Harrisburg is situated on the east bank of the Susquehanna River, southwest of Allentown, Pennsylvania, Allentown and northwest of Philadelphia. Harrisburg played a role in American history during the American frontier, Westward Migration, the American Civil War, and the Industrial Revolution. During part of the 19th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffalo Line
The Buffalo Line is a railroad line owned by the Norfolk Southern Railway in the U.S. states of New York and Pennsylvania. The line runs from Buffalo, New York southeast to Rockville, Pennsylvania near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania along a former Pennsylvania Railroad line. Its north end is at Seneca Yard in Buffalo, with no direct access to the Lake Erie district, and its south end is at the Pittsburgh Line at Rockville. The line is operated by the Buffalo and Pittsburgh Railroad between Buffalo and Machias, New York, the Western New York and Pennsylvania Railroad between Machias and Driftwood, Pennsylvania, and the Norfolk Southern Railway between Driftwood and Rockville. History The Sunbury and Erie Railroad opened from Williamsport, Pennsylvania south to Milton in 1854, Northumberland in 1855, and Sunbury in 1856. , March 2005 Edition Extensions west from Williamsport opened to Whetham in 1859, Keating (as the Philadelphia and Erie Railroad) in 1862, reorganize in 189 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harrisburg Line
The Harrisburg Line is a railroad, rail line owned and operated by the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS) in the United States, U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The line runs from Philadelphia (HP 5.2) west to Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, Harrisburg (HP 112.9). The Harrisburg Line was formed the day Conrail began operations, April 1, 1976, from two former Reading Company lines, the original Main Line (Reading Company), namesake main line to Reading, Pennsylvania, and the Lebanon Valley Branch. Today, the Harrisburg Line is owned by Norfolk Southern Railway under their Harrisburg Division. The Harrisburg Line runs through two tunnels, the Flat Rock Tunnel in Lower Merion Township, Pennsylvania, Lower Merion Township and the Black Rock Tunnel in Phoenixville, Pennsylvania, Phoenixville. History The Harrisburg Line, as a single rail line, was formed on April 1, 1976. However, under the Reading Company, the Harrisburg Line was two rail lines: the original main line from Reading, Pennsylvania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Yards In Pennsylvania
Rail or rails may refer to: Rail transport *Rail transport and related matters *Railway track or railway lines, the running surface of a railway Arts and media Film * ''Rails'' (film), a 1929 Italian film by Mario Camerini * ''Rail'' (1967 film), a film by Geoffrey Jones for British Transport Films * ''Rail'' (2024 film), a Tamil-language film Magazines * ''Rail'' (magazine), a British rail transport periodical * ''Rails'' (magazine), a former New Zealand based rail transport periodical Other arts *The Rails, a British folk-rock band * Rail (theater) or batten, a pipe from which lighting, scenery, or curtains are hung Technology *Rails framework or Ruby on Rails, a web application framework *Rail system (firearms), a mounting system for firearm attachments *Front engine dragster *Runway alignment indicator lights, a configuration of an approach lighting system *Rule Augmented Interconnect Layout, a specification for expressing guidelines for printed circuit boards; companion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |