|
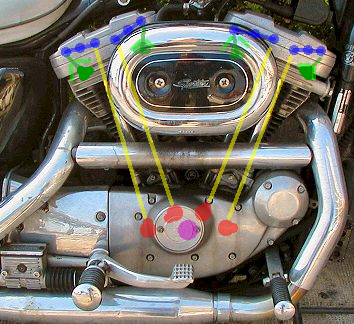
Harley-Davidson Evolution Engine
The Evolution engine (popularly known as Evo and sometimes as Blockhead ) is an air-cooled, 45-degree, V-twin engine manufactured from 1984 by Harley-Davidson for the company's motorcycles. It was made in the displacement for Harley-Davidson Big V-twins bikes, replacing the Shovelhead engine until 2000 when the last EVO was placed in a production factory custom FXR4 (FXR2 and FXR3 were the first CVOs). In 1999, it was replaced by the Harley-Davidson Twin Cam 88 in the Touring and Dyna model and in 2000 in the Softail models. Also available in the Sportster model beginning in 1986, it was made in the displacement until 1988 and is still made in the and displacements for the Harley-Davidson Sportster, replacing the ironhead Sportster engine. Most analysts consider the Evolution to be the engine that saved the reorganized Harley-Davidson company from certain bankruptcy. Harley-Davidson's official name for the engine was likely related to the company's attempt to reform it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harley-Davidson Museum February 2024 14 (Engine Room--Evolution, 1984-99)
Harley-Davidson, Inc. (H-D, or simply Harley) is an American motorcycle manufacturer headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Founded in 1903, it is one of two major American motorcycle manufacturers to survive the Great Depression along with its historical rival, Indian Motorcycles.Automotive – RSS Feed . ''Popular Mechanics''. Retrieved July 7, 2011. The company has survived numerous ownership arrangements, subsidiary arrangements, periods of poor economic health and product quality, and intense global competition to become an iconic brand widely known for its loyal following. There are owner clubs and events worldwide, as well as a company-sponsored, brand-focused museum. Harley-Davidson is noted for a style of customization that gave rise to the Chopper (moto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Valve
An overhead valve engine, abbreviated (OHV) and sometimes called a pushrod engine, is a piston engine whose valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with flathead (or "sidevalve") engines, where the valves were located below the combustion chamber in the engine block. Although an overhead camshaft (OHC) engine also has overhead valves, the common usage of the term "overhead valve engine" is limited to engines where the camshaft is located in the engine block. In these traditional OHV engines, the motion of the camshaft is transferred using pushrods (hence the term "pushrod engine") and rocker arms to operate the valves at the top of the engine. However, some designs have the camshaft in the cylinder head but still sit below or alongside the valves (the Ford CVH and Opel CIH are good examples), so they can essentially be considered overhead valve designs. Some early intake-over-exhaust engines used a hybrid design combining elemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harley-Davidson Milwaukee-Eight Engine
The Harley-Davidson Milwaukee-Eight engine is the ninth generation of "big twin" engines developed by the company. Introduced in 2016, it is Harley's fourth all-new Big Twin engine family. These engines differ from the traditional Harley Big Twin engines in that there are four valves per cylinder, totaling eight valves, hence the name. It also marked a return to the single-camshaft configuration as used on previous Harley Big Twin Engines from 1936 to 1999. In addition, the engines all have internal counterbalancers. 107, 114, 117, and 121 engines All engines have eight valves in two cylinders in the traditional Harley-Davidson Radial V-twin configuration at 45°, are combination of air-cooled and oil-cooled, and activate valves with push-rods. The model with a claimed is standard on all models, with the version making a claimed remaining as an option on some softails and all touring and trike models, and the is standard on CVO models with a claimed and rear wheel power of @ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S&S Cycle
S&S Cycle is an American motorcycle engine and parts engineer and manufacturer. The company was founded in 1958 by George J. Smith and Stanley Stankos in Blue Island, Illinois. The company started by selling high performance pushrods for Harley-Davidson motorcycles, and today they still make parts for a variety of V-twin, V-Twin bikes. The company's current president is Paul Skarie. History Soon after the formation of S&S, George's wife, Marjorie, bought out Stanley Stankos and Smith & Stankos became Smith & Smith. In 1969, the company moved from Blue Island to establish a new headquarters in Viola, Wisconsin. S&S still operates at this location, but opened an additional facility in La Crosse, Wisconsin in 2004. In July 2007 S&S purchased the Flathead Power (FHP) brand name and intellectual property (trademarks, patents and designs) along with the remaining inventory of parts and tooling and is continuing the vintage brand; the brand was resold in 2014 to the original owner. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William S
William is a masculine given name of Germanic languages, Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman Conquest, Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will (given name), Will or Wil, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill (given name), Bill, Billie (given name), Billie, and Billy (name), Billy. A common Irish people, Irish form is Liam. Scottish people, Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie). Female forms include Willa, Willemina, Wilma (given name), Wilma and Wilhelmina (given name), Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German language, German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harley-Davidson Knucklehead Engine
The knucklehead is a retronym used by enthusiasts to refer to a Harley-Davidson motorcycle engine, so named because of the distinct shape of the rocker boxes. The engine is a two-cylinder, 45 degree, pushrod actuated overhead valve V-twin engine with two valves per cylinder. It was the third basic type of V-Twin engine used by Harley-Davidson, replacing the Flathead-engined VL model in 1936 as HD's top-of-the-line model. The engine was manufactured until 1947 and was replaced by the Panhead engine in 1948. The Knucklehead-engined models were originally referred to as "Overhead valve, OHVs" by enthusiasts of the time and in Harley's official literature; the nickname arose from the California chopper culture of the late 1960s. As the design of Harley-Davidson engines has evolved through the years, the distinctive shape of each model's valve covers has allowed Harley enthusiasts to classify an engine simply by looking for those shapes. The contours of a knucklehead engine's valve c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a reciprocating engine, piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating Shaft (mechanical engineering), shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting rods. The crankpins are also called ''rod bearing journals'', and they rotate within the "big end" of the connecting rods. Most modern crankshafts are located in the engine block. They are made from steel or cast iron, using either a forging, casting (metalworking), casting or machining process. Design The crankshaft is located within the engine block and held in place via main bearings which allow the crankshaft to rotate within the block. The up-down motion of each piston is transferred to the crankshaft via connecting rods. A flywheel is often attached to one end of the crankshaft, in order to smoothen the power delivery and reduce vibration. A crankshaft is subjected to enormou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camshaft
A camshaft is a shaft that contains a row of pointed cams in order to convert rotational motion to reciprocating motion. Camshafts are used in piston engines (to operate the intake and exhaust valves), mechanically controlled ignition systems and early electric motor speed controllers. Camshafts in piston engines are usually made from steel or cast iron, and the shape of the cams greatly affects the engine's characteristics. History Trip hammers are one of the early uses of a form of cam to convert rotating motion, e.g. from a waterwheel, into the reciprocating motion of a hammer used in forging or to pound grain. Evidence for these exists back to the Han dynasty in China, and they were widespread by the medieval period. Camshafts were first described by Ismail al-Jazari in 1206. Once the rotative version of the steam engine was developed in the late 18th century, the operation of the valve gear was usually by an eccentric, which turned the rotation of the crankshaft i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buell Blast
The Buell Blast is a motorcycle that was made by the Buell Motorcycle Company from 2000 to 2009. The Blast was conceived as an entry-level motorcycle to attract newcomers to motorcycling in general and to Harley-Davidson in particular. As such, the design goals were low cost and ease of operation and maintenance. Steps to achieve these goals include the use of an automatically tensioned belt final drive, self-adjusting hydraulic valve lifters, and a carburetor with an automatic choke. The engine design was borrowed from Harley's Evolution Sportster engine with the rear cylinder eliminated. The plastic bodywork pieces of the Blast were made from Surlyn, a substance used to make the outside of golf balls, to protect the surfaces when the Blast is dropped, and the color is molded-in. The Blast was used in Harley-Davidson's Rider's Edge New Rider program, a similar course to the Motorcycle Safety Foundation's Basic "RiderCourse". In July 2009, prior to ceasing all motorcycle prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of a fuel injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines. All compression-ignition engines (e.g. diesel engines), and many spark-ignition engines (i.e. petrol (gasoline) engines, such as Otto or Wankel), use fuel injection of one kind or another. Mass-produced diesel engines for passenger cars (such as the Mercedes-Benz OM 138) became available in the late 1930s and early 1940s, being the first fuel-injected engines for passenger car use. In passenger car petrol engines, fuel injection was introduced in the early 1950s and gradually gained prevalence until it had largely replaced carburetors by the early 1990s. The primary difference between carburetion and fuel injection is that fuel injection atomizes the fuel through a small nozzle under high pressure, while carburetion relies on suction crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delphi Corporation
Aptiv PLC is an Irish- American automotive technology supplier with headquarters in Schaffhausen, Switzerland. Aptiv grew out of the now-defunct American company, Delphi Automotive Systems, which itself was formerly a component of General Motors. History The company was established as General Motors' Automotive Components Group in 1994, which changed its name to Delphi Automotive Systems in 1995. G.M. also renamed the various divisions within the newly created Delphi unit. Packard Electric became Delphi Packard Electric Systems; Delco Chassis became Delphi Chassis Systems; Inland Fisher-Guide became Delphi Interior and Lighting Systems; Saginaw became Delphi Saginaw Steering Systems; Harrison Radiator became Delphi Harrison Thermal Systems, and AC Delco became Delphi Energy and Engine Management Systems. Delphi disclosed some irregular accounting practices in 2005. Many executives, including CFO Alan Dawes, resigned. Delphi Chairman J.T. Battenberg retired. Delphi then filed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buell Motorcycle Company
Buell Motorcycles is an American motorcycle manufacturer based in Grand Rapids, Michigan. It was founded in 1983 by ex-Harley-Davidson engineer Erik Buell. Harley-Davidson acquired 49 percent of Buell in 1993, and Buell became a wholly owned subsidiary of Harley-Davidson by 2003. On November 17, 2006, Buell announced that it had produced and shipped its 100,000th motorcycle. On October 15, 2009, Harley-Davidson announced the discontinuation of the Buell product line as part of its strategy to focus on the Harley-Davidson brand. The last Buell motorcycle produced through Harley-Davidson was on October 30, 2009, bringing the number manufactured to 136,923. In November 2009, Erik Buell announced the launch of Erik Buell Racing, an independent company run by Erik Buell which initially produced race-only versions of the 1125R model, then subsequently offered an updated 1190RS model for the street or the track, and produced further improved 1190RX and 1190SX models which are inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |