|
Harifian Culture
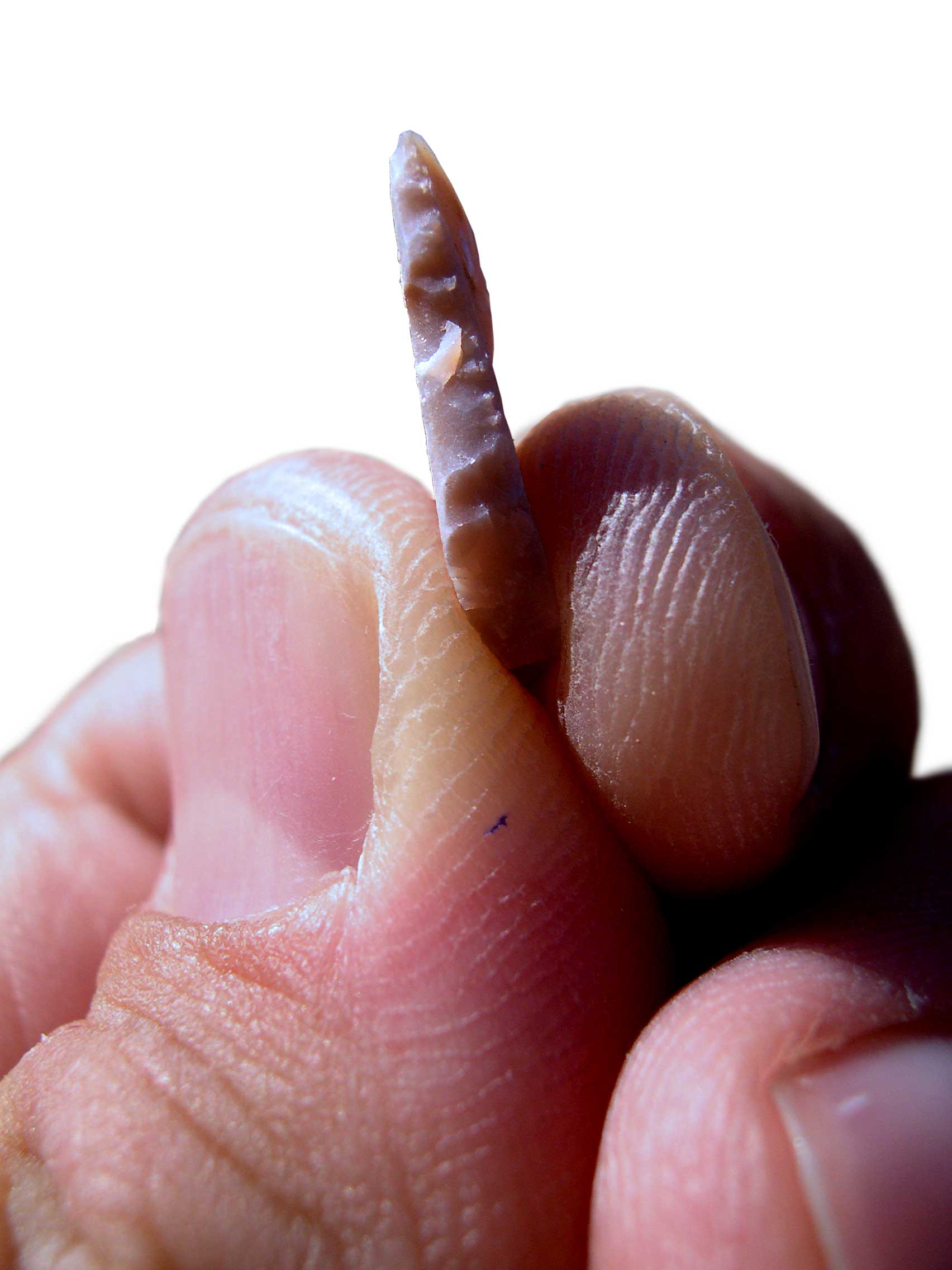
Harifian is a specialized regional cultural development of the Epipalaeolithic of the Negev Desert, in the southern part of the Levant. It corresponds to the latest stages of the Natufian culture, and represents a culmination of the local Natufian developments. History Like the Natufian, Harifian is characterized by semi-subterranean houses. These are often more elaborate than those found at Natufian sites. For the first time arrowheads are found among the stone tool kit. The Harifian dates to between approximately 10,800/10,500 BP and 10,000/10,200 BP. It is restricted to the Sinai Peninsula and Negev, and is probably broadly contemporary with the Late Natufian or Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA), although archeological chronology has shown it seems to have occurred during the transition from the Natufian to the PPNA. Microlithic points are a characteristic feature of the industry, with the Harif point being both new and particularly diagnostic – Bar-Yosef (1998) suggests t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negev
The Negev ( ; ) or Naqab (), is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort town, resort city and port of Eilat. It contains several development towns, including Dimona, Arad, Israel, Arad, and Mitzpe Ramon, as well as a number of small Negev Bedouin, Bedouin towns, including Rahat, Tel Sheva, and Lakiya. There are also several kibbutzim, including Revivim and Sde Boker; the latter became the home of Israel's first Prime Minister of Israel, prime minister, David Ben-Gurion, after his retirement from politics. Although historically part of a separate region (known during the Roman Empire, Roman period as Arabia Petraea), the Negev was added to the proposed area of Mandatory Palestine, of which large parts later became Israel, on 10 July 1922, having been conceded by British representative St John Philby "in Emirate of Transjordan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
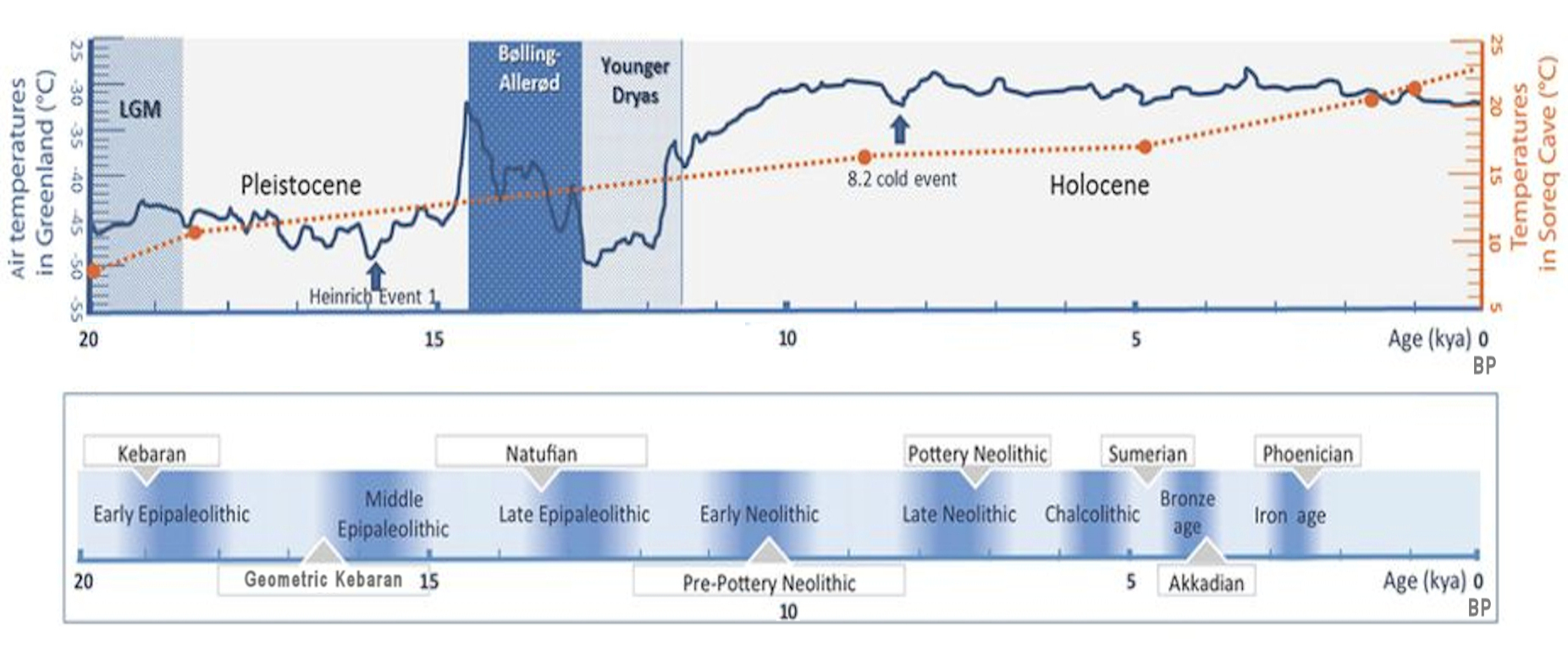
Epipalaeolithic Near East
The Epipalaeolithic Near East designates the Epipalaeolithic ("Final Old Stone Age") in the History of the Middle East#Prehistoric Near East, prehistory of the Near East. It is the period after the Upper Paleolithic, Upper Palaeolithic and before the Neolithic, between approximately 25,000 and 11,500 years Before Present. The people of the Epipalaeolithic were nomadic hunter-gatherers who generally lived in small, seasonal camps rather than permanent villages. They made sophisticated stone tools using microliths—small, finely-produced blades that were hafted in wooden implements. These are the primary artifacts by which archaeologists recognise and classify Epipalaeolithic sites. Although the appearance of microliths is an arbitrary boundary, the Epipalaeolithic does differ significantly from the preceding Upper Palaeolithic. Epipalaeolithic sites are more numerous, better preserved, and can be accurately Radiocarbon dating, radiocarbon dated. The period coincides with the gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natufian Culture
The Natufian culture ( ) is an archaeological culture of the late Epipalaeolithic Near East in West Asia from 15–11,500 Before Present. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentism, sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the Origins of agriculture in West Asia, introduction of agriculture. Natufian communities may be the ancestors of the builders of the region's first List of Neolithic settlements, Neolithic settlements, which may have been the earliest in the world. Some evidence suggests deliberate cultivation of cereals, specifically rye, by the Natufian culture at Tell Abu Hureyra, the site of the earliest evidence of agriculture in the world. The world's oldest known evidence of the production of bread-like foodstuff has been found at Shubayqa 1, a 14,400-year-old site in Jordan, Jordan's northeastern desert, 4,000 years before the Origins of agriculture in West Asia, emergence of agriculture in Southwest Asia. In addition, the oldest known evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khiamian Culture
The Khiamian culture is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southwest Asia, dating to the earliest part of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA), around 9700 to 8600 BC. It is primarily characterised by a distinctive type of stone arrowhead—the "El Khiam point"—first found at the type site of El Khiam. Overview The Khiamian owes its name to the site of El Khiam, situated on banks of the Dead Sea, where researchers have recovered the oldest chert arrows heads, with lateral notches, the so-called "El Khiam points".. 2007. ''Zivilisationen – wie die Kultur nach Sumer kam.'' Munich. p126 They have served to identify sites of this period, which are found in Israel, as well as in Jordan (Azraq), Sinai ( Abu Madi), and to the north as far as the Middle Euphrates ( Mureybet). El Khiam points and other chert stone tools alike are often referred to as projectile points or arrowheads. While it is true that they were used as arrowheads, the given names imply function and are therefo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in Western AsiaGasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. p. 5: "... today the term ''Levantine'' can describe shared cultural products, such as Levantine cuisine or Levantine archaeology". .Steiner & Killebrew, p9: "The general limits ..., as defined here, begin at the Plain of 'Amuq in the north and extend south until the Wâdī al-Arish, along the northern coast of Sinai. ... The western coastline and the eastern deserts set the boundaries for the Levant ... The Euphrates and the area around Jebel el-Bishrī mark the eastern boundary of the northern Levant, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa. Sinai has a land area of about (6 percent of Egypt's total area) and a population of approximately 600,000 people. Administratively, the vast majority of the area of the Sinai Peninsula is divided into two Governorates of Egypt, governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal, crossing into African Egypt: Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate in the center, and Port Said Governorate in the north. In the classical era, the region was known as Arabia Petraea. The peninsula acquired the name ''Sinai'' in modern times due to the assumption that a mountain near Saint Catherine's Monastery is the Biblical Mount Sinai. Mount Sinai i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Pottery Neolithic A
Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) denotes the first stage of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, in early Levantine and Anatolian Neolithic culture, dating to years ago, that is, 10,000–8800 BCE. Archaeological remains are located in the Levantine and Upper Mesopotamian region of the Fertile Crescent. The time period is characterized by tiny circular mud-brick dwellings, the cultivation of crops, the hunting of wild game, and unique burial customs in which bodies were buried below the floors of dwellings. The Pre-Pottery Neolithic A and the following Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) were originally defined by Kathleen Kenyon in the type site of Jericho, State of Palestine. During this time, pottery was not yet in use. They precede the ceramic Neolithic Yarmukian culture. PPNA succeeds the Natufian culture of the Epipalaeolithic Near East. Settlements PPNA archaeological sites are much larger than those of the preceding Natufian hunter-gatherer culture, and contain traces of commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microlith
A microlith is a small Rock (geology), stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 60,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. The microliths were used in spear points and arrowheads. Microliths are produced from either a small blade (Microblade technology, microblade) or a larger blade-like piece of flint by abrupt or truncated retouch (lithics), retouching, which leaves a very typical piece of waste, called a microburin. The microliths themselves are sufficiently worked so as to be distinguishable from workshop waste or accidents. Two families of microliths are usually defined: laminar and geometric. An assemblage of microliths can be used to date an archeological site. Laminar microliths are slightly larger, and are associated with the end of the Upper Paleolithic and the beginning of the Epipaleolithic era; geometric microliths are characteristic of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helwan Retouch
The Helwan retouch was a bifacial microlithic flint-tool fabrication technology characteristic of the Early Natufian culture The Natufian culture ( ) is an archaeological culture of the late Epipalaeolithic Near East in West Asia from 15–11,500 Before Present. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentism, sedentary or semi-sedentary population even befor ... in the Levant, a region in the Eastern Mediterranean (12,500 BP – 11,000 BP) such as the Harifian culture. The decline of the Helwan Retouch was largely replaced by the "backing" technique and coincided with the emergence of microburin methods, which involved snapping bladelets on an anvil. Natufian lithic technology throughout the usage of the Helwan Retouch was dominated by lunate-shaped lithics, such as picks and axes and especially sickles (which were predominantly—at least 80% of the time—used for harvesting wild cereals).Unger-Hamilton, Romana. The Epi-Palaeolithic Southern Levant and the Origins of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khiam
Al-Khiyam (; sometimes spelled Khiam) is a large town and municipality in the Nabatieh Governorate of Southern Lebanon. Etymology According to Edward Henry Palmer, the name means tents. Haifa Nassar, a Khiyam-based journalist, cites sources that confirm this. Muhammad Qubaisi, author of a book on South Lebanon, writes that according to the Torah, Jacob moved his family and livestock to the plain of Al-Khiam, where he lived in tents. Location Al-Khiyam is situated approximately south from the capital city of Beirut and south-east from the city of Nabatieh. The border with Israel is to the south. Khiam lies at a height of above sea level. History Ottoman period In 1596, the village of Hiyam was an Ottoman empire, Ottoman ''nahiya'' (subdistrict) of Tibnin under the ''Liwa (Arabic), liwa''' (district) of Safad, with a population of 111 Muslim households and 7 bachelors. The villagers paid a tax on wheat, barley, olive trees, vineyards, goats and beehives, in addition to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology Of Palestine
Levantine archaeology is the archaeological study of the Levant. It is also known as Syro-Palestinian archaeology or Palestinian archaeology (particularly when the area of inquiry centers on ancient PalestineOn page 16 of his book, Rast notes that the term Palestine is commonly used by archaeologists in Jordan and Israel to refer to the region encompassed by modern-day Israel, Jordan and the West Bank. On page ix, he defines "ancient Palestine" the same way but also includes the Gaza Strip.). Besides its importance to the discipline of Biblical archaeology, the Levant is highly important when forming an understanding of the history of the earliest peoples of the Stone Age. Current archaeological digs in Israel are carried out by the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA), and in the areas governed by the Palestinian Authority (PA), by its Ministry of Tourism and Antiquity, working under the auspices of the IAA. The Palestinian Authority prohibits unrestricted excavation at sites of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology Of Israel
The archaeology of Israel is the study of the archaeology of the present-day Israel, stretching from prehistory through three millennia of documented history. The ancient Land of Israel was a geographical bridge between the political and cultural centers of Mesopotamia and Egypt. Despite the importance of the country to three major religions, serious archaeological research only began in the 15th century.''Encyclopedia of Zionism and Israel'', edited by Raphael Patai, Herzl Press and McGraw-Hill, New York, 1971, vol. I, pp. 66–71 Although he never travelled to the Levant, or even left the Netherlands, the first major work on the antiquities of Israel is considered to be Adriaan Reland's ''Antiquitates Sacrae veterum Hebraeorum,'' published in 1708. Edward Robinson, an American theologian who visited the country in 1838, published its first topographical studies. Lady Hester Stanhope performed the first modern excavation at Ashkelon in 1815. A Frenchman, Louis Felicien de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |