|
Harewood (material)
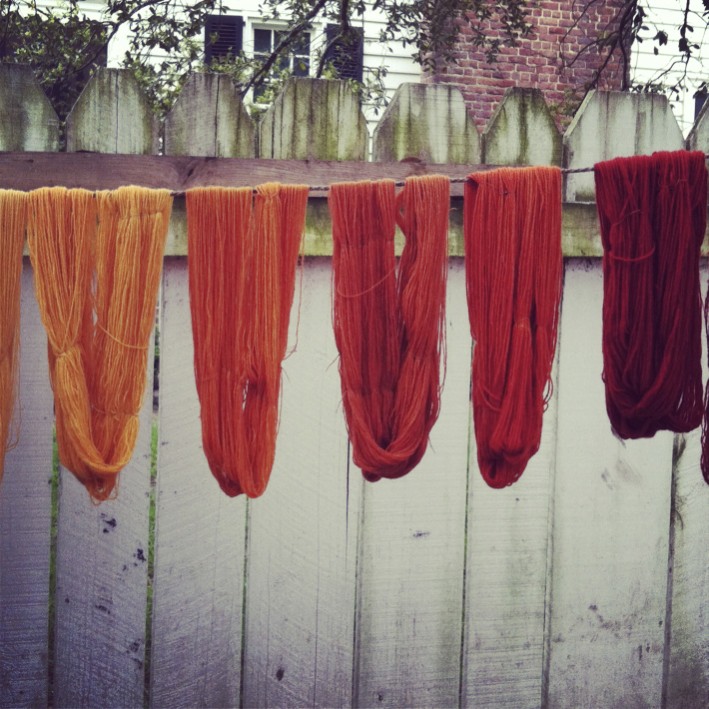
The term harewood or airwood originally described a type of maple wood, including sycamore maple, with a curled or "fiddleback" figure, used to make the backs of stringed instruments. In 17th-century England it was imported from Germany. The earliest published use of the term is probably that in the 1670 edition of '' Sylva'': In the 18th century airwood came to be used by marqueteurs; for most artificial colours they used holly, which takes vegetable dyes very well, but airwood was employed either in its natural off-white state or stained with iron sulphate to produce a range of silver and silver-grey hues.Peter Weber, ''The Cabinet-Maker's Guide'', 2nd edn., London (1809), p. 9. The reason that airwood was preferred to holly for this colour was that it gave a metallic sheen or lustre, while holly dyed by the same process turned a rather dead grey. The use of airwood in this way meant that by the 19th century it was associated specifically with that colour, and at the same tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maple
''Acer'' is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the soapberry family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/. There are approximately 132 species, most of which are native to Asia, with a number also appearing in Europe, northern Africa, and North America. Only one species, '' Acer laurinum'', extends to the Southern Hemisphere.Gibbs, D. & Chen, Y. (2009The Red List of Maples Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI) The type species of the genus is the sycamore maple ''Acer pseudoplatanus'', one of the most common maple species in Europe.van Gelderen, C. J. & van Gelderen, D. M. (1999). '' Maples for Gardens: A Color Encyclopedia'' Most maples usually have easily identifiable palmate leaves (with a few exceptions, such as '' Acer carpinifolium'', '' Acer laurinum'', and '' Acer negundo'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Sulphate
Iron sulfate may refer to: * Ferrous sulfate, Iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4 * Ferric sulfate, Iron(III) sulfate Iron(III) sulfate or ferric sulfate (British English: sulphate instead of sulfate) is a family of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe2(SO4)3(H2O)n. A variety of hydrates are known, including the most commonly encountered form of "ferric sulf ..., Fe2(SO4)3 {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trees
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only plants that are usable as lumber, or only plants above a specified height. But wider definitions include taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos. Trees are not a monophyletic taxonomic group but consist of a wide variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some trees reaching several thousand years old. Trees evolved around 400 million years ago, and it is estimated that there are around three trillion mature trees in the world currently. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported clear o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction. There are two classes of redox reactions: * Electron transfer, Electron-transfer – Only one (usually) electron flows from the atom, ion, or molecule being oxidized to the atom, ion, or molecule that is reduced. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * Atom transfer – An atom transfers from one Substrate (chemistry), substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemicals
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combined without reacting, they may form a chemical mixture. If a mixture is separated to isolate one chemical substance to a desired degree, the resulting substance is said to be chemically pure. Chemical substances can exist in several different physical states or phases (e.g. solids, liquids, gases, or plasma) without changing their chemical composition. Substances transition between these phases of matter in response to changes in temperature or pressure. Some chemical substances can be combined or converted into new substances by means of chemical reactions. Chemicals that do not possess this ability are said to be inert. Pure water is an example of a chemical substance, with a constant composition of two hydrogen atoms bonded to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey
Grey (more frequent in British English) or gray (more frequent in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning that it has no chroma. It is the color of a cloud-covered sky, of ash, and of lead. The first recorded use of ''grey'' as a color name in the English language was in 700 CE.Maerz and Paul ''A Dictionary of Color'' New York:1930 McGraw-Hill Page 196 ''Grey'' is the dominant spelling in European and Commonwealth English, while ''gray'' is more common in American English; however, both spellings are valid in both varieties of English. In Europe and North America, surveys show that gray is the color most commonly associated with neutrality, conformity, boredom, uncertainty, old age, indifference, and modesty. Only one percent of respondents chose it as their favorite color. Etymology ''Grey'' comes from the Middle English or , from the Old English , and is related to the Dutch and Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallic Color
A metallic color is a color that appears to be that of a polished metal. The visual sensation usually associated with metals is its metallic shine. This cannot be reproduced by a simple solid color, because the shiny effect is due to the material's brightness varying with the surface angle to the light source. In addition, there is no mechanism for showing metallic or fluorescent colors on a computer without resorting to rendering software which simulates the action of light on a shiny surface. Consequently in art and in heraldry one would normally use a metallic paint that glitters like a real metal. Especially in sacral art in Christian churches, real gold (as gold leaf) was used for rendering gold in paintings, e.g. for the halo of saints. Gold can also be woven into sheets of silk to give an East Asian traditional look. More recent art styles, for example Art Nouveau, also used a metallic, shining gold. However, the metallic finish of such paints was added using fine al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
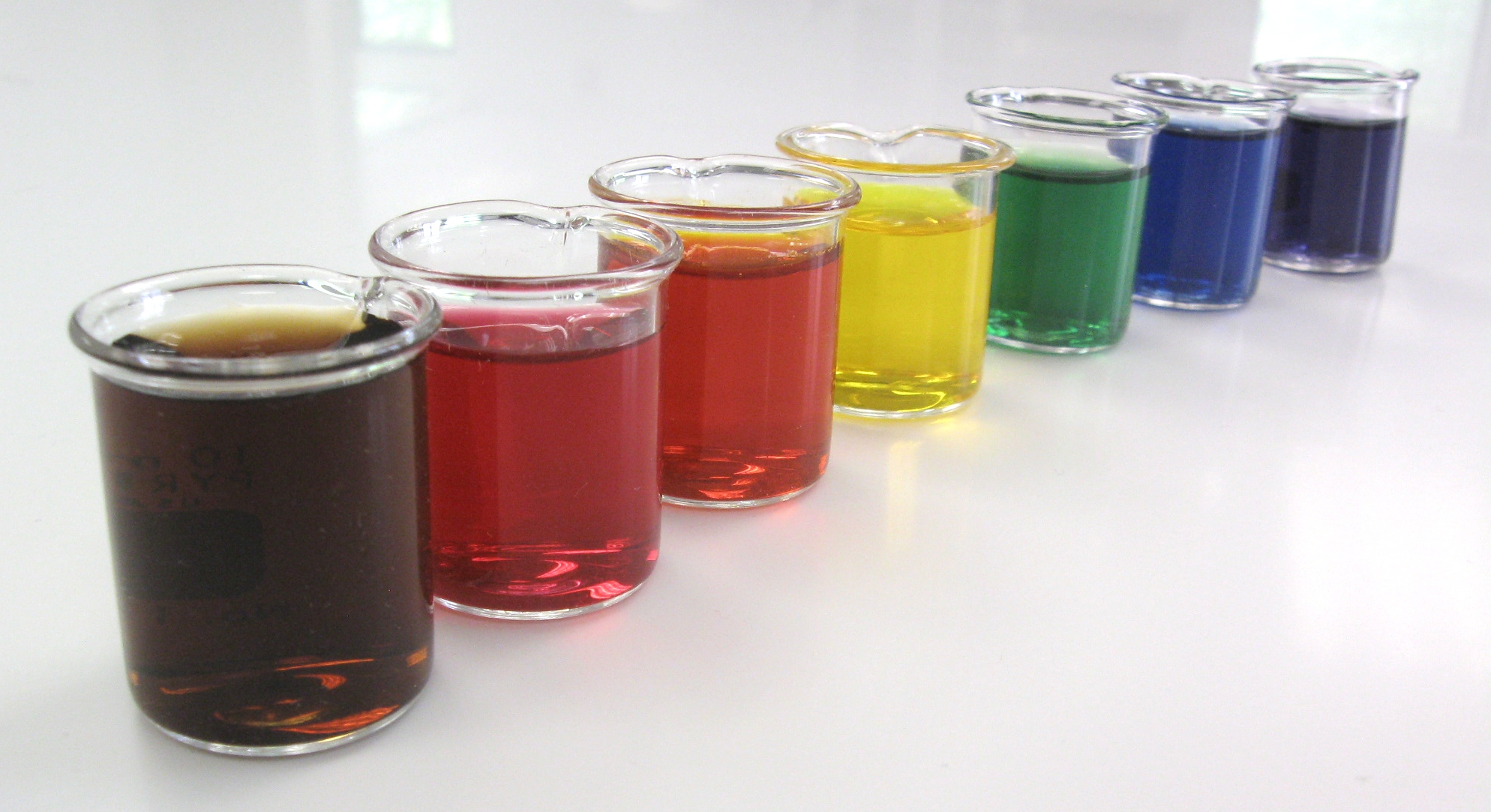
Vegetable Dye
Natural dyes are dyes or colorants derived from plants, invertebrates, or minerals. The majority of natural dyes are vegetable dyes from plant sources—roots, berries, bark, leaves, and wood—and other biological sources such as fungi. Archaeologists have found evidence of textile dyeing dating back to the Neolithic period. In China, dyeing with plants, barks and insects has been traced back more than 5,000 years.Goodwin (1982), p. 11. The essential process of dyeing changed little over time. Typically, the dye material is put in a pot of water and heated to extract the dye compounds into solution with the water. Then the textiles to be dyed are added to the pot, and held at heat until the desired color is achieved. Textile fibre may be dyed before spinning or weaving ("dyed in the wool"), after spinning ("yarn-dyed") or after weaving ("piece-dyed"). Many natural dyes require the use of substances called mordants to bind the dye to the textile fibres. Mordants () are metal salts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
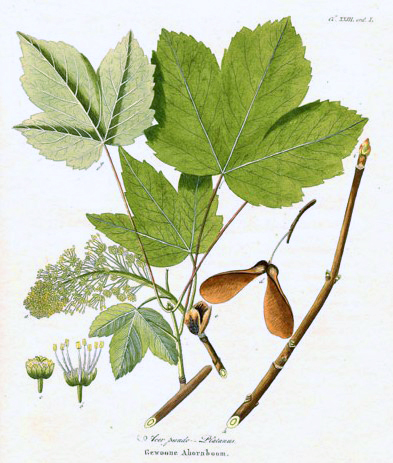
Acer Pseudoplatanus
''Acer pseudoplatanus'', known as the sycamore in the British Isles and as the sycamore maple in the United States, is a species of maple native to Central Europe and Western Asia. It is a large deciduous, broad-leaved tree, tolerant of wind and coastal exposure. Although native to an area ranging from France eastward to Ukraine, northern Turkey and the Caucasus, and southward to the mountains of Italy and northern Iberia, the sycamore establishes itself easily from seed and was introduced to the British Isles by 1500. It is now Naturalisation (biology), naturalised there and in other parts of Europe, North America, Australia and New Zealand, where it may become an invasive species. The sycamore can grow to a height of about and the branches form a broad, rounded Crown (botany), crown. The Bark (botany), bark is grey, smooth when young and later flaking in irregular patches. The leaves grow on long Petiole (botany), leafstalks and are large and List of botanical terms#palmate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holly
''Ilex'' () or holly is a genus of over 570 species of flowering plants in the family Aquifoliaceae, and the only living genus in that family. ''Ilex'' has the most species of any woody dioecious angiosperm genus. The species are evergreen or deciduous trees, shrubs, and climbers from tropics to temperate zones worldwide. The type species is '' Ilex aquifolium'', the common European holly used in Christmas decorations and cards. Description The genus is widespread throughout the temperate and subtropical regions of the world. It includes species of trees, shrubs, and climbers, with evergreen or deciduous foliage and inconspicuous flowers. Its range was more extended in the Tertiary period and many species are adapted to laurel forest habitats. It occurs from sea level to more than with high mountain species. It is a genus of small, evergreen trees with smooth, glabrous, or pubescent branchlets. The plants are generally slow-growing with some species growing to tall. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Colours
Food coloring, color additive or colorant is any dye, pigment, or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or beverages. Colorants can be supplied as liquids, powders, gels, or pastes. Food coloring is commonly used in commercial products and in domestic cooking. Food colorants are also used in various non-food applications, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, home craft projects, and medical devices. Some colorings may be natural, such as with carotenoids and anthocyanins extracted from plants or cochineal from insects, or may be synthesized, such as tartrazine yellow. In the manufacturing of foods, beverages and cosmetics, the safety of colorants is under constant scientific review and certification by national regulatory agencies, such as the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and by international reviewers, such as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Purpose of food coloring People associate c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |