|
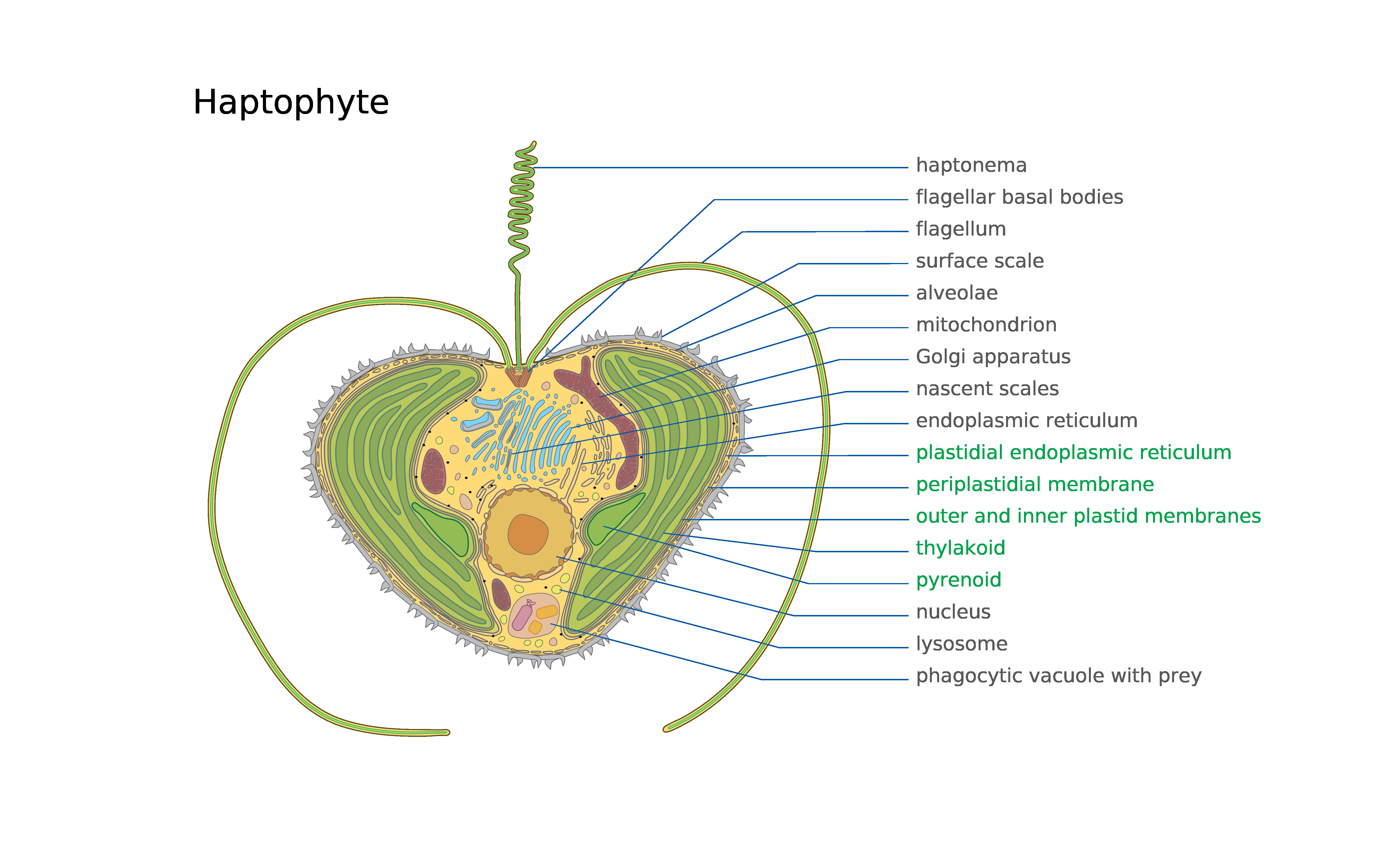
Haptophyceae
The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta (named for ''Prymnesium''), are a clade of algae. The names Haptophyceae or Prymnesiophyceae are sometimes used instead. This ending implies classification at the class (biology), class Taxonomic rank, rank rather than as a division. Although the phylogenetics of this group has become much better understood in recent years, there remains some dispute over which rank is most appropriate. Characteristics The chloroplasts are pigmented similarly to those of the heterokonts, but the structure of the rest of the cell is different, so it may be that they are a separate line whose chloroplasts are derived from similar red algae, red algal endosymbionts. Haptophyte chloroplasts contain chlorophylls Chlorophyll a, a, Chlorophyll_c#Chlorophyll_c1, c1, and Chlorophyll_c#Chlorophyll_c2, c2 but lack chlorophyll Chlorophyll_b, b. For carotenoids, they have beta-carotene, beta-, Α-Carotene, alpha-, and γ-Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prymnesiales
Prymnesiales is an order of Haptophyceae. It currently consists of three families: * Prymnesiaceae * Chrysochromulinaceae * Chrysoculteraceae References Haptophyte orders Haptista orders {{Haptophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccolithales
Coccolithales is an order of Haptophyceae. The Coccolithales has long been considered one of only two orders in the Coccolithophyceae Prymnesiophyceae is a haptophyte class (biology), class. Although it was originally described by Siegfried Jost Casper, Casper in 1972, it did not receive a Latin diagnosis (a requirement for valid publication under the International Code of Bota ..., the other order being the Isochrysidales. References Haptophyte orders Haptista orders {{Haptophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prymnesiophyceae
Prymnesiophyceae is a haptophyte class. Although it was originally described by Casper in 1972, it did not receive a Latin diagnosis (a requirement for valid publication under the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature The ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN or ICNafp) is the set of rules and recommendations dealing with the formal botanical names that are given to plants, fungi and a few other groups of organisms, all tho ...) until Hibberd provided one in 1976. References Haptophyte classes Haptista classes {{Haptophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isochrysidales
Isochrysidales is an order of Haptophyceae The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta (named for ''Prymnesium''), are a clade of algae. The names Haptophyceae or Prymnesiophyceae are sometimes used instead. This ending implies classification at t .... References Haptophyte orders Haptista orders {{Haptophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccolithophyceae
Prymnesiophyceae is a haptophyte class (biology), class. Although it was originally described by Siegfried Jost Casper, Casper in 1972, it did not receive a Latin diagnosis (a requirement for valid publication under the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature) until David John Hibberd, Hibberd provided one in 1976. References Haptophyte classes Haptista classes {{Haptophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
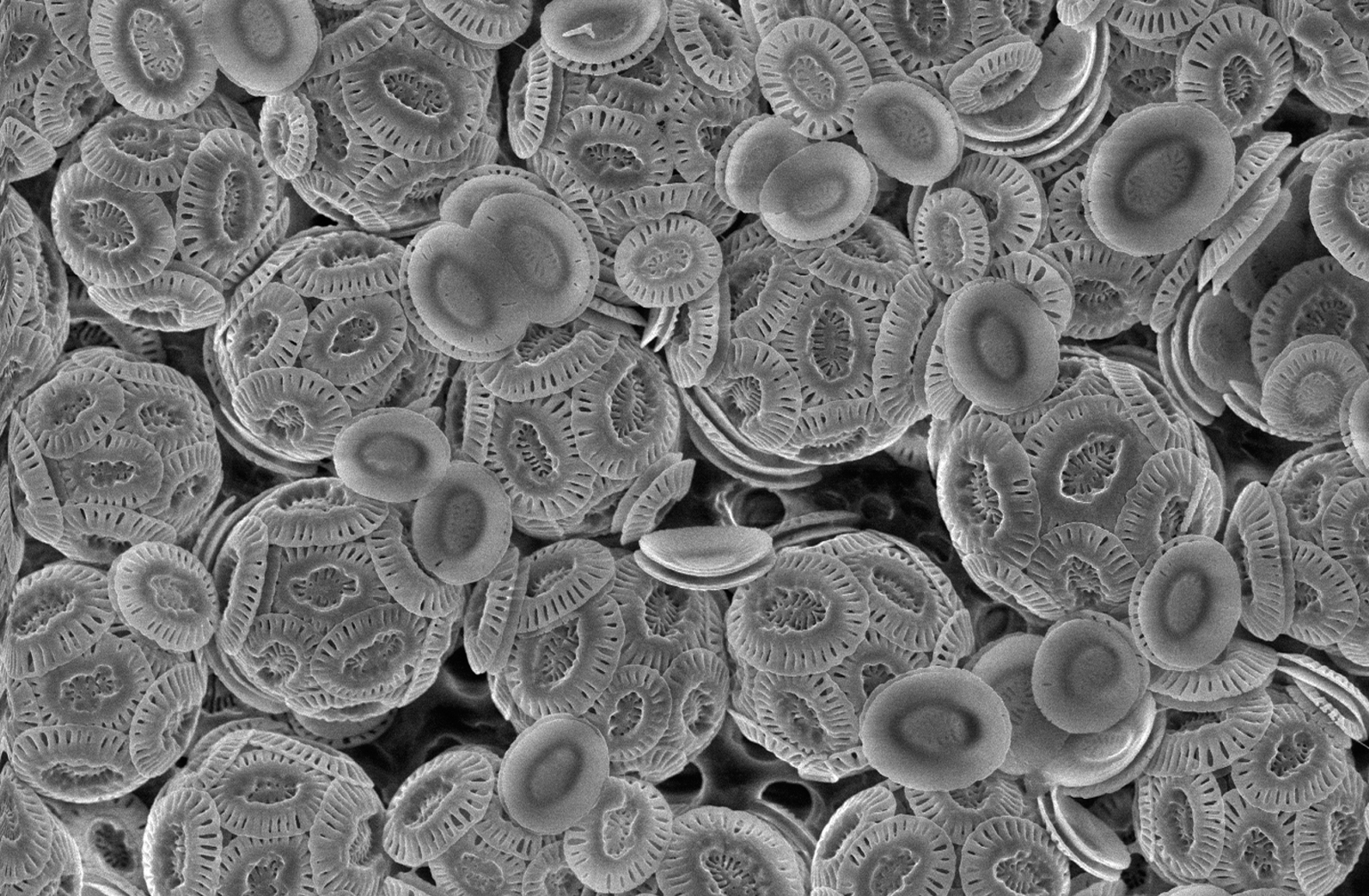
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single-celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker (ecologist), Robert Whittaker's five-kingdom system, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division (botany), division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively Marine (ocean), marine, are photosynthesis, photosynthetic and mixotrophic, and exist in large numbers throughout the Photic zone, sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a ''coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remain elusive. One key function may be that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as cyanobacteria, ''Chlorella'', and diatoms, to multicellular macroalgae such as kelp or brown algae which may grow up to in length. Most algae are aquatic organisms and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem, and phloem that are found in embryophyte, land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds. In contrast, the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a Division (taxonomy), division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. Algae that are carried passively by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton. Algae constitute a Polyphyly, polyphyletic group because they do not include a common ancestor, and although Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (biology)
In biological classification, class () is a taxonomic rank, as well as a taxonomic unit, a taxon, in that rank. It is a group of related taxonomic orders. Other well-known ranks in descending order of size are domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class ranking between phylum and order. History The class as a distinct rank of biological classification having its own distinctive name – and not just called a ''top-level genus'' ''(genus summum)'' – was first introduced by French botanist Joseph Pitton de Tournefort in the classification of plants that appeared in his '' Eléments de botanique'' of 1694. Insofar as a general definition of a class is available, it has historically been conceived as embracing taxa that combine a distinct ''grade'' of organization—i.e. a 'level of complexity', measured in terms of how differentiated their organ systems are into distinct regions or sub-organs—with a distinct ''type'' of construction, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomic Rank
In biology, taxonomic rank (which some authors prefer to call nomenclatural rank because ranking is part of nomenclature rather than taxonomy proper, according to some definitions of these terms) is the relative or absolute level of a group of organisms (a ''taxon'') in a hierarchy that reflects evolutionary relationships. Thus, the most inclusive clades (such as Eukarya and Animalia) have the highest ranks, whereas the least inclusive ones (such as ''Homo sapiens'' or ''Bufo bufo'') have the lowest ranks. Ranks can be either relative and be denoted by an indented taxonomy in which the level of indentation reflects the rank, or absolute, in which various terms, such as species, genus, Family (biology), family, Order (biology), order, Class (biology), class, Phylum (biology), phylum, Kingdom (biology), kingdom, and Domain (biology), domain designate rank. This page emphasizes absolute ranks and the rank-based codes (the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, Zoological Code, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2023 Haptophyte
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in question. In addition to their use for inferring phylogenetic pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prymnesium
''Prymnesium'' is a genus of haptophytes, including the species '' Prymnesium parvum''. The genus is a unicellular motile alga. It is ellipsoidal in shape one flagellum is straight and there are two longer ones which enable movement. The name Latinizes the Greek ' ‘cable (for mooring)’, from ' ‘stern’, from ' ‘hindmost’. ''Prymnesium'' was likely first recognized and drawn (although not named as such) on July 1, 1920, and then (seemingly independently) officially named shortly afterwards on July 6, 1920. Morphology Species The taxonomy of Prymnesiales Prymnesiales is an order of Haptophyceae. It currently consists of three families: * Prymnesiaceae * Chrysochromulinaceae * Chrysoculteraceae References Haptophyte orders Haptista orders {{Haptophyte-stub ... was revised in 2011. With this revision, ten additional species were added to the genus, namely '' P. neolepis'' (previously assigned to '' Hyalolithus''), '' P. palpebrale'', '' P. polylepis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |