|
Haplogroup L4 (mtDNA)
Haplogroup L4 is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is a small maternal clade primarily restricted to Africa. L4 is important in East Africa. The highest frequencies are in Tanzania Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ... among the Hadza at 60-83% and Sandawe at 48%. It has two branches, L4a and L4b. Subgroup L4a was formerly called L7 and considered a separate subclade of L3'4'7. It has been recognized as a subclade of L4, with L3 as its outgroup by Behar et al. (2008). The parent clade L3'4 is to have emerged at 106–66 kya. L4 is not much later than this, estimated at 87 kya by Fernandes et al. (2015).Fernandes V, Triska P, Pereira JB, Alshamali F, Rito T, Machado A, et al. (2015) Genetic Stratigraphy of Key Demographic Events in Arabia. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroup
In human genetics, a human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by differences in human mitochondrial DNA. Haplogroups are used to represent the major branch points on the mitochondrial phylogenetic tree. Understanding the evolutionary path of the female lineage has helped population geneticists trace the matrilineal inheritance of modern humans back to human origins in Africa and the subsequent spread around the globe. The letter names of the haplogroups (not just mitochondrial DNA haplogroups) run from A to Z. As haplogroups were named in the order of their discovery, the alphabetical ordering does not have any meaning in terms of actual genetic relationships. The hypothetical woman at the root of all these groups (meaning just the mitochondrial DNA haplogroups) is the matrilineal most recent common ancestor (MRCA) for all currently living humans. She is commonly called Mitochondrial Eve. The rate at which mitochondrial DNA mutates is known as the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the region is recognized in the United Nations Statistics Division United Nations geoscheme for Africa, scheme as encompassing 18 sovereign states and 4 territories. It includes the Horn of Africa to the North and Southeastern Africa to the south. Definitions In a narrow sense, particularly in English-speaking contexts, East Africa refers to the area comprising Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda, largely due to their shared history under the Omani Empire and as parts of the British East Africa Protectorate and German East Africa. Further extending East Africa's definition, the Horn of Africa—comprising Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia—stands out as a distinct geopolitical entity within East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup L3'4 (mtDNA)
In human mitochondrial genetics, L is the mitochondrial DNA macro-haplogroup that is at the root of the anatomically modern human (''Homo sapiens'') mtDNA phylogenetic tree. As such, it represents the most ancestral mitochondrial lineage of all currently living modern humans, also dubbed "Mitochondrial Eve". Its two sub-clades are L1-6 and L0. The split occurred during the Penultimate Glacial Period; L1-6 is estimated to have formed ca. 170 kya, and L0 ca. 150 kya. The formation of L0 is associated with the peopling of Southern Africa by populations ancestral to the Khoisan, ca. 140 kya, at the onset of the Eemian interglacial. L is further subdivided into L1-6 and L1, dated ca. 150 kya and 130 kya, respectively. Haplogroups L5 (120 kya), L2 and L6 (90 kya), L4 (80 kya) and L3 (70 kya). Origin The outgroup for mtDNA phylogeny of modern humans is the mtDNA of archaic humans, specifically Neanderthals and Denisovans. The split of the modern human lineage from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup L4a (mtDNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the , ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and ) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplotype is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (haplogroup) is also a subset of a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Maps Based On HVS-I Data For Haplogroups L4
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. The interval of time between events is called the period. It is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times per minute (2 hertz), its period is one half of a second. Special definitions of frequency are used in certain contexts, such as the angular frequency in rotational or cyclical properties, when the rate of angular progress is measured. Spatial frequency is defined for properties that vary or cccur repeatedly in geometry or space. The unit of measurement of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) is the hertz, having the symbol Hz. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
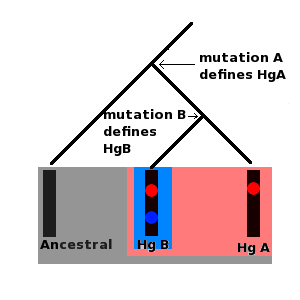
Schematic Tree Of MtDNA Haplogroups L4 And L6
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the schematic is intended to convey, and may include oversimplified elements in order to make this essential meaning easier to grasp, as well as additional organization of the information. For example, a subway map intended for passengers may represent a subway station with a dot. The dot is not intended to resemble the actual station at all but aims to give the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols in place of detailed representations of the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment that compose the system, thus emphasizing the functions of the individual elements and the interconnections among them and suppresses their physical details. In an electronic circuit d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. According to a 2024 estimate, Tanzania has a population of around 67.5 million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania. In the Stone and Bronze Age, prehistoric migrations into Tanzania included South Cushitic languages, Southern Cushitic speakers similar to modern day Iraqw people who moved south from present-day Ethiopia; Eastern Cushitic people who moved into Tanzania from north of Lake Turkana about 2,000 and 4,000 years ago; and the Southern Nilotic languages, Southern Nilotes, including the Datooga people, Datoog, who originated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadza People
The Hadza, or Hadzabe (''Wahadzabe'', in Swahili), are a protected hunter-gatherer Tanzanian indigenous ethnic group, primarily based in Baray, an administrative ward within Karatu District in southwest Arusha Region. They live around the Lake Eyasi basin in the central Rift Valley and in the neighboring Serengeti Plateau. As descendants of Tanzania's aboriginal, pre- Bantu expansion hunter-gatherer population, they have probably occupied their current territory for thousands of years with relatively little modification to their basic way of life until the last century. They have no known close genetic relatives and their language is considered an isolate. Since the first European contact in the late 19th century, governments and missionaries have made many attempts to settle the Hadza by introducing farming and Christianity. These efforts have largely failed, and many Hadza still pursue a life similar to their ancestors. Since the 18th century, the Hadza have come into in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandawe People
The Sandawe are an indigenous ethnic group of Southeast Africa, based in the Chemba District kwamtoro ward of Dodoma Region in central Tanzania. In 2000, the Sandawe population was estimated to be 40,000. The Sandawe language is a tonal language that uses click consonants, as do the Khoe languages of southern Africa. History Origins There has been debate on whether the Sandawe represent a link to the Khoisan hunter-gatherers of Southern Africa, though recent research suggests Khoisan are older and mostly unrelated to Sandawe.Lorente-Galdos, B., Lao, O., Serra-Vidal, G. et al. Whole-genome sequence analysis of a Pan African set of samples reveals archaic gene flow from an extinct basal population of modern humans into sub-Saharan populations. ''Genome Biol'' 20, 77 (2019). OI: 10.1186/s13059-019-1684-5https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1684-5) The Sandawe today are considered descendants of an original Bushmen-like people, unlike their modern neighbours, the Gogo. They li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup L3-4 (mtDNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the , ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and ) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplotype is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (haplogroup) is also a subset of a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup L3 (mtDNA)
Haplogroup L3 is a Human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup, human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. The clade has played a pivotal role in the early dispersal of anatomically modern humans. It is strongly associated with the Southern Dispersal, out-of-Africa migration of modern humans of about 70–50,000 years ago. It is inherited by all modern non-African populations, as well as by some populations in Africa. Origin Haplogroup L3 arose close to 70,000 years ago, near the time of the Southern Dispersal, recent out-of-Africa event. This dispersal originated in East Africa and expanded to West Asia, and further to South and Southeast Asia in the course of a few millennia, and some research suggests that L3 participated in this migration out of Africa. A 2007 estimate for the age of L3 suggested a range of 104–84,000 years ago. More recent analyses, including Soares et al. (2012) arrive at a more recent date, of roughly 70–60,000 years ago. Soares et al. also suggest that L3 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |