|
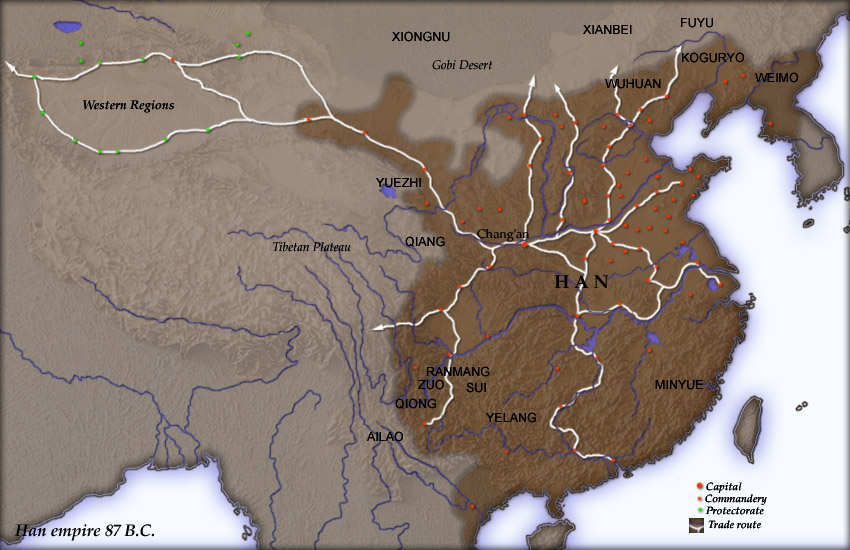
Han–Xiongnu Wars
The Han–Xiongnu Wars. or Sino–Xiongnu Wars, were a series of military conflicts fought over two centuries (from 133 BC to 89 AD) between the agrarian society, agrarian Ancient China, Chinese Han dynasty, Han Empire and the Eurasian nomads, nomadic Xiongnu confederacy, although extended conflicts can be traced back as early as 200 BC and ahead as late as 188 AD. The History of China, Chinese civilization initially clashed with Inner Asian nomadic tribes (then collectively known as ''Beidi, Di'') that would later become the Xiongnu during the Warring States period, and various northern ancient Chinese states, states built elongated fortifications (which later became the Great Wall) to defend against raid (military), raids down from the Mongolian Plateau. The unified Qin dynasty, who Qin's wars of unification, conquered all other states under the First Emperor, dispatched General Meng Tian in 215 BC in Qin's campaign against the Xiongnu, a successful campaign to expel the Xiongnu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Wu Of Han
Emperor Wu of Han (156 – 29 March 87BC), born Liu Che and courtesy name Tong, was the seventh Emperor of China, emperor of the Han dynasty from 141 to 87 BC. His reign lasted 54 years – a record not broken until the reign of the Kangxi Emperor more than 1,800 years later – and remains the record for ethnic Han Chinese, Han emperors. His reign resulted in a vast expansion of geopolitical influence for the Sinosphere, Chinese civilization, and the development of a strong centralized state via governmental policies, economical reorganization and promotion of a hybrid legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalist–Confucianism, Confucian doctrine. In the field of historical social and cultural studies, Emperor Wu is known for his religious innovations and patronage of the poetic and musical arts, including the development of the Music Bureau, Imperial Music Bureau into a prestigious entity. It was also during his reign that cultural contact with western Eurasia was greatly incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuhuan
The Wuhuan (, < Eastern Han Chinese: *''ʔɑ-ɣuɑn'', < (c. 78 BCE): *''ʔâ-wân'' < *''Awar'') were a Proto-MongolicPulleyblank, Edwin G. (1983). "The Chinese and Their Neighbors in Prehistoric and Early Historic China," in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, University of California Press p. 452 of pp. 411–466. or |
Huo Qubing
Huo Qubing (140 BC – October 117 BC, formerly ''Ho Ch'ii-ping'') was a Chinese military general and politician of the Western Han dynasty during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han. He was a nephew of the general Wei Qing and Empress Wei Zifu (Emperor Wu's wife), and a half-brother of the statesman Huo Guang. Along with Wei Qing, he led a campaign into the Gobi Desert of what is now Mongolia to defeat the Xiongnu nomadic confederation, winning decisive victories such as the Battle of Mobei in 119 BC. Huo Qubing was one of the most legendary commanders in Chinese history, and still lives on in Chinese culture today. Early life Huo Qubing was an illegitimate son from the love affair between Wei Shaoer (), the daughter of a lowly maid from the household of Princess Pingyang (Emperor Wu's older sister), and Huo Zhongru (), a low-ranking civil servant employed there at the time. However, Huo Zhongru did not want to marry a lower class serf girl like Wei Shaoer, so he abandoned her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wei Qing
Wei Qing (died Jun 106 BC?In Emperor Wu's biography in ''Book of Han'' and volume 21 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'', the record of Wei Qing's death appeared after the 4th month of the 5th year of the ''Yuan'feng'' era. Thus, it is likely (but not certain) that Wei Qing died in that month, which corresponds to 15 May to 12 Jun 106 BC in the proleptic Julian calendar. The 5th year of the ''Yuan'feng'' era ends on 7 Nov 106 BC in the proleptic Julian calendar.), courtesy name Zhongqing, born Zheng Qing in Linfen, Shanxi, was a Chinese military general and politician of the Western Han dynasty who was acclaimed for his Han-Xiongnu War, campaigns against the Xiongnu, and his rags to riches life. He was a consort kin of Emperor Wu of Han as the younger half-brother of Emperor Wu's wife Empress Wei Zifu, and later the third husband of Emperor Wu's older sister Princess Pingyang (Han dynasty), Eldest Princess Yangxin. He was also the maternal uncle of Huo Qubing, another decorated Han general wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor He Of Han
Emperor He of Han (; 79 – 13 February 106) was an emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty who ruled from 88 to 106. He was the 4th emperor of the Eastern Han, and the 20th emperor of the Han dynasty. Emperor He was a son of Emperor Zhang and, the then Empress Dou. He ascended the throne at the age of nine and ruled for 17 years. It was during Emperor He's reign that the Eastern Han dynasty began its decline. Strife between consort clans and eunuchs began when Empress Dowager Dou (Emperor He's adoptive mother) made her own family members important government officials. Her family was corrupt and intolerant of dissension. In 92, Emperor He was able to fix the situation by removing the empress dowager's brothers with the aid of the eunuch Zheng Zhong and his half-brother Liu Qing the Prince of Qinghe. This in turn created a precedent for eunuchs to be involved in important affairs of state. The trend would continue to escalate for the next century, contributing to the eventual e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Guangwu Of Han
Emperor Guangwu of Han (; 15 January 5 BC29 March AD 57), born Liu Xiu (), courtesy name Wenshu (), was a Chinese monarch. He served as an emperor of the Han dynasty by restoring the dynasty in AD 25, thus founding the Eastern Han dynasty. He ruled over parts of China at first since his dynasty was formed through rebellion against the short-lived Xin dynasty, and through suppression and conquest of regional warlords, the whole of China proper was consolidated by the time of his death in AD 57. During his reign, Taoism was made the official religion of China, and the Chinese folk religion began to decline. Liu Xiu was one of the many descendants of the Han imperial family. Following the usurpation of the Han throne by Wang Mang and the ensuing civil war during the disintegration of Wang's Xin dynasty, he emerged as one of several descendants of the fallen dynasty claiming the imperial throne. After assembling forces and proclaiming himself emperor in the face of competitors, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xuan Of Han
Emperor Xuan of Han (; 91 BC – 10 January 48 BC), born Liu Bingyi (劉病已), was the tenth emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning from 74 to 48 BC, and was one of the only four Western Han emperors to receive a temple name (along with Emperor Gaozu, Emperor Wen and Emperor Wu). During his reign, the Han dynasty prospered economically and militarily became a regional superpower, and was considered by many to be the peak period of the entire Han history. His time of rule, along with his predecessor Emperor Zhao's are known by historians as Zhaoxuan Restoration (昭宣中興). He was succeeded by his son Emperor Yuan after his death in 48 BC. Emperor Xuan's life story was a riches-to- rags-to-riches story. He was born a prince as a great-grandson of Emperor Wu. His grandfather Liu Ju, was a son of Emperor Wu and Empress Wei and the crown prince of the Han Empire, who in 91 BC was framed for witchcraft practice against Emperor Wu and committed suicide after being forced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhizhi Chanyu
Zhizhi or Chi-Chi (, from Old Chinese (58 BCE): *''tśit-kie'' < *''tit-ke'';Schuessler 2014, p. 277 died 36 BCE), also known as Jzh-jzh, was a of the at the time of the first Xiongnu , who held the north and west in contention with his younger brother Huhanye who held the south. His original name in Chinese transcription was Luandi Hutuwusi (), i.e. one of the Worthy Prince< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiutu
Xiutu ( zh, c=休屠王, p=Xiūtú Wáng, also romanized as Hsiu-t'u, lit. "The one who puts an end to massacres") was a king in the Hexi Corridor of the Gansu region, west of Wuwei, during the 2nd century BCE. "Xiutu" (休屠) is also an early Chinese transliteration for the name of the Buddha. According to the ''Shiji'' and the ''Book of Han'', King Xiutu, together with King Hunye, was a vassal of the Xiongnu under their ruler Yizhixie (伊稚邪 126–114 BCE), and was antagonistic towards the Han dynasty. King Xiutu, considered as ''" Hu"'' (barbarian) by the Han, was positioned between the Xiongnu tribes of the Mongolian steppes to the north, the Han to the east, the Saka to the northwest, the Tocharians to the west, and the Southern Qiang to the south. Although a vassal, Xiutu was probably not himself a Xiongnu: it is actually reported that his territory was occupied by the Xiongnu as they were pushed westward by the Han. Kingdom of Xiutu The Kingdom of Xiutu is close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yizhixie Chanyu
Yizhixie ( zh, c=伊稚邪; Late Old Chinese: ; r. 126–114 BC) was the brother of Junchen Chanyu and his successor to the Xiongnu throne. Yizhixie ruled during a time of conflict with the Han dynasty under the military expansionist Emperor Wu (r. 141–87 BC). Defeating Yudan Originally the Eastern Luli-Prince, Yizhixie, a younger brother of Junchen, had to stage a coup against the previous ''chanyu'''s son Yudan, the Eastern Tuqi (Wise Prince). Yudan was defeated by Yizhixie in battle and fled to the Han dynasty, where Emperor Wu gave him a princely title. A few months later Yudan died. Life In 125 BC, the Xiongnu raided Chinese provinces in 3 groups, each with 30,000 cavalry. The Western Jükü-Prince, angry that Chinese Court took Ordos and built Shuofang, attacked the borders of China a few times; and when he entered the Ordos, plundered Shuofang, and killed and captured many officials and other people. In early 124 BC, Wei Qing and four other generals led a for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junchen Chanyu
Junchen (, Old Chinese (Reconstructions of Old_Chinese#Zhengzhang (1981–1995), ZS): *''kun-gin''; r. 161–126 BCE) was the son and successor to Laoshang Chanyu. As chanyu, ''chanyu'' of the Xiongnu Empire, Junchen outlived the Han emperors Emperor Wen of Han, Wen (r. 180–157 BC) and Emperor Jing of Han, Jing (r. 157–141 BC). He died during the reign of the Emperor Wu of Han (r. 141–87 BC). All three Han emperors confirmed the ''heqin'' peace and kinship treaty with the Xiongnu. Life Junchen succeeded his father, Laoshang Chanyu, in 161 BCE. Although peace with the Han dynasty generally persisted under his reign, Xiongnu raids still occurred in 158, 148, 144, and 142 BCE. The Chinese annals note that mutual relations were imperiled on a number of occasions, which included appeals of the Chinese contenders for the Xiongnu's assistance and protection, the Xiongnu's retaliatory raids as punishments for violation of the treaty terms, and one direct Chinese assault against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were an ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. The Xianbei were likely not of a single ethnicity, but rather a multilingual, multi-ethnic confederation consisting of mainly Proto-Mongols (who spoke either pre-Proto-Mongolic,, quote: "The Xianbei confederation appears to have contained speakers of Pre-Proto-Mongolic, perhaps the largest constituent linguistic group, as well as former Xiongnu subjects, who spoke other languages, Turkic almost certainly being one of them."Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1983). "The Chinese and Their Neighbors in Prehistoric and Early Historic China," in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, University of California Pressp. 452of pp. 411–466. or Para-Mongolic languages), and, to a minor degree, Tungusic and Turkic peoples. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the Wuhuan and Xianbei when they were defeated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |