|
Hans Von Luck
Hans–Ulrich Freiherr von Luck und Witten (15 July 1911 – 1 August 1997), usually shortened to Hans von Luck, was a German officer in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II. Von Luck served with the 7th Panzer Division and 21st Panzer Division. Von Luck is the author of the book ''Panzer Commander''. Early life and interwar period Luck was born in Flensburg, into a Prussian family with old military roots. Luck's father, Otto von Luck, served in the Imperial German Navy and died in July 1918 of an influenza virus. His mother remarried a Reichsmarine Chaplain. In 1929, Luck joined the ''Reichswehr'' (army). Through the winter of 1931−1932, Luck attended a nine-month course for officer cadets, led by then Captain Erwin Rommel, at the infantry school in Dresden. On 30 June 1934 Luck's unit took part in the Night of the Long Knives, arresting several ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA) members in Stettin. In 1939 Luck was posted to the 2nd Light Division, serving in its armour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flensburg
Flensburg (; Danish language, Danish and ; ; ) is an independent city, independent town in the far north of the Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein. After Kiel and Lübeck, it is the third-largest city in Schleswig-Holstein. Flensburg's city centre lies about from the Denmark, Danish border. Known for In Germany, Flensburg is known for: * the Kraftfahrt-Bundesamt (roughly: National Driver and Vehicle Register) with its ''Verkehrssünderkartei'' (literally: "traffic sinner card file"), where details of traffic offences are stored * its beer ''Flensburger Brauerei, Flensburger Pilsener'', also called "''Flens''" * the centre of the Danish minority of Southern Schleswig, Danish national minority in Germany * the greeting ''moin'' * the large erotic mail-order companies ''Beate Uhse AG, Beate Uhse'' and ''Orion'' * its handball team, SG Flensburg-Handewitt * the Naval Academy at Mürwik * being the final seat of the Nazi Germany, Third Reich from 1 May 1945, following Adol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
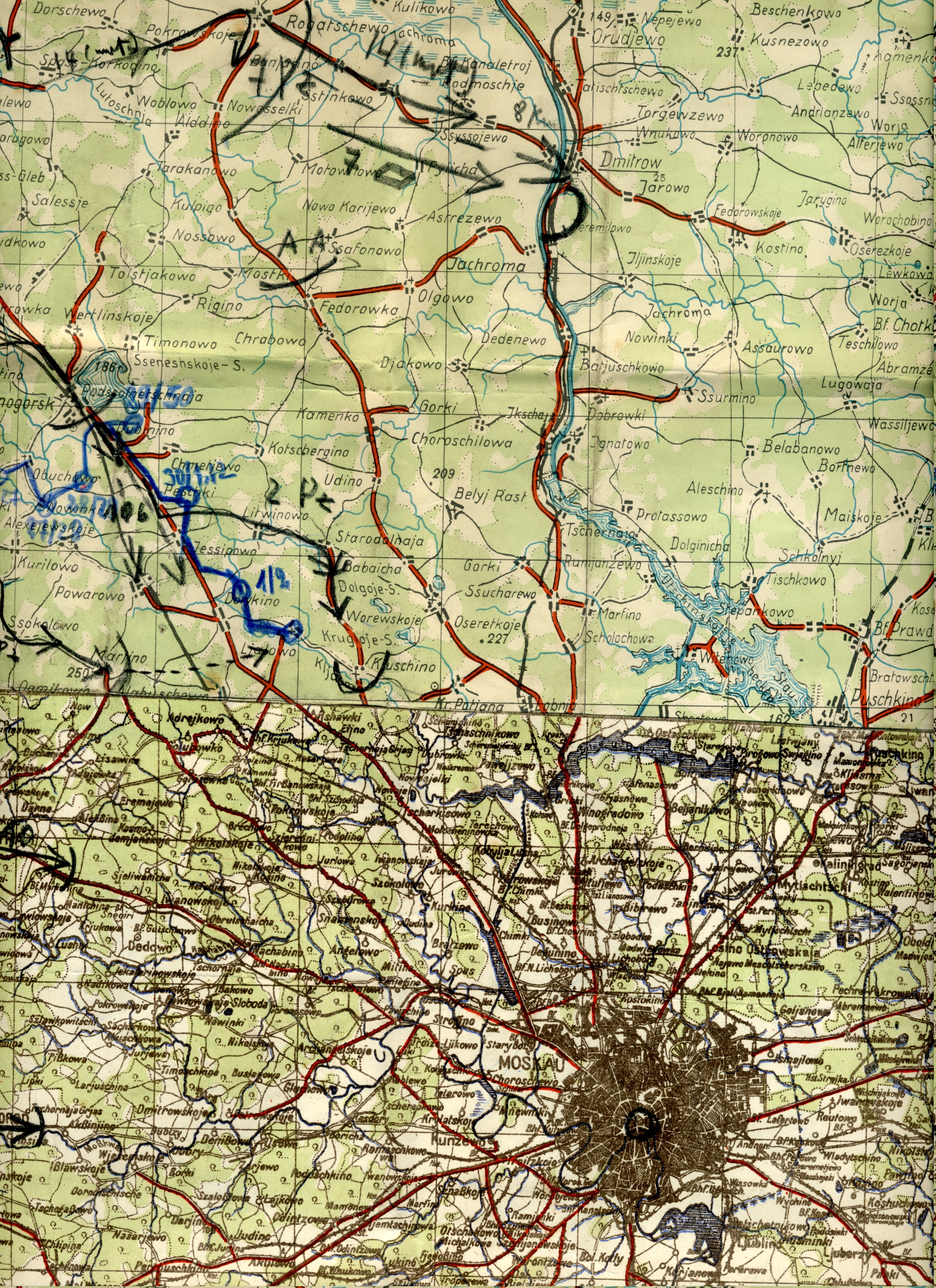
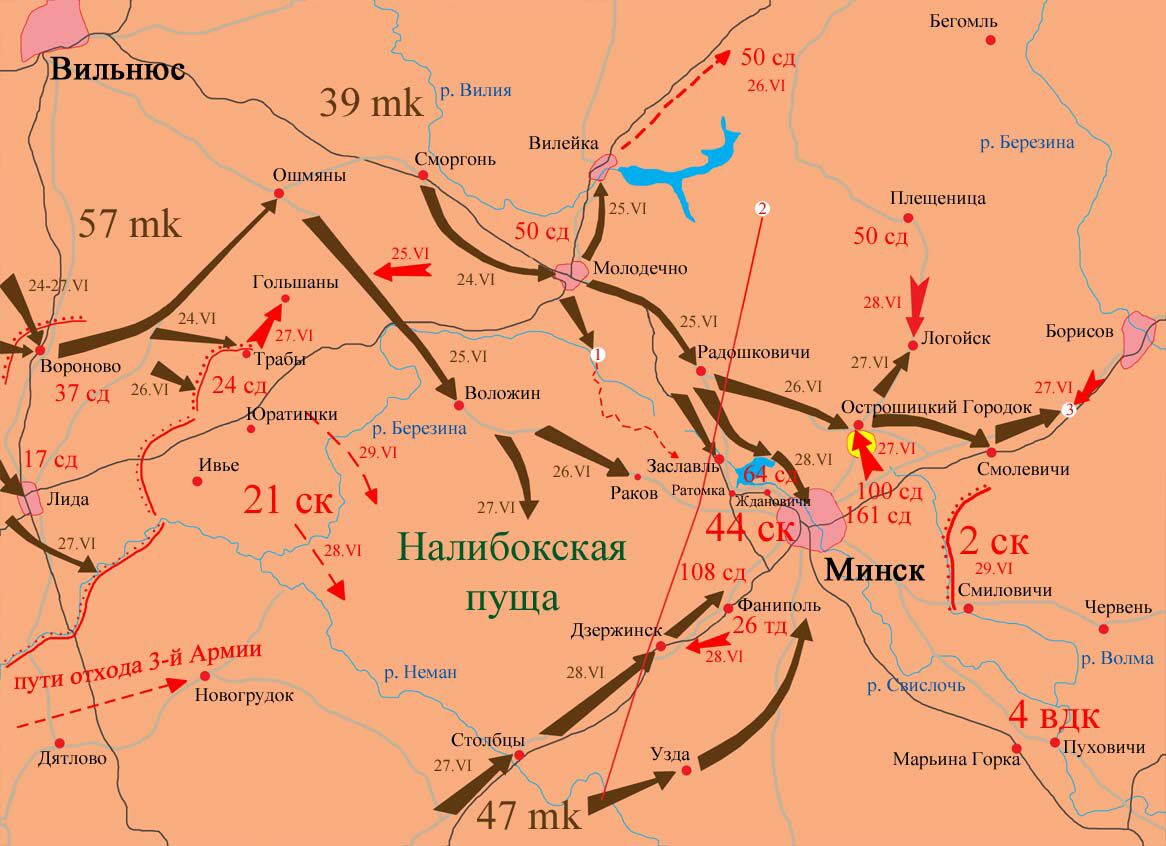
Battle Of Białystok–Minsk
The Battle of Białystok–Minsk was a German strategic operation conducted by the Wehrmacht's Army Group Centre under Field Marshal Fedor von Bock during the penetration of the Soviet border region in the opening stage of Operation Barbarossa, lasting from 22 June to 9 July 1941. The Army Group's 2nd Panzer Group under Colonel General Heinz Guderian and the 3rd Panzer Group under Colonel General Hermann Hoth decimated the Soviet frontier defenses, defeated all Soviet counter-attacks and encircled four Soviet Armies of the Red Army's Western Front near Białystok and Minsk by 30 June. The majority of the Western Front was enclosed within, and the pockets were destroyed by 9 July. The Red Army lost from 420,000 to 474,000 men, against Wehrmacht casualties estimated between 12,157 and 67,244. The Germans destroyed the Soviet Western Front in 18 days and advanced 460 kilometers into the Soviet Union, causing many to believe that the Germans had effectively won the war aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term (''Reich Defence'') and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to German rearmament, rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Adolf Hitler's rise to power, Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and bellicose moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi regime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and Military budget, defence spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight's Cross Of The Iron Cross
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. While it was order of precedence, lower in precedence than the Grand Cross of the Iron Cross#1939 Grand Cross, Grand Cross of the Iron Cross, the Grand Cross was never awarded at-large to Nazi German military and paramilitary forces. The Grand Cross's sole award was made to ''Reichsmarschall'' Hermann Göring in September 1939, making the Knight's Cross (specifically, the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross#Grades, Knight's Cross with Golden Oak Leaves, Swords, and Diamonds grade) the ''de facto'' highest award among the Orders, decorations, and medals of Nazi Germany, decorations of Nazi Germany. The Knight's Cross was awarded for a wide range of reasons and across all ranks, from a senior commander for skilled leadership of his troops in battle to a low-ranking soldier for a single act of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Halbe
The Battle of Halbe (, Battle of the Halbe Pocket; , Halbe pocket) was a battle lasting from April 24 – May 1, 1945 in which the German Ninth Army—under the command of General Theodor Busse—was destroyed as a fighting force by the Red Army during the Battle of Berlin. The Ninth Army, encircled in a large pocket in the Spree Forest region south-east of Berlin, attempted to break out westwards through the village of Halbe and the pine forests south of Berlin to link up with the German Twelfth Army commanded by General Walther Wenck with the intention of heading west and surrendering to the Western Allies. To do this, the Ninth Army had to fight its way through three lines of Soviet troops of the 1st Ukrainian Front under the command of Marshal Ivan Konev, while at the same time units of the 1st Belorussian Front, under the command of Marshal Georgy Zhukov, attacked the German rearguard from the northeast. After heavy fighting, about 30,000 German soldiers—just o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Nordwind
Operation Northwind () was the last major German offensive of World War II on the Western Front. Northwind was launched to support the German Ardennes offensive campaign in the Battle of the Bulge, which by late December 1944 had decisively turned against the German forces. It began on 31 December 1944 in Rhineland-Palatinate, Alsace and Lorraine in southwestern Germany and northeastern France, and ended on 25 January 1945. The German offensive was an operational failure, with its main objectives not achieved. Objectives By 21 December 1944, the German momentum during the Battle of the Bulge had begun to dissipate, and it was evident that the operation was on the brink of failure. The German high command believed that an attack against the United States Seventh Army further south, which had extended its lines and taken on a defensive posture to cover the area vacated by the United States Third Army which had turned north to assist at the site of the German breakthrough, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falaise Pocket
The Falaise pocket or battle of the Falaise pocket (; 12–21 August 1944) was the decisive engagement of the Battle of Normandy in the Second World War. Allied forces formed a pocket around Falaise, Calvados, in which German Army Group B, consisting of the 7th Army and the Fifth Panzer Army (formerly ), were encircled by the Western Allies. The battle resulted in the destruction of most of Army Group B west of the Seine, which opened the way to Paris and the Franco-German border. Six weeks after the 6 June 1944 Allied invasion of Normandy, German forces were in turmoil, having expended irreplaceable resources defending the frontline and with Allied air superiority threatening the availability of food and ammunition. However, on the Allied side, British forces had expected to liberate Caen immediately after the invasion, an operation which ended up taking nearly two months, and US forces had expected to control Saint-Lô by the 7 June, yet German resistance delayed this u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle For Caen
The Battle for Caen (June to August 1944) was a military engagement between the British Second Army and the German in the Second World War for control of the city of Caen and its vicinity during the Battle of Normandy. Caen is about inland from the Calvados coast astride the Orne River and Caen Canal, at the junction of several roads and railways. The communication links made it an important operational objective for both sides. Caen and the area to its south are flatter and more open when compared to the bocage country of western Normandy, and Allied air force commanders wanted the area captured quickly in order to construct airfields to base more aircraft in France proper. The British 3rd Infantry Division was to seize Caen on D-Day or alternatively, dig in short of the city. Caen, Bayeux and Carentan were not captured on D-Day, and the Allies concentrated on linking the beachheads. British and Canadian forces captured the area of Caen north of the Orne during Operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Normandy
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful liberation of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 ( D-Day) with the Normandy landings (Operation Neptune). A 1,200-plane airborne assault preceded an amphibious assault involving more than 5,000 vessels. Nearly 160,000 troops crossed the English Channel on 6 June, and more than two million Allied troops were in France by the end of August. The decision to undertake cross-channel landings in 1944 was made at the Trident Conference in Washington in May 1943. American General Dwight D. Eisenhower was appointed commander of Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force, and British General Bernard Montgomery was named commander of the 21st Army Group, which comprised all the land forces involved in the operation. The Normandy coast in northwestern France was chosen as the site of the landings, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
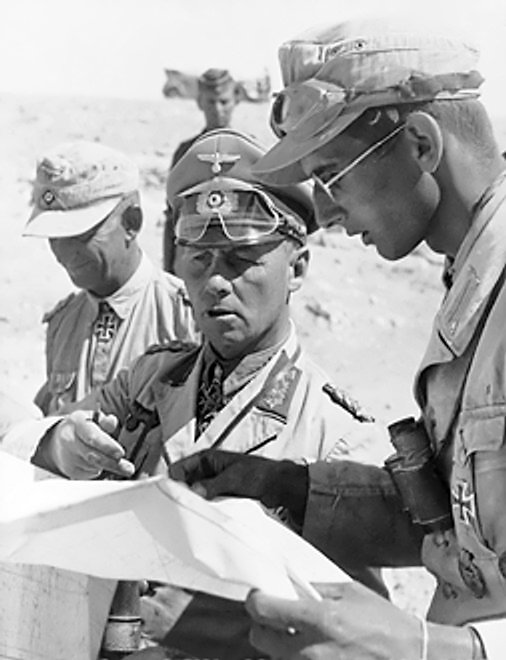
Battle Of Kasserine Pass
The Battle of Kasserine Pass took place from 19-24 February 1943 at Kasserine Pass, a gap in the Grand Dorsal chain of the Atlas Mountains in west central Tunisia. It was a part of the Tunisian campaign of World War II. The Axis forces, led by ''Generalfeldmarschall'' Erwin Rommel, were primarily from the ''Afrika Korps'' Assault Group, the Italian ''131st Armored Division "Centauro", Centauro'' Armored Division and two Panzer divisions detached from the 5th Panzer Army, while the Allies of World War II, Allied forces were from the U.S. II Corps (United States), II Corps (Major general (United States), Major General Lloyd Fredendall), the British 6th Armoured Division (United Kingdom), 6th Armoured Division (Major-general (United Kingdom), Major-General Charles Keightley) and other parts of the First Army (United Kingdom), First Army (Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom), Lieutenant-General Kenneth Anderson (British Army officer), Kenneth Anderson). The battle was the first maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
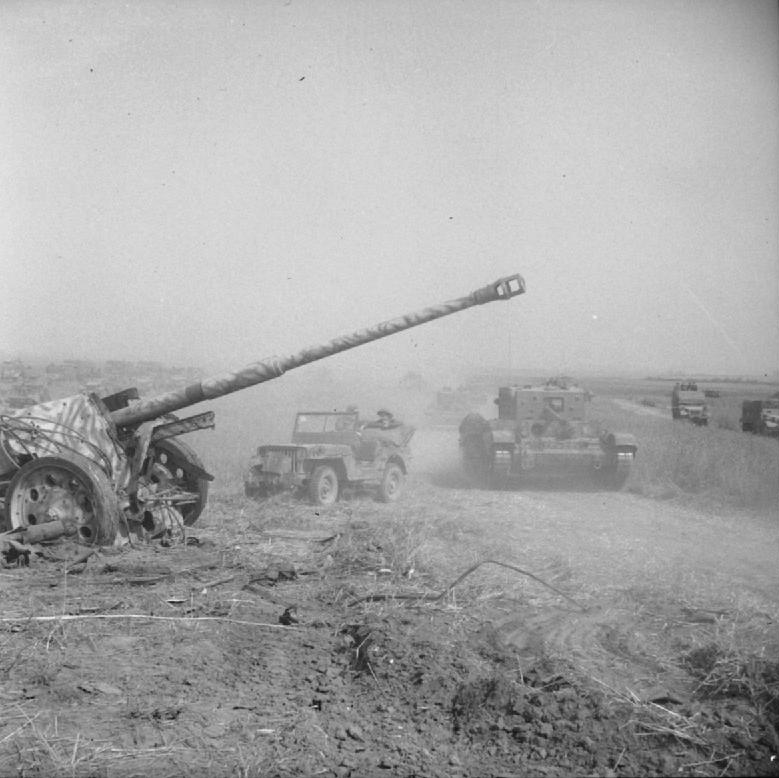
Second Battle Of El Alamein
The Second Battle of El Alamein (23 October – 11 November 1942) was a battle of the Second World War that took place near the Egyptian Railway station, railway halt of El Alamein. The First Battle of El Alamein and the Battle of Alam el Halfa had prevented the Axis powers, Axis from advancing further into Egypt. In October 1942 Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom), Lieutenant-General Bernard Montgomery, commander of Eighth Army (United Kingdom), Eighth Army, opened his offensive against the Axis forces. In a 13-day battle the Axis ''Panzerarmee Afrika'' was crushed and forced to retreat from Egypt and Libya to the borders of Tunisia. The Allied victory at El Alamein was the beginning of the end of the Western Desert Campaign. The battle ended the Axis threat to the Middle East and Iran and revived the morale of the western Allies, being their first big success against the Axis since Operation Crusader in late 1941. The end of the battle coincided with the Allied invasion of F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gazala
The Battle of Gazala, also the Gazala Offensive (Italian language, Italian: ''Battaglia di Ain el-Gazala'') was fought near the village of Gazala during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War, west of the port of Tobruk in Libya, from 26 May to 21 June 1942. Axis powers, Axis troops consisting of Nazi Germany, German (; Erwin Rommel) and Kingdom of Italy, Italian units fought the British Eighth Army (United Kingdom), Eighth Army (General (United Kingdom), General Sir Claude Auchinleck, also Commander-in-chief, Commander-in-Chief Middle East Command, Middle East) composed mainly of British Commonwealth, Indian and Free French troops. The Axis troops made a decoy attack in the north as the main attack moved round the southern flank of the Gazala position. Unexpected resistance at the south end of the line around the Bir Hakeim box by the Free French garrison left with a long and vulnerable supply route around the Gazala Line. Rommel retired to a defensive position b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |