|
Hans Pacejka
Hans Bastiaan Pacejka (12 September 1934 – 17 September 2017) was an expert in vehicle system dynamics and particularly in tire dynamics, fields in which his works are now standard references. He was Professor emeritus at Delft University of Technology in Delft, Netherlands. Magic Formula tire models Pacejka developed a series of tire design models during his career. They were named the "Magic Formula" because there is no particular physical basis for the structure of the equations chosen, but they fit a wide variety of tire constructions and operating conditions. Each tire is characterized by 10–20 coefficients for each important force that it can produce at the contact patch, typically lateral and longitudinal force, and self-aligning torque, as the best fit between experimental data and the model. These coefficients are then used to generate equations showing how much force is generated for a given vertical load on the tire, camber angle and slip angle. The Pacejka ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle System Dynamics
Vehicle dynamics is the study of vehicle motion, e.g., how a vehicle's forward movement changes in response to driver inputs, propulsion system outputs, ambient conditions, air/surface/water conditions, etc. Vehicle dynamics is a part of engineering primarily based on classical mechanics. It may be applied for motorized vehicles (such as automobiles), bicycles and motorcycles, aircraft, and watercraft. Factors affecting vehicle dynamics The aspects of a vehicle's design which affect the dynamics can be grouped into drivetrain and braking, suspension and steering, distribution of mass, aerodynamics and tires. Drivetrain and braking * Automobile layout (i.e. location of engine and driven wheels) * Powertrain * Braking system Suspension and steering Some attributes relate to the geometry of the suspension, steering and chassis. These include: * Ackermann steering geometry * Axle track * Camber angle * Caster angle * Ride height * Roll center * Scrub radius * Steering ratio * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Data
Experimental data in science and engineering is data produced by a measurement, test method, experimental design or quasi-experimental design. In clinical research any data produced are the result of a clinical trial. Experimental data may be qualitative or quantitative, each being appropriate for different investigations. Generally speaking, qualitative data are considered more descriptive and can be subjective in comparison to having a continuous measurement scale that produces numbers. Whereas quantitative data are gathered in a manner that is normally experimentally repeatable, qualitative information is usually more closely related to phenomenal meaning and is, therefore, subject to interpretation by individual observers. Experimental data can be reproduced by a variety of different investigators and mathematical analysis may be performed on these data. See also * Accuracy and precision * Computer science * Data analysis * Empiricism * Epistemology * Informatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tire Industry People
A tire (North American English) or tyre (Commonwealth English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a Rim (wheel), wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide Traction (engineering), traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, providing a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, designed to match the vehicle's weight and the bearing on the surface that it rolls over by exerting a pressure that will avoid deforming the surface. The materials of modern pneumatic tires are synthetic rubber, natural rubber, fabric, and wire, along with carbon black and other chemical compounds. They consist of a tire tread, tread and a body. The tread provides Traction (engineering), traction while the body provides containment for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The Delft University Of Technology
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. The Royal Spanish Academy defines academy as scientific, literary or artistic society established with public authority and as a teaching establishment, public or private, of a professional, artistic, technical or simply practical nature. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle And Motorcycle Dynamics
Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics is the science of the motion of bicycles and motorcycles and their components, due to the forces acting on them. Dynamics falls under a branch of physics known as classical mechanics. Bike motions of interest include balancing, steering, braking, accelerating, suspension activation, and vibration. The study of these motions began in the late 19th century and continues today. Bicycles and motorcycles are both single-track vehicles and so their motions have many fundamental attributes in common and are fundamentally different from and more difficult to study than other wheeled vehicles such as dicycles, tricycles, and quadracycles. As with unicycles, bikes lack lateral stability when stationary, and under most circumstances can only remain upright when moving forward. Experimentation and mathematical analysis have shown that a bike stays upright when it is steered to keep its center of mass over its wheels. This steering is usually supplied b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Dynamics
Vehicle dynamics is the study of vehicle motion, e.g., how a vehicle's forward movement changes in response to driver inputs, propulsion system outputs, ambient conditions, air/surface/water conditions, etc. Vehicle dynamics is a part of engineering primarily based on classical mechanics. It may be applied for motorized vehicles (such as automobiles), bicycles and motorcycles, aircraft, and watercraft. Factors affecting vehicle dynamics The aspects of a vehicle's design which affect the dynamics can be grouped into drivetrain and braking, suspension and steering, distribution of mass, aerodynamics and tires. Drivetrain and braking * Automobile layout (i.e. location of engine and driven wheels) * Powertrain * Braking system Suspension and steering Some attributes relate to the geometry of the suspension, steering and chassis. These include: * Ackermann steering geometry * Axle track * Camber angle * Caster angle * Ride height * Roll center * Scrub radius * Stee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenvalues
In linear algebra, an eigenvector ( ) or characteristic vector is a vector that has its direction unchanged (or reversed) by a given linear transformation. More precisely, an eigenvector \mathbf v of a linear transformation T is scaled by a constant factor \lambda when the linear transformation is applied to it: T\mathbf v=\lambda \mathbf v. The corresponding eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root is the multiplying factor \lambda (possibly a negative or complex number). Geometrically, vectors are multi-dimensional quantities with magnitude and direction, often pictured as arrows. A linear transformation rotates, stretches, or shears the vectors upon which it acts. A linear transformation's eigenvectors are those vectors that are only stretched or shrunk, with neither rotation nor shear. The corresponding eigenvalue is the factor by which an eigenvector is stretched or shrunk. If the eigenvalue is negative, the eigenvector's direction is reversed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stiff Equation
In mathematics, a stiff equation is a differential equation for which certain numerical methods for solving the equation are numerically unstable, unless the step size is taken to be extremely small. It has proven difficult to formulate a precise definition of stiffness, but the main idea is that the equation includes some terms that can lead to rapid variation in the solution. When integrating a differential equation numerically, one would expect the requisite step size to be relatively small in a region where the solution curve displays much variation and to be relatively large where the solution curve straightens out to approach a line with slope nearly zero. For some problems this is not the case. In order for a numerical method to give a reliable solution to the differential system sometimes the step size is required to be at an unacceptably small level in a region where the solution curve is very smooth. The phenomenon is known as ''stiffness''. In some cases there may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
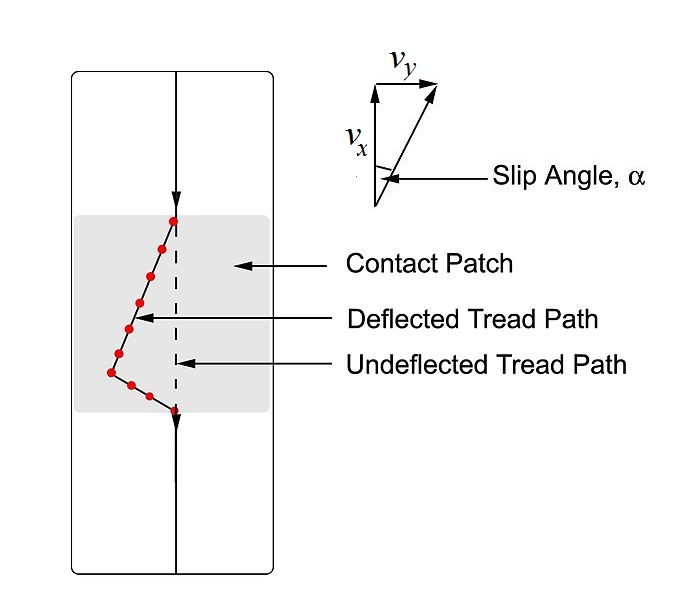
Slip Angle
In vehicle dynamics, slip angle or sideslip angle is the angle between the direction in which a wheel is pointing and the direction in which it is actually traveling (i.e., the angle between the forward velocity vector v_x and the vector sum of wheel forward velocity v_x and lateral velocity v_y, as defined in the image to the right). This slip angle results in a force, the cornering force, which is in the plane of the contact patch and perpendicular to the intersection of the contact patch and the midplane of the wheel. This cornering force increases approximately linearly for the first few degrees of slip angle, then increases non-linearly to a maximum before beginning to decrease. The slip angle, \alpha is defined as \alpha \triangleq -\arctan\left(\frac\right) Causes A non-zero slip angle arises because of deformation in the tire carcass and tread. As the tire rotates, the friction between the contact patch and the road results in individual tread 'elements' (finite s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camber Angle
Camber angle is one of the angles made by the wheels of a vehicle; specifically, it is the angle between the vertical axis of a wheel and the vertical axis of the vehicle when viewed from the front or rear. It is used in the creation of steering and suspension (vehicle), suspension. If the top of the wheel is further out than the bottom (that is, tilted away from the axle), it is called positive camber; if the bottom of the wheel is further out than the top, it is called negative camber. Effect on handling Camber angle alters the Automobile handling, handling qualities of some suspension designs; in particular, negative camber improves grip in corners especially with a Double wishbone suspension#Short long arms suspension, short long arms suspension. This is because it places the tire at a better angle to the road, transmitting the Centrifugal force#Examples, centrifugal forces through the vertical plane of the tire rather than through a Shear strength, shear force across i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self Aligning Torque
Self aligning torque (SAT), also known as aligning torque or aligning moment (Mz, moment about the z direction), is the torque that a tire creates as it rolls along, which tends to steer it, i.e. rotate it around its vertical axis. In the presence of a non-zero slip angle, this torque tends to steer the tire toward the direction in which it is traveling, hence its name. The magnitude of this torque can be calculated as the product of the lateral force generated at the contact patch and the distance behind the wheel centre at which that force acts. This distance is known as the pneumatic trail. The steering torque around a non-vertical steer axis with non-zero mechanical trail is given by: : Even if the slip angle and camber angle are zero, and the road is flat, this torque will still be generated due to asymmetries in the tire's construction and the asymmetrical shape and pressure distribution of the contact patch. Typically for a production tire this torque reaches a maxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |