|
Hanabusa Domain
was a Japanese feudal domain of the early Meiji period, located in Nagasa District, Awa Province. It was centered at what is now the area of the city of Kamogawa in modern Chiba Prefecture. History In 1867, during the Meiji Restoration, the final ''shōgun'', Tokugawa Yoshinobu resigned his office to Emperor Meiji and leadership of the Tokugawa clan to Tokugawa Iesato. In 1868, Iesato was demoted in status to that of an ordinary ''daimyō'', and assigned the newly created Shizuoka Domain, which included all of former Sunpu Domain, neighboring Tanaka and Ojima Domains, and additional lands in Tōtōmi and Mutsu Provinces for a total revenue of 700,000 ''koku''. The new domain covered the western two-thirds of Shizuoka Prefecture, plus the Chita Peninsula in Aichi Prefecture. In the process, the existing ''daimyōs'' in Suruga and Tōtōmi Provinces were displaced. This included the eighth (and final) ''daimyō'' of Yokosuka Domain, Nishio Tadaatsu. As Tadaatsu had proved h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han (administrative Division)
( ja, 藩, "domain") is a Japanese historical term for the estate of a daimyo in the Edo period (1603–1868) and early Meiji period (1868–1912). Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Han"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 283. or (daimyo domain) served as a system of ''de facto'' administrative divisions of Japan alongside the ''de jure'' provinces until they were abolished in the 1870s. History Pre-Edo period The concept of originated as the personal estates of prominent warriors after the rise of the Kamakura Shogunate in 1185, which also saw the rise of feudalism and the samurai noble warrior class in Japan. This situation existed for 400 years during the Kamakura Shogunate (1185–1333), the brief Kenmu Restoration (1333–1336), and the Ashikaga Shogunate (1336–1573). became increasingly important as ''de facto'' administrative divisions as subsequent Shoguns stripped the Imperial provinces () and their officials of their legal powers. Edo period Toyotomi Hideyoshi, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nishio Kamon
is a city located in Aichi Prefecture, in the Chūbu region of Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 169,984 in 65,553 households, with a population density of 1,054 persons per km². The total area of the city was . It is a regional commercial and manufacturing center and the country's leading producer of powdered green tea. Geography Nishio is situated on the northern coast of Mikawa Bay on the Pacific Ocean in southern Aichi Prefecture. The city lies along the eastern bank of the Yahagi River. Sheltered by Chita Peninsula and Atsumi Peninsula, the local climate is mild. Parts of the city lie within the borders of the Mikawa Wan Quasi-National Park Climate The city has a climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and relatively mild winters (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa''). The average annual temperature in Nishio is 15.7 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1596 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abolition Of The Han System
The in the Empire of Japan and its replacement by a system of prefectures in 1871 was the culmination of the Meiji Restoration begun in 1868, the starting year of the Meiji period. Under the reform, all daimyos (, ''daimyō'', feudal lords) were required to return their authority to the Emperor Meiji and his house. The process was accomplished in several stages, resulting in a new centralized government of Meiji Japan and the replacement of the old feudal system with a new oligarchy. Boshin War After the defeat of forces loyal to the Tokugawa shogunate during the Boshin War in 1868, the new Meiji government confiscated all lands formerly under direct control of the Shogunate (''tenryō'') and lands controlled by daimyos who remained loyal to the Tokugawa cause. These lands accounted for approximately a quarter of the land area of Japan and were reorganized into prefectures with governors appointed directly by the central government. Return of the domains The second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fudai Daimyō
was a class of ''daimyō'' (大名) in the Tokugawa Shogunate (徳川幕府) of Japan who were hereditary vassals of the Tokugawa before the Battle of Sekigahara. ''Fudai daimyō'' and their descendants filled the ranks of the Tokugawa administration in opposition to the ''tozama daimyō'' and held most of the power in Japan during the Edo period. Origins ''Fudai daimyōs'' originated from the families and clans who had served the prominent Tokugawa clan before its rise to national primacy during the Azuchi–Momoyama period in the late Sengoku period, including the Honda, Sakai, Sakakibara, Ii, Itakura, and Mizuno clans. A number of other clans which were not retainers of the Tokugawa before the Azuchi–Momoyama period also came to be counted as ''fudai'', such as the Ogasawara and the Doi. Honda Tadakatsu, Sakakibara Yasumasa, Sakai Tadatsugu, and Ii Naomasa — Tokugawa Ieyasu's " Four Great Generals" — were all pre-Edo period ''fudai'' who went on to become '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boshin War
The , sometimes known as the Japanese Revolution or Japanese Civil War, was a civil war in Japan fought from 1868 to 1869 between forces of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate and a clique seeking to seize political power in the name of the Imperial Court. The war stemmed from dissatisfaction among many nobles and young samurai with the shogunate's handling of foreigners following the opening of Japan during the prior decade. Increasing Western influence in the economy led to a decline similar to that of other Asian countries at the time. An alliance of western samurai, particularly the domains of Chōshū, Satsuma, and Tosa, and court officials secured control of the Imperial Court and influenced the young Emperor Meiji. Tokugawa Yoshinobu, the sitting '' shōgun'', realizing the futility of his situation, abdicated and handed over political power to the emperor. Yoshinobu had hoped that by doing this the House of Tokugawa could be preserved and participate in the future g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satchō Alliance
The , or was a powerful military alliance between the feudal domains of Satsuma and Chōshū formed in 1866 to combine their efforts to restore Imperial rule and overthrow the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan. History The name ''Satchō'' () is an abbreviation combining the names of the provinces Satsuma (present day Kagoshima Prefecture) and Chōshū (present-day Yamaguchi Prefecture), two of the strongest Imperialist '' tozama'' domains in Edo-period Japan. In the 1860s, Satsuma tended to take a moderate position towards maintenance of the status quo, whereas Chōshū had become the center of an uprising aimed at overthrowing the government. Through the mediation of Sakamoto Ryōma of Tosa Domain (present day Kōchi Prefecture), Satsuma military leaders Saigō Takamori and Ōkubo Toshimichi were brought together with Katsura Kogorō of Chōshū Domain. Although the two domains were traditionally fierce enemies, their leaders agreed that the time was right for a change, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Government
The was the government that was formed by politicians of the Satsuma Domain and Chōshū Domain in the 1860s. The Meiji government was the early government of the Empire of Japan. Politicians of the Meiji government were known as the Meiji oligarchy, who overthrew the Tokugawa shogunate. Early developments After the Meiji Restoration, the leaders of the ''samurai'' who overthrew the Tokugawa shogunate had no clear agenda or pre-developed plan on how to run Japan. They did have a number of things in common; according to Andrew Gordon, “It was precisely their intermediate status and their insecure salaried position, coupled with their sense of frustrated ambition and entitlement to rule, that account for the revolutionary energy of the Meiji insurgents and their far-reaching program of reform”. most were in their mid-40s, and most were from the four '' tozama'' domains of western Japan (Chōshū, Satsuma, Tosa and Hizen). Although from lower-ranked ''samurai'' families, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nishio Tadaatsu
Viscount was the final ''daimyō'' of Yokosuka Domain in Tōtōmi Province in late-Edo period Japan, and the first (and only) ''daimyō'' of Hanabusa Domain in Awa Province in the early years of the Meiji period, and the 11th hereditary chieftain of the Yokosuka-Nishio clan. Tadaatsu was the son of Nishio Tadasaka, the 7th ''daimyō'' of Yokosuka Domain. His mother was a daughter of Toki Yorinobu, the ''daimyō'' of Numata Domain in Kōzuke Province. He became ''daimyō'' of Yokosuka and head of the Nishio clan upon his father's death in 1861 and was received in formal audience by Shogun Tokugawa Iemochi the following year. During the Boshin War of the Meiji Restoration, Tadaatsu's retainers were divided as to whether or not the domain should continue to support the shogunate, or join forces with the Satchō Alliance in support of the new imperial government. Thanks to the persuasion of Yaso Tomiho and Aoyama Zen'ichirō, the pro-shogunate elements in Yokosuka dropped their ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
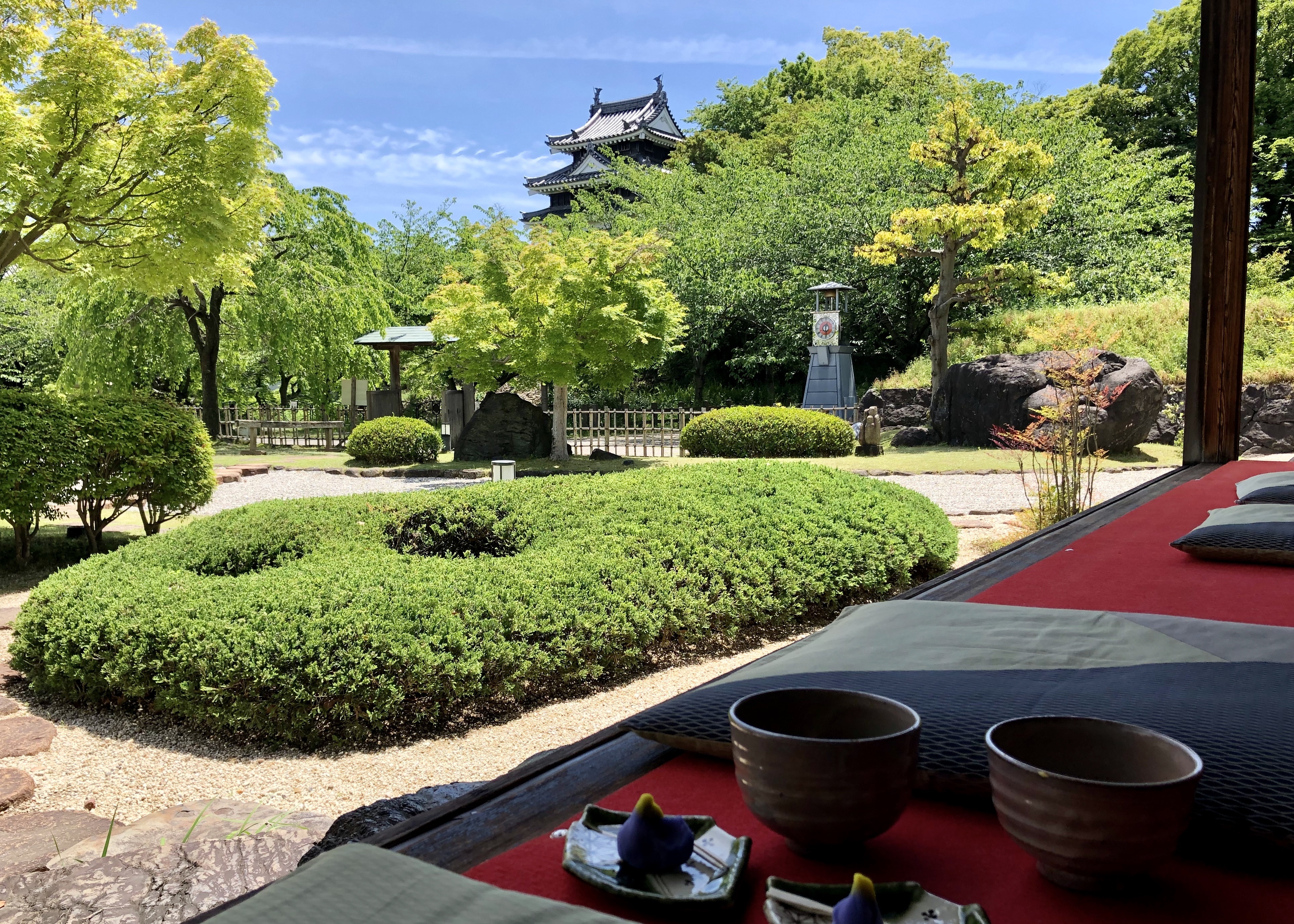
Yokosuka Domain
was a feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo period Japan, located in Tōtōmi Province. It was centered at Yokosuka Castle in what is now the Matsuo district of the city of Kakegawa in Shizuoka Prefecture."Tōtōmi Province" at JapaneseCastleExplorer.com retrieved 2013-8-14. History In February 1601, Ōsuga Tadamasa, lord of in , was allowed by |
Suruga Province
was an old province in the area that is today the central part of Shizuoka Prefecture. Suruga bordered on Izu, Kai, Sagami, Shinano, and Tōtōmi provinces; and was bordered by the Pacific Ocean through Suruga Bay to the south. Its abbreviated form name was . History Early period Suruga was one of the original provinces of Japan established in the Nara period under the Taihō Code. The original capital of the province was located in what is now Numazu, which also had the ''Kokubun-ji'' and the Ichinomiya (Mishima Taisha) of the province. Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Suruga was ranked as a "major country" (上国), and was governed by a '' Kuni no miyatsuko'' and under the ''ritsuryō'' system was classed as a "middle country" (中国) In a 680 AD cadastral reform, the districts forming Izu Province were administratively separated from Suruga, and the provincial capital was relocated to the right bank of the Abe River in what is now Shizuoka City. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aichi Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshū. Aichi Prefecture has a population of 7,552,873 () and a geographic area of with a population density of . Aichi Prefecture borders Mie Prefecture to the west, Gifu Prefecture and Nagano Prefecture to the north, and Shizuoka Prefecture to the east. Overview Nagoya is the capital and largest city of Aichi Prefecture, and the fourth-largest city in Japan, with other major cities including Toyota, Okazaki, and Ichinomiya. Aichi Prefecture and Nagoya form the core of the Chūkyō metropolitan area, the third-largest metropolitan area in Japan and one of the largest metropolitan areas in the world. Aichi Prefecture is located on Japan's Pacific Ocean coast and forms part of the Tōkai region, a subregion of the Chūbu region and Kansai region. Aichi Prefecture is home to the Toyota Motor Corporation. Aichi Prefecture had many locations with the Higashiyama Zoo and Botanical Gardens, The Chubu Centrair Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |