|
Halligen Frisian
Halligen Frisian ( frr, Halifreesk) is the dialect of the North Frisian language North Frisian (''nordfriisk'') is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are thems ... spoken on the Halligen islands, primarily Langeneß and Hooge, in the German region of North Frisia. The dialect has survived despite the islands' being home to less than 300 people and unprotected by dikes, mandating evacuations during storms. However, it is now in danger of extinction. Although it is spoken on islands, it is considered part of the Mainland North Frisian dialects as opposed to the Insular North Frisian Dialects, due to its linguistic features. Grammar Verbs Below are six commonly used verbs in Halligen Frisian: * The future tense is formed with the verbs ''wal'' or ''skal''. * The perfect tense is formed with either ''hääw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of . It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and Czechia to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in what is now Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halligen
The ''Halligen'' (German, singular ''Hallig'', ) or the ''halliger'' (Danish, singular ''hallig'') are small islands without protective dikes. They are variously pluralized in English as the Halligen, Halligs, Hallig islands, or Halligen islands. There are ten German ''halligen'' in the North Frisian Islands on Schleswig-Holstein's Wadden Sea-North Sea coast in the district of Nordfriesland and one hallig at the west coast of Denmark (Mandø). The name is cognate to Old-English ''halh'', meaning "slightly raised ground isolated by marsh". The very existence of the ''halligen'' is a result of frequent floods and poor coastal protection. The floods were much more common in the Middle Ages and coastal protection was much poorer. The ''halligen'' have areas ranging from 7 to 956 ha, and are often former parts of the mainland, separated therefrom by storm tide erosion. Some are also parts of once much bigger islands sundered by the same forces. Sometimes, owing to sediment deposition, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
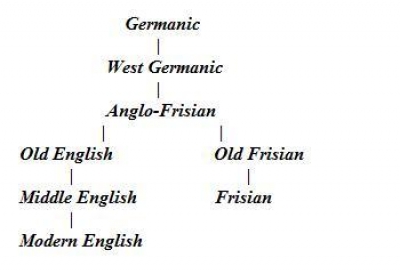
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English, is also the world's most widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch, with over 7.1 million native speakers; Low German, considered a separate collection of unstandardized dialects, with roughly 4.35–7.15 million native speakers and probably 6.7–10 million people who can understand it [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Germanic Languages
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into three branches: Ingvaeonic, which includes English and Frisian, Istvaeonic, which includes Dutch and its close relatives, and Irminonic, which includes German and its close relatives and variants. English is by far the most-spoken West Germanic language, with more than 1 billion speakers worldwide. Within Europe, the three most prevalent West Germanic languages are English, German, and Dutch. Frisian, spoken by about 450,000 people, constitutes a fourth distinct variety of West Germanic. The language family also includes Afrikaans, Yiddish, Luxembourgish, and Scots, which are closely related to Dutch, German and English respectively. Additionally, several creoles, patois, and pidgins are based on Dutch, English, or German. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Sea Germanic
North Sea Germanic, also known as Ingvaeonic , is a postulated grouping of the northern West Germanic languages that consists of Old Frisian, Old English, and Old Saxon, and their descendants. Ingvaeonic is named after the Ingaevones, a West Germanic cultural group or proto-tribe along the North Sea coast that was mentioned by both Tacitus and Pliny the Elder (the latter also mentioned that tribes in the group included the Cimbri, the Teutoni and the Chauci). It is thought of as not a monolithic proto-language but as a group of closely related dialects that underwent several areal changes in relative unison. The grouping was first proposed in ''Nordgermanen und Alemannen'' (1942) by German linguist and philologist Friedrich Maurer as an alternative to the strict tree diagrams, which had become popular following the work of 19th-century linguist August Schleicher and assumed the existence of a special Anglo-Frisian group. The other groupings are Istvaeonic, from the Istvaeone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Frisian Languages
The Anglo-Frisian languages are the Anglic ( English, Scots, and Yola) and Frisian varieties of the West Germanic languages. The Anglo-Frisian languages are distinct from other West Germanic languages due to several sound changes: besides the Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law, which is present in Low German as well, Anglo-Frisian brightening and palatalization of are for the most part unique to the modern Anglo-Frisian languages: * English ''cheese'', Scots ' and West Frisian ', but Dutch ', Low German ', and German ' * English ''church'', and West Frisian ', but Dutch ', Low German ', ', and German ', though Scots ' * English ''sheep'', Scots ' and West Frisian ', but Dutch (pl. ), Low German , German (pl. ) The grouping is usually implied as a separate branch in regards to the tree model. According to this reading, English and Frisian would have had a proximal ancestral form in common that no other attested group shares. The early Anglo-Frisian varieties, like Old Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frisian Languages
The Frisian (, ) languages are a closely related group of West Germanic languages, spoken by about 500,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. The Frisian languages are the closest living language group to the Anglic languages; the two groups make up the Anglo-Frisian languages group and together with the Low German dialects these form the North Sea Germanic languages. However, modern English and Frisian are not mutually intelligible, nor are Frisian languages intelligible among themselves, owing to independent linguistic innovations and foreign influences. There are three different Frisian branches, which are usually called the Frisian languages, despite the fact that their so-called dialects are often not mutually intelligible even within these branches. These branches are: West Frisian, which is by far the most spoken of the three and is an official language in the Dutch province of Friesland, where it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Frisian Language
North Frisian (''nordfriisk'') is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are themselves divided into an insular and a mainland group. North Frisian is closely related to the Saterland Frisian language of Northwest Germany and West Frisian which is spoken in the Netherlands. All of these are also closely related to the English language forming the Anglo-Frisian group. The phonological system of the North Frisian dialects is strongly being influenced by Standard German and is slowly adapting to that of the German language. With a number of native speakers probably even less than 10,000 and decreasing use in mainland North Frisia, the North Frisian language is endangered. It is protected as a minority language and has become an official language in the Nordfriesland district and on Heligoland island. Classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strand Frisian
Strand Frisian was a dialect of the North Frisian language which was originally spoken on Strand island, Duchy of Schleswig. Strand was destroyed in the Burchardi flood of 1634 with its remnants forming the islands Pellworm and Nordstrand which are now part of Germany. Strand Frisian is counted among the mainland group of North Frisian dialects. History The Frisian language became extinct on Nordstrand in the 17th century while it was spoken on Pellworm until the 18th century. After the 1634 flood, refugees from Strand brought their dialect to Wyk auf Föhr where it was spoken until the 19th century. Like the now extinct Wyk dialect, the Halligen Frisian can be seen as a continuation of the former Strand Frisian. Notable works The most notable piece of literature in Strand Frisian is a translation of Martin Luther's '' Small Catechism'' from the time before 1634. Other works include the "Yn Miren-Söngh" Morning Songand "Yn Een-Söngh" n Evening Songby preacher Anton Heimr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena: One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. Under this definition, the dialects or varieties of a particular language are closely related and, despite their differences, are most often largely mutually intelligible, especially if close to one another on the dialect continuum. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors, such as social class or ethnicity. A dialect that is associated with a particular social class can be termed a sociolect, a dialect that is associated with a particular ethnic group can be termed an ethnolect, and a geographical/regional dialect may be termed a regiolectWolfram, Walt and Schilling, Natalie. 2016. ''American Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langeneß
( da, Langenæs, North Frisian ''Nees'') is a municipality in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou .... It consists of the halligen (islands) Langeneß and Oland. Before the flood of 1634 the two islands were directly attached. Langeneß itself has 16 Warften and is the largest Hallig. It has about 100 inhabitants and 58 households. There is a junior school and an information centre providing information about the national park and the Wadden-Sea at Peterswarf. A railway connects Langeneß to the mainland at Dagebüll via Oland. There is also a daily ferry service. References External links * Halligen Tidal islands of Germany Nordfriesland Islands of Schleswig-Holstein {{german ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooge, Germany
Hooge (; da, Hoge, North Frisian: ''Huuge'') is a municipality in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The municipality is located on the island of Hooge – a small island off the coast of Germany. It is the second largest of the ten halligen in the Wadden Sea, after Langeneß. It is frequently called the Queen of the Halligen. The houses on the island are built on ten ''Warften'' ('artificial dwelling mounds'). The municipality (''Gemeinde'') Hooge also includes the uninhabited hallig Norderoog. Settlements and geography Hooge has 9 populated Warften: * Backenswarft * Kirchwarft * Ockelützwarft * Hanswarft * Ockenswarft * Lorenzwarft/Mitteltritt (double-terpen) * Volkertswarft * Ipkenswarft * Westerwarft The Pohnswarft still can be found close to the shore of Hooge. The Pohnswarft is an unpopulated ''Warft'' which has been abandoned due to its unfavourable location. There is only a water gauge on it. The small island of Hainshallig, located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |