|
Halecium Muricatum
''Halecium muricatum'', commonly known as the sea hedgehog hydroid, is a species of hydrozoan in the family Haleciidae. It occurs mainly in arctic and northern temperate waters, in both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Description ''Halecium muricatum'' is a colonial hydrozoan. It is arborescent, forming stiff bushy colonies usually between in height but sometimes . The main stems are robust and mostly straight, with a few large side branches diverging irregularly, each forming an angle of 30° with the main stem. Finer tertiary branches are formed as the polyps each elongate and bud new polyps on alternate sides of the often single plane branch; there is a clearly defined node between each segment. Gonothecae (reproductive structures) develop on the stem and main branches; both male and female gonathecae are ovate and covered with rows of spines and appear identical. The colony is typically yellowish. Distribution and habitat ''Halecium muricatum'' is found in the northwester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrozoa
Hydrozoa (hydrozoans; ) are a taxonomic class of individually very small, predatory animals, some solitary and some colonial, most of which inhabit saline water. The colonies of the colonial species can be large, and in some cases the specialized individual animals cannot survive outside the colony. A few genera within this class live in freshwater habitats. Hydrozoans are related to jellyfish and corals and belong to the phylum Cnidaria. Some examples of hydrozoans are the freshwater jelly ('' Craspedacusta sowerbyi''), freshwater polyps (''Hydra''), '' Obelia'', Portuguese man o' war (''Physalia physalis''), chondrophores (Porpitidae), " air fern" (''Sertularia argentea''), and pink-hearted hydroids ('' Tubularia''). Anatomy Most hydrozoan species include both a polypoid and a medusoid stage in their lifecycles, although a number of them have only one or the other. For example, ''Hydra'' has no medusoid stage, while '' Liriope'' lacks the polypoid stage. Polyps The hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haleciidae
Haleciidae is a family of hydrozoans. Their hydroid colonies emerge from a creeping hydrorhiza and usually form upright branching colonies, although some species' colonies are stolonal. Their gonophores are typically sporosacs, growing singly or bunched into a glomulus. They remain attached to the hydroids or break off to be passively drifted away; in a few, the gonophores are naked.Schuchert (2005) Some enigmatic actively swimming medusae have been tentatively placed in this family as a kind of "wastebin taxon". Should their associated hydroids turn out to belong elsewhere, they are to be moved to that family and genus. The relationships of this fairly small but distinctive radiation to other families of Leptothecata are not well understood at present. However, the family Lovenellidae, often turn out to contain the hydroid stage of medusae formerly placed in the family Haleciidae. Description The shallow, usually even-rimmed hydrothecae are sessile or borne on a hydrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyp (zoology)
A polyp in zoology Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and ... is one of two forms found in the phylum Cnidaria, the other being the medusa (biology), medusa. Polyps are roughly cylindrical in shape and elongated at the axis of the vase-shaped body. In solitary polyps, the aboral (opposite to oral) end is attached to the substrate (biology), substrate by means of a disc-like holdfast (biology), holdfast called a pedal disc, while in colony (biology), colonies of polyps it is connected to other polyps, either directly or indirectly. The oral end contains the mouth, and is surrounded by a circlet of tentacles. Classes In the class (biology), class Anthozoa, comprising the sea anemones and corals, the individual is always a polyp; in the class Hydrozoa, however, the indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonotheca
''Oldenlandia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It is pantropical in distribution and has about 240 species.Inge Groeninckx, Steven Dessein, Helga Ochoterena, Claes Persson, Timothy J. Motley, Jesper Kårehed, Birgitta Bremer, Suzy Huysmans, and Erik Smets. 2009. "Phylogeny of the herbaceous tribe Spermacoceae (Rubiaceae) based on plastid DNA data". ''Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden'' 96(1):109–132.David J. Mabberley. 2008. ''Mabberley's Plant-Book'' third edition (2008). Cambridge University Press: UK. The type species for the genus is ''Oldenlandia corymbosa''.''Oldenlandia'' In: Index Nominum Genericorum. In: Regnum Vegetabile (see ''External links'' below). ''Oldenlandia'' was named by Linnaeus in 1753 in Species Plantarum.Carolus Linnaeus. 1753. ''Species Plantarum'' 1:119. Laurentii Salvii. (see ''External Links'' below). The name honors the Danish botanist Henrik Bernard Oldenland (1697).Umberto Quattrocchi. 2000. ''CRC World Dictionar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Hatteras
Cape Hatteras is a cape located at a pronounced bend in Hatteras Island, one of the barrier islands of North Carolina. Long stretches of beach, sand dunes, marshes, and maritime forests create a unique environment where wind and waves shape the topography. A large area of the Outer Banks is part of a National Park, called the Cape Hatteras National Seashore. It is also the nearest landmass on the North American mainland to Bermuda, which is about to the east-southeast. The treacherous waters off the coast of the Outer Banks are known as the Graveyard of the Atlantic, Over 600 ships wrecked here as victims of shallow shoals, storms, and war. Diamond Shoals, a bank of shifting sand ridges hidden beneath the turbulent sea off Cape Hatteras, has never promised safe passage for ships. In the past 400 years, the graveyard has claimed many lives, but island villagers saved many. As early as the 1870s, villagers served in the United States Life-Saving Service. Others staffed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
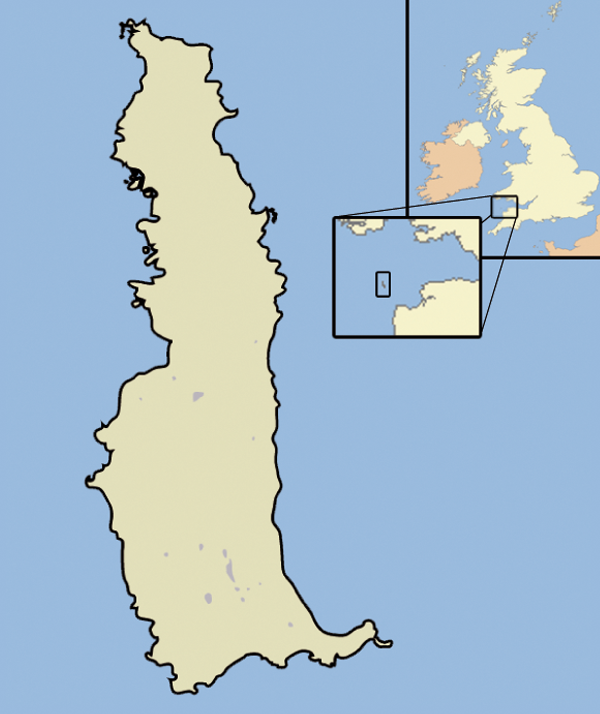
Lundy
Lundy is an English island in the Bristol Channel. It was a micronation from 1925–1969. It forms part of the district of Torridge District, Torridge in the county of Devon. About long and wide, Lundy has had a long and turbulent history, frequently changing hands between the British crown and various usurpers. In the 1920s, one self-proclaimed king, Martin Coles Harman, Martin Harman, tried to issue his own coinage and was fined by the House of Lords. In 1941, two German Heinkel He 111 bombers crash landed on the island, and their crews were captured. In 1969, Lundy was purchased by British millionaire Jack Hayward, who donated it to the National Trust. It is now managed by the Landmark Trust, a conservation charity that derives its income from day trips and holiday lettings, most visitors arriving by boat from Bideford or Ilfracombe. A local tourist curiosity is the special "Puffin" postage stamp, a category known by philatelists as "local carriage labels", a collectors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skomer
Skomer () or Skomer Island is an island off the coast of Pembrokeshire, in the community of Marloes and St Brides in west Wales. It is well known for its wildlife: around half the world's population of Manx shearwaters nest on the island, the Atlantic puffin colony is the largest in southern Britain, and the Skomer vole (a subspecies of the bank vole) is unique to the island. Skomer is a national nature reserve, a Site of Special Scientific Interest and a Special Protection Area. It is surrounded by a marine nature reserve and is managed by the Wildlife Trust of South and West Wales. Skomer is known for its archaeological interest: stone circles, standing stone and remains of prehistoric houses. Much of the island has been designated an ancient monument. Description The island has an area of . Its highest point is above sea level at Gorse Hill, while the majority of the island sits at around above sea level. Skomer is intersected by a series of slopes and ridges giving i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or of different species ( interspecific interactio ... where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush predation, ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nudibranch
Nudibranchs () are a group of soft-bodied marine gastropod molluscs which shed their shells after their larval stage. They are noted for their often extraordinary colours and striking forms, and they have been given colourful nicknames to match, such as "clown", "marigold", "splendid", "dancer", "dragon", or "sea rabbit". Currently, about 3,000 valid species of nudibranchs are known.Ocean Portal (2017)A Collage of Nudibranch Colors Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. Retrieved 17 April 2018. The word "nudibranch" comes from the Latin "naked" and the Ancient Greek () " gills". Nudibranchs are often casually called sea slugs, as they are a family of opistobranchs (sea slugs), within the phylum Mollusca (molluscs), but many sea slugs belong to several taxonomic groups which are not closely related to nudibranchs. A number of these other sea slugs, such as the photosynthetic '' Sacoglossa'' and the colourful Aglajidae, are often confused with nudibranchs. Dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zelentia Pustulata
''Zelentia pustulata'' is a species of sea slug, an aeolid nudibranch, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Trinchesiidae. Distribution This species was described from Cullercoats, North Sea, England. It has been reported from the NE Atlantic from Orkney south to Lundy Island in the Bristol Channel.Picton, B.E. & Morrow, C.C. (2015)''Zelentia pustulata'' (Alder & Hancock, 1854). n/nowiki> Encyclopedia of Marine Life of Britain and Ireland Also reported from the Atlantic coast of North America. This species has been reported from Maine, the Barents Sea and the White Sea.Korshunova, T.; Martynov, A.; Picton, B. (2017)Ontogeny as an important part of integrative taxonomy in tergipedid aeolidaceans (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia) with a description of a new genus and species from the Barents Sea.Zootaxa. 4324(1): 1. Ecology ''Zelentia pustulata'' feeds on the hydroid '' Halecium muricatum'', family Haleciidae Haleciidae is a family of hydrozoans. Their hydroid colonie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_with_its_prey.jpg)
