|
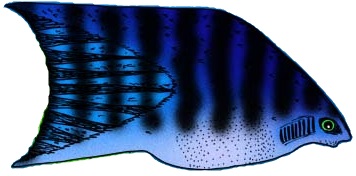
Haemulon Plumierii
''Haemulon plumierii'', the white grunt or common grunt, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Haemulidae native to the western Atlantic Ocean. It grows to a length of about and is a silvery-cream color, with narrow yellow and blue longitudinal stripes, but can modify its color somewhat to match its surroundings. It is closely related to the bluestriped grunt and the French grunt, and often schools with these species. It feeds on shrimp, other crustaceans, annelids, and mollusks, and is preyed on by larger piscivores such as barracuda and shark. It is sometimes caught by anglers as a game fish, and its flaky white flesh can be eaten. It is also a popular aquarium fish. Habitat and distribution The white grunt is found near mangroves, reefs, docks, and nearly any sort of structure in its range, which extends in the Western Atlantic from Chesapeake Bay through the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico south to Brazil. It normally lives in depths similar to that of its relative, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Germain De Lacépède
Bernard-Germain-Étienne de La Ville-sur-Illon, comte de Lacépède or La Cépède (; 26 December 17566 October 1825) was a French natural history, naturalist and an active freemason. He is known for his contribution to the Comte de Buffon's great work, the ''Histoire Naturelle''. Biography Lacépède was born at Agen in Guienne. His education was carefully conducted by his father, and the early perusal of Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon, Buffon's Natural History (''Histoire naturelle, Histoire naturelle, générale et particulière'') awakened his interest in that branch of study, which absorbed his chief attention. His leisure he devoted to music, in which, besides becoming a good performer on the piano and organ, he acquired considerable mastery of composition, two of his operas (which were never published) meeting with the high approval of Christoph Willibald Gluck, Gluck; in 1781–1785 he also brought out in two volumes his ''Poétique de la musique''. Meantime h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngeal Teeth
Pharyngeal teeth are teeth in the pharyngeal arch of the throat of cyprinids, suckers, and a number of other fish species otherwise lacking teeth."Suckers ''Catostomidae''" Iowa Department of Natural Resources Many popular aquarium fish such as and es have these structures. Members of the genus '' Botia'' such as [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Gulf Of Mexico
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Caribbean
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Western Atlantic
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal (phylogenetics), basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all extant taxon, living cartilaginous fish, cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single Class (biology), class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are ectotherm, cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large nekton, active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communication in aquatic animals#Acoustic, communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemulon
''Haemulon'' is a genus of fish in the Haemulidae, grunt family known as the scaled-fin grunts. Most are found in the western Atlantic Ocean, with a few species known from the eastern Pacific Ocean.Rocha, L. A. and I. L. Rosa. (1999)New species of ''Haemulon'' (Teleostei: Haemulidae) from the northeastern Brazilian coast. ''Copeia'' (1999)2 447–52. This genus is considered to be one of the most important fish groups of the coral reefs of Brazil due to its commercial value and crucial ecological role.Pereira, P. H. C. and B. P. Ferreira. (2012)Agonistic behaviour among ''Haemulon'' spp. (Actinopterygii: Haemulidae) and other coral reef fishes in northeastern Brazil. ''Cybium'' 36(2) 361–67. Species The 23 or so species in this genus include:Froese, R. and D. Pauly, eds''Haemulon'': Species.FishBase. 2017. * ''Haemulon album'' Georges Cuvier, G. Cuvier, 1830 (white margate) * ''Haemulon aurolineatum'' G. Cuvier, 1830 (tomtate grunt) * ''Haemulon bonariense'' G. Cuvier, 1830 (bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grits And Grunts
Grits and grunts is a breakfast dish eaten in the U.S. state of Florida. The dish is prepared by serving small fried fish fillets, typically white grunts, over cooked grits. It is similar to shrimp and grits. History The dish is considered to be a staple of Floridian cuisine. It was invented during the colonial period and became popular in Key West during the early 20th century. Barry Popik stated that this popularization occurred around 1900. Stetson Kennedy William Stetson Kennedy (October 5, 1916 – August 27, 2011) was an American author, folklorist and human rights activist. One of the pioneer folklore collectors during the first half of the 20th century, he is remembered for having infiltrated t ...'s book ''Grits and Grunts: Folkloric Key West'' was named after the dish. References Porridges Florida cuisine American fish dishes {{US-cuisine-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Plumier
Charles Plumier (; 20 April 1646 – 20 November 1704) was a French botanist after whom the frangipani genus '' Plumeria'' is named. Plumier is considered one of the most important of the botanical explorers of his time. He made three botanizing expeditions to the West Indies, which resulted in a massive work ''Nova Plantarum Americanarum Genera'' (1703–1704) and was appointed botanist to King Louis XIV of France. Biography Born in Marseille, at the age of 16, he entered the religious order of the Minims. He devoted himself to the study of mathematics and physics, made physical instruments, and was an excellent draughtsman, painter, and turner. On being sent to the French monastery of Trinità dei Monti at Rome, Plumier studied botany under two members of the order, and especially under Cistercian botanist, Paolo Boccone. After his return to France, he became a pupil of Joseph Pitton de Tournefort, whom he accompanied on botanical expeditions. He also explored the coasts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Friars Minor
The Order of Friars Minor (commonly called the Franciscans, the Franciscan Order, or the Seraphic Order; Post-nominal letters, postnominal abbreviation OFM) is a Mendicant orders, mendicant Catholic religious order, founded in 1209 by Francis of Assisi. The order adheres to the teachings and spiritual disciplines of the founder and of his main associates and followers, such as Clare of Assisi, Anthony of Padua, and Elizabeth of Hungary, among many others. The Order of Friars Minor is the largest of the contemporary Religious institute#Categorization, First Orders within the Franciscan movement. Francis began preaching around 1207 and traveled to Rome to seek approval of his order from Pope Innocent III in 1209. The original Rule of Saint Francis approved by the pope disallowed ownership of property, requiring members of the order to beg for food while preaching. The austerity was meant to emulate the life and ministry of Jesus Christ. Franciscans traveled and preached in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet, species epithet, or epitheton) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Etymology Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinique
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼnja. A part of the French West Indies (Antilles), Martinique is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region and a single territorial collectivity of France. It is a part of the European Union as an outermost region within the special territories of members of the European Economic Area, and an associate member of the Caribbean Community, CARICOM, the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS), the Association of Caribbean States (ACS), and the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) but is not part of the Schengen Area or the European Union Customs Union. The currency in use is the euro. It has been a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve since 2021 for its entire land and sea territory. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturalist
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is called a naturalist or natural historian. Natural history encompasses scientific research but is not limited to it. It involves the systematic study of any category of natural objects or organisms, so while it dates from studies in the ancient Greco-Roman world and the mediaeval Arabic world, through to European Renaissance naturalists working in near isolation, today's natural history is a cross-discipline umbrella of many specialty sciences; e.g., geobiology has a strong multidisciplinary nature. Definitions Before 1900 The meaning of the English term "natural history" (a calque of the Latin ''historia naturalis'') has narrowed progressively with time, while, by contrast, the meaning of the related term "nature" has widened (see also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |