|
Hadavalli
Hadavalli is a small village, situated about 17 km from Bhatkala in Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka, India. History Hadavalli, which finds its name in history as Sangeetapura, was once believed to be an abode for musicians and also a center for art and architecture. Nature Surrounded by scenic beauty, this place interests Nature-lovers and historians alike. There a number of Jain Basadi in Hadavalli. The basadis are housed in the Chandragiri and Indragiri hills that stand facing each other. It is said about these hills that the tatwapada (songs of principles), which used to be sung on Chandragiri, were interpreted by the scholars sitting on top of Indragiri. A special sound system like that of a dome was said to have been constructed on the hill for the same. Indragiri has two footprints inscribed on stone and on Chandragiri is a small basadi with no shrine. Temples Though it is said that several basadis existed in the area, there are very few which have overcom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''asteya'' (not stealing), ''brahmacharya'' (chastity), and ''aparigraha'' (non-possessiveness). These pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain Temples In Karnataka
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''asteya'' (not stealing), ''brahmacharya'' (chastity), and ''aparigraha'' (non-possessiveness). These pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism In Maharashtra
Jainism has been present in Maharashtra since ancient times. The famous Ellora Caves demonstrate that Jainism was part of a thriving religious culture in Maharashtra in premodern times. History Jainism in Maharashtra has a long history. The oldest inscription in Maharashtra is a 2nd-century BC Jain inscription in a cave near Pale village in the Pune District. It was written in the Jain Prakrit and includes the Navkar Mantra. The first Marathi inscription known is at Shravanabelagola, Karnataka near the left foot of the statue of Bahubali, dated 981 CE. Maharashtra was ruled many Jain rulers such as the Rashtrakuta dynasty and the Shilaharas. Many of forts were built by kings from these dynasties and thus Jain temples or their remains are found in them. Texts such as the ''Shankardigvijaya'' and ''Shivlilamruta'' suggest that a large number of Marathi people followed jainism in the ancient period. Jain communities in present day Maharashtra There are many native jain c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangalore
Mangalore (), officially known as Mangaluru, is a major port city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It is located between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bangalore, the state capital, 20 km north of Karnataka– Kerala border, 297 km south of Goa. Mangalore is the state's only city to have all four modes of transport—air, road, rail and sea. The population of the urban agglomeration was 619,664 national census of India. It is known for being one of the locations of the Indian strategic petroleum reserves. The city developed as a port in the Arabian Sea during ancient times, and has since become a major port of India that handles 75 percent of India's coffee and cashew exports. It is also the country's seventh largest container port. Mangalore has been ruled by several major powers, including the Kadambas, Alupas, Vijayanagar Empire, Keladi Nayaks, and the Portuguese. The city was a source of contention between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udupi
Udupi (alternate spelling Udipi; also known as Odipu) is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. Udupi is situated about north of the educational, commercial and industrial hub of Mangalore and about west of state capital Bangalore by road. It is the administrative headquarters of Udupi district, and one of the fastest-growing cities in Karnataka. Udupi is one of the top tourist attractions in Karnataka and has various educational institutions. It is notable for the Krishna Temple and is also known as the temple city. It also lends its name to the popular Udupi cuisine, is also known as Parashurama Kshetra , and is famous for Kanakana kindi. A centre of pilgrimage, Udupi is known as Rajata Peetha and Shivalli (Shivabelle). Etymology The name ''Udupi'' is the stylized form of the city. History In the 13th century, Vaishnavite saint Madhvacharya founded the Sri Krishna Temple. He set up eight ''mathas'' - Ashta Mathas- In Kannada - ಅಷ್ಟ ಮಠಗಳು in Ud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain Bunt
The Jain Bunt are the Jainists of Bunt caste from Tulunaad area of India. It has been said that the Jain Bunts also have the highest per capita income in India. They have a feudal and martial race heritages, because of ties to the erstwhile royalty of the area. They are classified as Other Backward Class (OBC) by the Government of Karnataka.:p2.”Candidates belonging to Category-ll(A),. 1(B), III(A), and III(B) shall be entitled to reservation in the manner specified in the new Comprehensive Creamy Layer policy”;p15. Jain Bunt is listed under III(B) Origin Some Jain Bunts are hereditary trustees and administrators of Hindu Temples, an example being at the Dharmasthala Temple, whose hereditary administrators are the Pergade family. Tradition Achieving moksha or liberation is the highest goal of life for the Jains. Jain monastics and renouncers of worldly life are highly revered, especially Bahubali, a king who turned into an ascetic. His virtues are greatly extolled in leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism In North Karnataka
Jainism in North Karnataka flourished under the Chalukyas, Kadamba, Rashtrakutas, and Vijayanagara empire. Imbued with religious feeling, patronage was extended towards the building of Jain temple and it garnered high repute among the people, particularly the ruling classes and the mercantile community; effectively getting treated as the state religion. Literature The Kannada poet Adikavi Pampa’s wrote Vikramarjuna Vijaya, also known as ''Pampa Bharata'', and also '' Adipurana'' which narrates the story of Shri Rishabhadev, the first Tirthankara. ''Neminatha Purana'' a history of the 22nd Tirthankara, provides a Jain interpretation for the story of Krishna and the Pandavas. Jain architecture Jain architecture can be classified into two categories namely ''basadi'' and ''betta''. ''Basadi'' is a Jain monastery or temple where an image of one of the twenty-four tirthankaras (saints) is installed and worshipped. They were built in the Dravidian style and the oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
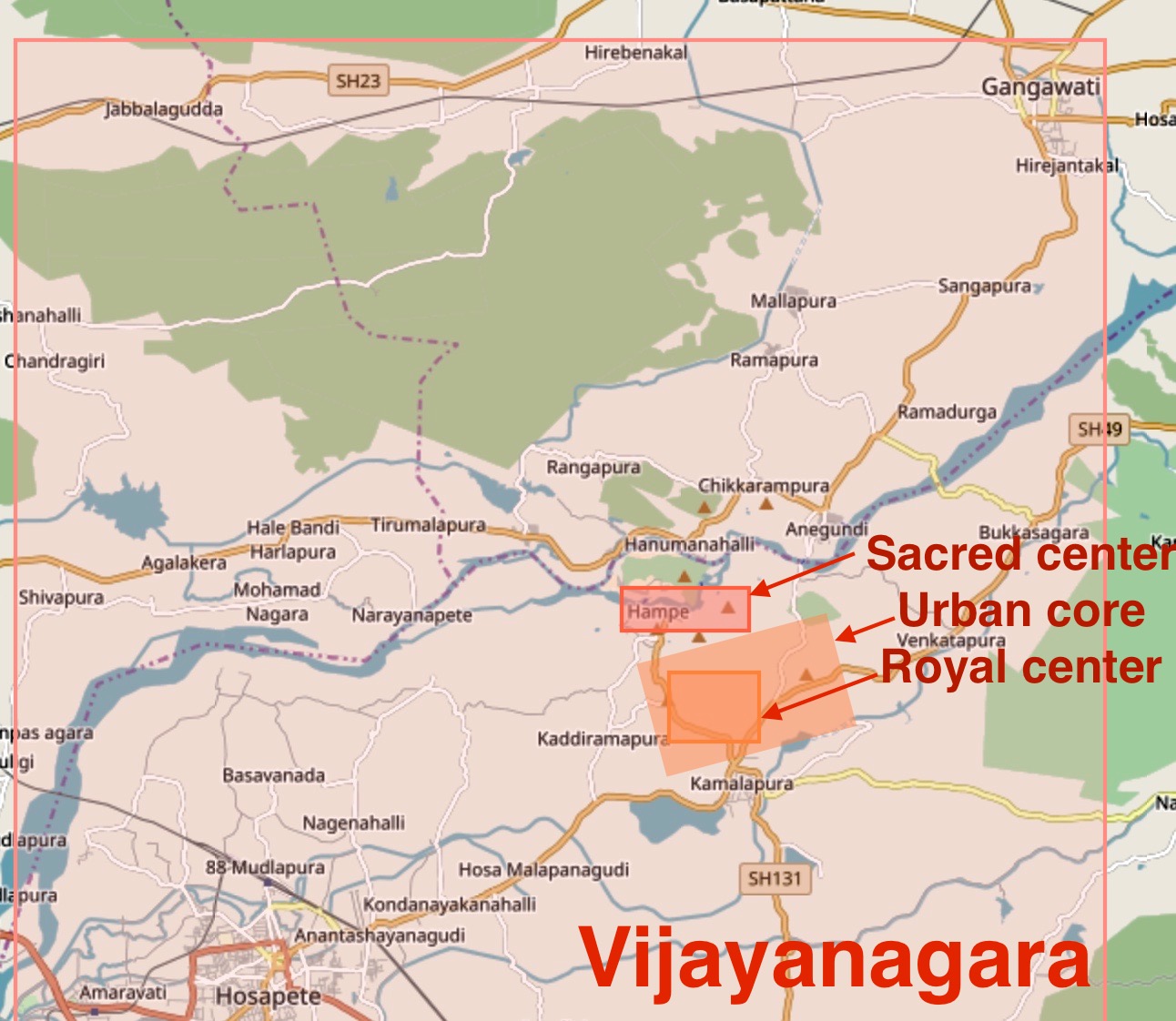
Vijayanagara
Vijayanagara () was the capital city of the historic Vijayanagara Empire. Located on the banks of the Tungabhadra River, it spread over a large area and included the modern era Group of Monuments at Hampi site in Vijayanagara district, Bellary district and others in and around these districts in Karnataka, India. A part of Vijayanagara ruins known as Hampi has been designated as a UNESCO world heritage site. Vijayanagara is in the eastern part of central Karnataka, close to the Andhra Pradesh border.Vijayanagara Encyclopaedia Britannica Hampi is an ancient human settlement, mentioned in Hindu texts and has pre-Vijayanagara temples and monuments. In early 14th century, the Deccan region including the dominant |
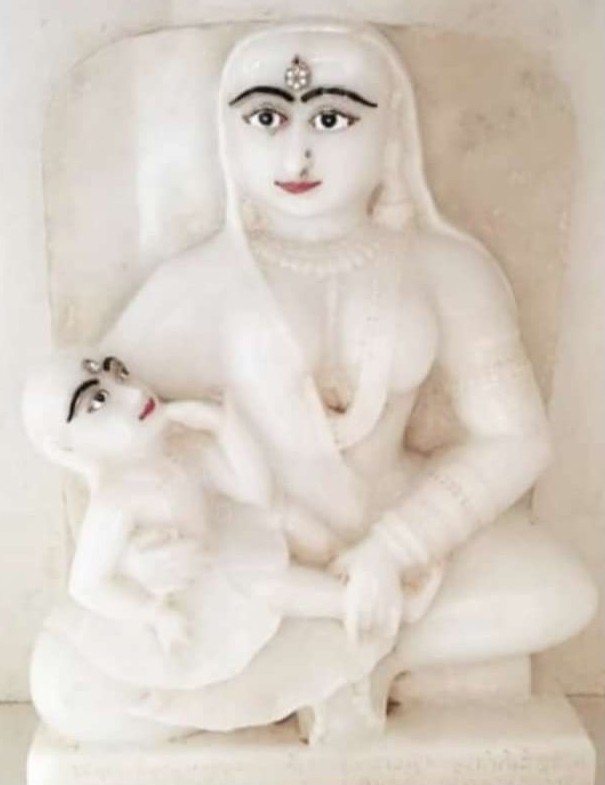
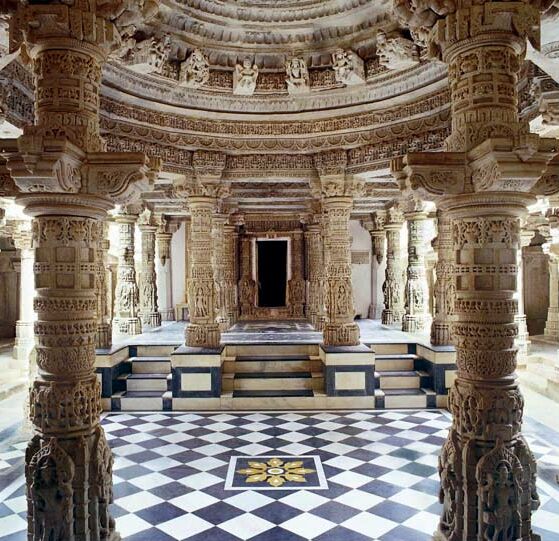
Basadi
A Jain temple, Derasar (Gujarati: દેરાસર) or Basadi (Kannada: ಬಸದಿ) is the place of worship for Jains, the followers of Jainism. Jain architecture is essentially restricted to temples and monasteries, and Jain buildings generally reflect the prevailing style of the place and time they were built. Jain temple architecture is generally close to Hindu temple architecture, and in ancient times Buddhist architecture. Normally the same builders and carvers worked for all religions, and regional and period styles are generally similar. For over 1,000 years, the basic layout of a Hindu or most Jain temples has consisted of a small garbhagriha or sanctuary for the main murti or cult images, over which the high superstructure rises, then one or more larger mandapa halls. Māru-Gurjara architecture or the "Solanki style" is, a particular temple style from Gujarat and Rajasthan (both regions with a strong Jain presence) that originated in both Hindu and Jain temples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rishabhanatha
Rishabhanatha, also ( sa, ऋषभदेव), Rishabhadeva, or Ikshvaku is the first (Supreme preacher) of Jainism and establisher of Ikshvaku dynasty. He was the first of twenty-four teachers in the present half-cycle of time in Jain cosmology, and called a "ford maker" because his teachings helped one across the sea of interminable rebirths and deaths. The legends depict him as having lived millions of years ago. He was the spiritual successor of Sampratti Bhagwan, the last Tirthankar of previous time cycle. He is also known as Ādinātha which translates into "First (''Adi'') Lord (''nātha'')", as well as Adishvara (first Jina), Yugadideva (first deva of the yuga), Prathamarajeshwara (first God-king), Ikshvaku and Nabheya (son of Nabhi). Along with Mahavira, Parshvanath, Neminath, and Shantinath; Rishabhanath is one of the five Tirthankaras that attract the most devotional worship among the Jains. According to traditional accounts, he was born to king Nabhi and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basadi
A Jain temple, Derasar (Gujarati: દેરાસર) or Basadi (Kannada: ಬಸದಿ) is the place of worship for Jains, the followers of Jainism. Jain architecture is essentially restricted to temples and monasteries, and Jain buildings generally reflect the prevailing style of the place and time they were built. Jain temple architecture is generally close to Hindu temple architecture, and in ancient times Buddhist architecture. Normally the same builders and carvers worked for all religions, and regional and period styles are generally similar. For over 1,000 years, the basic layout of a Hindu or most Jain temples has consisted of a small garbhagriha or sanctuary for the main murti or cult images, over which the high superstructure rises, then one or more larger mandapa halls. Māru-Gurjara architecture or the "Solanki style" is, a particular temple style from Gujarat and Rajasthan (both regions with a strong Jain presence) that originated in both Hindu and Jain temples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |