|
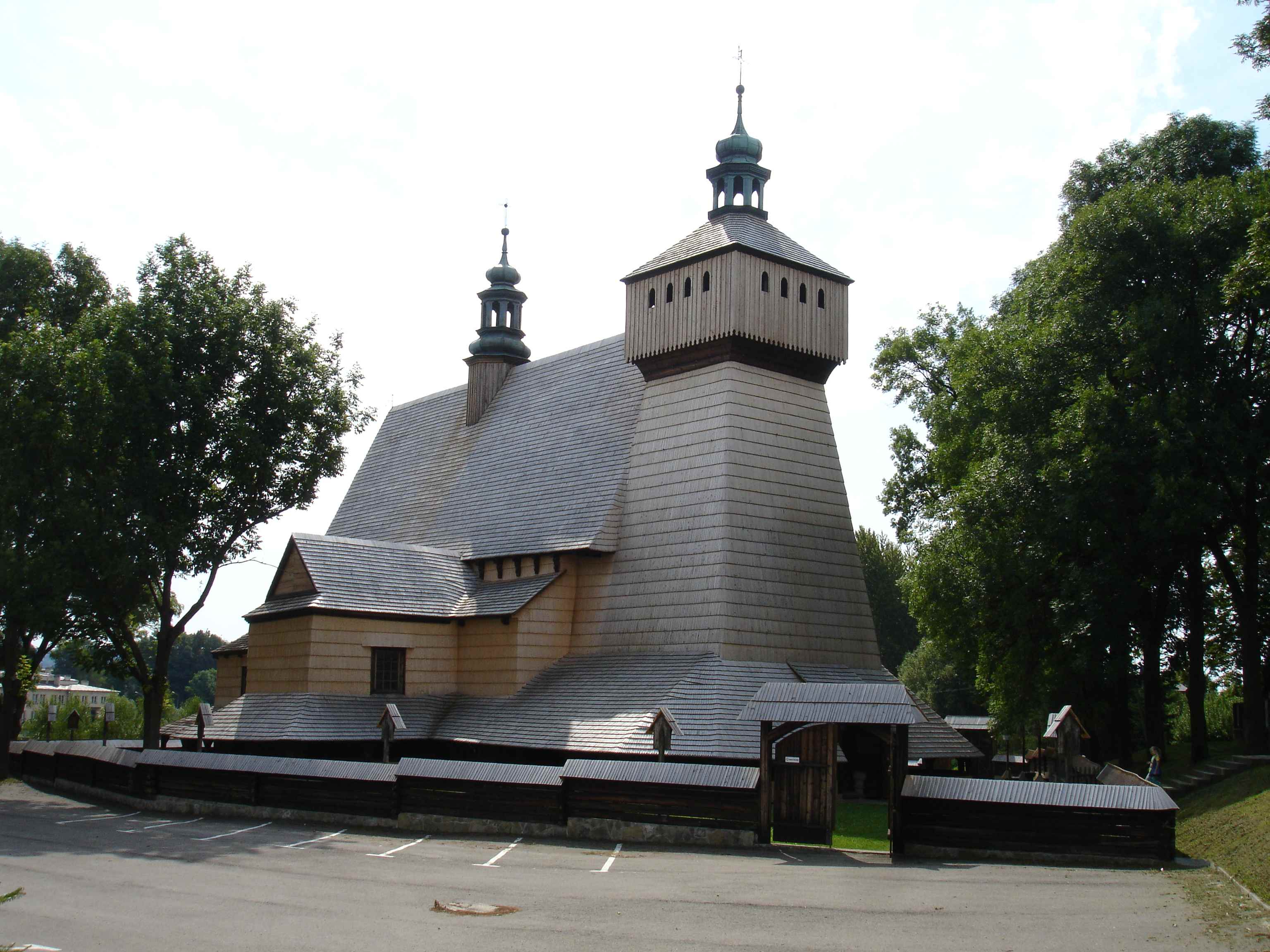
Haczów Old Latin Church
Haczów is a village in Brzozów County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Haczów. It lies approximately west of Brzozów and south of the regional capital Rzeszów. In 1975–1998, Haczów was located in the Krosno Voivodeship. The village is the site of Assumption of Mary and St. Michael's Archangel church, built in the end of the 14th century. In 1624, it was severely damaged by Tatar attacks. The site is one of the six with Wooden Churches of Southern Little Poland, on the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites since 2003. Inside a valuable figural wall paintings dating from 1494 can be seen. The church has recently been renovated. It is believed that the Haczów church is the biggest Gothic wooden church in Europe. Dwor w Haczowie 1934 (69651117) (cropped).jpg, Manor house in Haczów, 1934 Haczow monografja 1936 (84845204) (cropped).jpg, Manor house in Haczów, before 1934 Haczow mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International security, security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 194 Member states of UNESCO, member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the Non-governmental organization, non-governmental, Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 National Commissions for UNESCO, national commissions. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the events of World War II, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandomierz
Sandomierz (pronounced: ; , ) is a historic town in south-eastern Poland with 23,863 inhabitants (), situated on the Vistula River near its confluence with the San, in the Sandomierz Basin. It has been part of Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (Holy Cross Province) since its transfer from the Tarnobrzeg Voivodeship in 1999. It is the capital of Sandomierz County. Sandomierz is known for its preserved Old Town, a major cultural and tourist attraction which the President of Poland declared a National Monument of Poland in 2017. In the past, Sandomierz was one of the most important urban centers not only of Lesser Poland, but also of the whole country. It was a royal city of the Polish Crown and functioned as a regional administrative centre from the High Middle Ages to the 19th century. Etymology The name of the city might have originated from the Old Polish ', composed of ' (from the verb ' "to judge") and ' ("peace"), or more likely from the antiquated given name Sędzimir, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg Law
Magdeburg rights (, , ; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by the local ruler. Named after the city of Magdeburg, these town charters were perhaps the most important set of medieval laws in Central Europe. They became the basis for the German town laws developed during many centuries in the Holy Roman Empire. The Magdeburg rights were adopted and adapted by numerous monarchs, including the rulers of Bohemia, Hungary, Poland, and Lithuania, a milestone in the urbanization of the region which prompted the development of thousands of villages and cities. Provisions Being a member of the Hanseatic League, Magdeburg was one of the most important trade cities, maintaining commerce with the Low Countries, the Baltic states, and the interior (for example Braunschweig). As with most medieval city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walddeutsche
(lit. "Forest Germans" or – "Deaf Germans"; – "deaf Germans") was the name for a group of German-speaking people, originally used in the 16th century for two language islands around Łańcut and Krosno, in southeastern Poland. Both of them were fully polonised before the 18th century, the term, however, survived up to the early 20th century as the designation , broadly and vaguely referring to the territory of present-day Sanockie Pits, which has seen a partial German settlement since the 14th century, mostly Slavicised long before the term was coined. Nomenclature The term – coined by the Polish historians Marcin Bielski (1531), Szymon Starowolski (1632), Bishop Ignacy Krasicki, and Wincenty Pol – also sometimes refers to Germans living between Wisłoka and the San River part of the West Carpathian Plateau and the Central Beskidian Piedmont in Poland. The Polish term is a sort of pun; it means "deaf-mutes", but sounds like "forest Germans": , Polish for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir III The Great
Casimir III the Great (; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, retaining the title throughout the Galicia–Volhynia Wars. He was the last Polish king from the Piast dynasty. Casimir inherited a kingdom weakened by war and under his rule it became relatively prosperous and wealthy. He reformed the Polish army and doubled the size of the kingdom. He reformed the judicial system and introduced several undying codified statutes, gaining the title "the Polish Justinian I, Justinian". Casimir built extensively and founded the Jagiellonian University (back then simply called the University of Krakow),Saxton, 1851, p. 535 the oldest List of universities in Poland, Polish university and List of oldest universities in continuous operation, one of the oldest in the world. He also confirmed privileges and protections previously granted to Jews and encouraged them to settle in Poland in great numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisłok
Wisłok is a river in south-eastern Poland, a tributary of the San River, with a length of 220 kilometres and a basin area of 3,538 km2 (all in Poland). The root of the name ''Vis-lok'' is Indo-European or pre-Indo-European. The first metal bridges on highways were built in Galicia. They were bridges on the Wisłok river in Rzeszów (1877) and Raba in Książnica (1877). The construction of the first latticework metal bridges in Poland's territories. History There is no data on the settlements in the early Iron period when an old trade route crossed the region along Wisłok River Valley. The Wisłok valley must have been an important trade route and human settlement axis as early as 9th or 10th century. The region subsequently became part of the Great Moravian state. Upon the invasion of the Hungarian tribes into the heart of the Great Moravian Empire around 899, the Lendians of the area declared their allegiance to Hungarian Empire. The region then became a site of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krosno
Krosno (in full ''The Royal Free City of Krosno'', ) is a historical town and Krosno County, county in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in southeastern Poland. The estimated population of the town is 47,140 inhabitants as of 2014. The functional urban area of Krosno has a population of 115,000 inhabitants. Krosno is a medieval Defensive wall, fortified town, a former Royal Free Town and centre of Textile, cloth, linen, canvas, baize and Hungary, Hungarian wine trade. It is also notable for its glassmaking traditions, which became known as the Krosno Glassware. Until recently it was a provincial capital. Geography The River Wisłok passes by Krosno. Slovakia is about south, and Ukraine is about east of the city. It is located in the heartland of the Doły Jasielsko Sanockie, Doły (Pits), and its average altitude is above mean sea level, above sea level, but some hills are located within the confines of the city. Neighbouring municipalities are Korczyna, Lesser Poland Voivodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemko
Lemkos (; ; ; ) are an ethnic group inhabiting the Lemko Region (; ) of Carpathian Ruthenia, Carpathian Rus', an ethnographic region in the Carpathian Mountains and Carpathian Foothills, foothills spanning Ukraine, Slovakia, and Poland. Lemkos are often considered to be a sub-group of Rusyns. Members of these groups have historically also been given other designations, such as ''Verkhovyntsi'' ("highlanders"). Among people of the Carpathian highlands, communities speaking the same dialect will identify with a different ethnic label when crossing borders due to the influence of state-sponsored education and media. As well, the same community may switch its preferred identification over time. In Slovakia, between the 1991 and 2001 censuses, the number of people identifying as "Ukrainian" declined by 2,467 (an 18.6% decrease), while those reporting Rusyn as their national identity increased by 7,004 people (a 40.6% increase). It is not clear, however, if this refers to the same indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary ethnic groups, second largest ethno-linguistic community. At around 46 million worldwide, Ukrainians are the second largest Slavs, Slavic ethnic group after Russians. Ukrainians have been Endonym and exonym, given various names by foreign rulers, which have included Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Habsburg monarchy, the Austrian Empire, and then Austria-Hungary. The East Slavic population inhabiting the territories of modern-day Ukraine were known as Ruthenians, referring to the territory of Ruthenia; the Ukrainians living under the Russian Empire were known as Little Russians, named after the territory of Little Russia. The ethnonym Ukrainian, which was associated with the Cossack Hetmanate, was adopted following the Ukrainian natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (, , or simply , ) is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic language of the Lechitic languages, Lechitic subgroup, within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is written in the Latin script. It is primarily spoken in Poland and serves as the official language of the country, as well as the language of the Polish diaspora around the world. In 2024, there were over 39.7 million Polish native speakers. It ranks as the sixth-most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional Dialects of Polish, dialects. It maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, Honorifics (linguistics), honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (, , , , , , , , ) to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet. The traditional set compri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |