|
Hackney (automobile)
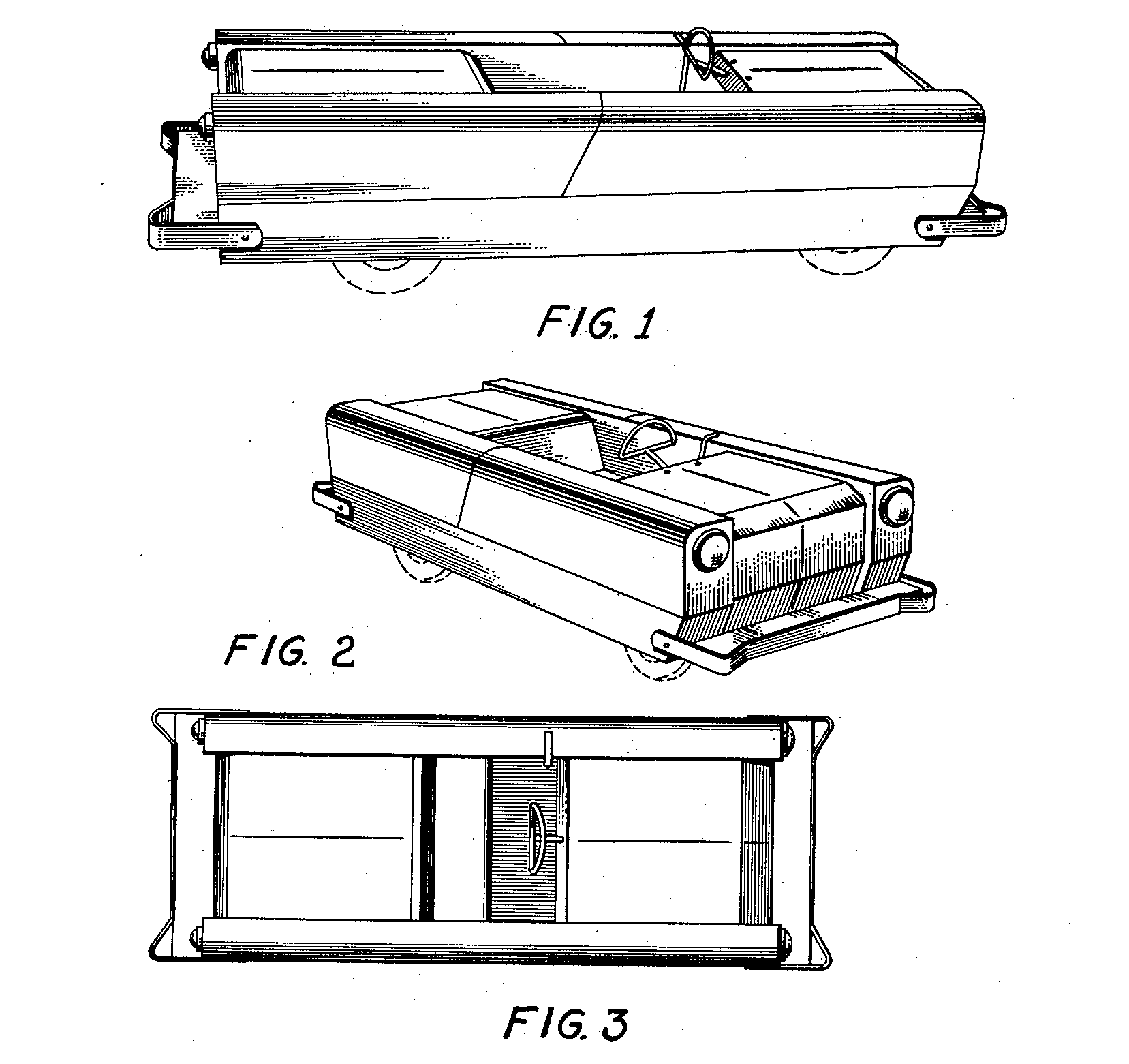
The Hackney was a marque of microcar which seated one adult or two children, built in the mid-to-later 1950s by the Gordon W. Morton Company of High Point Road in Greensboro, North Carolina. Hubert H. Hackney applied for a patent for this miniature car design on August 19, 1955, and the patent was approved by the United States Patent Office on March 19, 1957 for a term of 14 years. The Hackney somewhat resembled the concurrent Eshelman automobile, but differed in its most remarkable engineering features, which included what the manufacturer termed its "Floating Power Unit" (FPU)—a self-contained rear-mounted engine, clutch, and drivetrain combination—in concert with the rear wheels and independent of the body. The FPU was mounted on pivots at front and back. Also, a floorboard-mounted one-stick control operated both forward and rear motions, and even operated braking action. The throttle control was mounted on the dashboard; a rope-recoil starter was used. Two models were of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windshield
The windshield (North American English) or windscreen (Commonwealth English) of an aircraft, car, bus, motorbike, truck, train, boat or streetcar is the front window, which provides visibility while protecting occupants from the elements. Modern windshields are generally made of laminated safety glass, a type of treated glass, which consists of, typically, two curved sheets of glass with a plastic layer laminated between them for safety, and bonded into the window frame. Motorcycle windshields are often made of high-impact polycarbonate or acrylic plastic. Usage Windshields protect the vehicle's occupants from wind and flying debris such as dust, insects, and rocks, and provide an aerodynamically formed window towards the front. UV coating may be applied to screen out harmful ultraviolet radiation. However, this is usually unnecessary since most auto windshields are made from laminated safety glass. The majority of UV-B is absorbed by the glass itself, and any r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcars
Microcar is a term often used for the smallest size of cars, with three or four wheels and often an engine smaller than . Specific types of microcars include bubble cars, cycle cars, invacar, quadricycles and voiturettes. Microcars are often covered by separate regulations to normal cars, having relaxed requirements for registration and licensing. Predecessors Voiturette is a term used by some small cars and tricycles manufactured from 1895 to 1910. Cyclecars are a type of small, lightweight and inexpensive car manufactured mainly between 1910 and the late 1920s. Europe 1940-1970: Microcars The first cars to be described as microcars (earlier equivalents were called voiturettes or cyclecars) were built in the United Kingdom and Germany following World War II, and remained popular until the 1960s. They were originally called minicars, but later became known as microcars. France also produced large numbers of similar tiny vehicles called voiturettes, but they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crosley
Crosley was a small, independent American manufacturer of subcompact cars, bordering on microcars. At first called the Crosley Corporation and later Crosley Motors Incorporated, the Cincinnati, Ohio, firm was active from 1939 to 1952, interrupted by World War II production. Their station wagons were the most popular model, but also offered were sedans, pickups, convertibles, a sports car, and even a tiny jeep-like vehicle. For export, the cars were badged Crosmobile. Crosley introduced several "firsts" in American automotive history, including the first affordable, mass-market car with an overhead camshaft engine in 1946; the first use of the term ' Sport(s-) Utility' in 1947, for a 1948 model year convertible wagon; and the first American cars to be fitted with 4-wheel caliper type disc brakes, as well as America's first post-war sports car, the Hotshot, in the 1949 model year. All of Crosley's models were lightweight () body-on-frame cars with rigid axles front and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleet Vehicle
Fleet vehicles are groups of motor vehicles owned or leased by a business, government agency, or other organization rather than by an individual or family. Typical examples include vehicles operated by car rental companies, taxicab companies, public utilities, public bus companies, and police departments. In addition, many businesses purchase or lease fleet vehicles to deliver goods to customers, as well as provide vehicles for sales representatives to travel to clients. In some jurisdictions and countries, fleet vehicles can also be privately owned by employees. These vehicles are called the 'grey fleet' and are used for work purposes. Fleet vehicles can be managed by a fleet manager or transport manager using fleet management software. Vehicles may be connected to a fleet telematics system by way of a Fleet Management System also known as FMS. Federal Vehicle Fleet In the United States, Federal Vehicle Fleets refer to the federal government A federation (also k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amusement Park
An amusement park is a park that features various attractions, such as rides and games, as well as other events for entertainment purposes. A theme park is a type of amusement park that bases its structures and attractions around a central theme, often featuring multiple areas with different themes. Unlike temporary and mobile funfairs and carnivals, amusement parks are stationary and built for long-lasting operation. They are more elaborate than city parks and playgrounds, usually providing attractions that cater to a variety of age groups. While amusement parks often contain themed areas, theme parks place a heavier focus with more intricately-designed themes that revolve around a particular subject or group of subjects. Amusement parks evolved from European fairs, pleasure gardens, and large picnic areas, which were created for people's recreation. World's fairs and other types of international expositions also influenced the emergence of the amusement park industry. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propulsion
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from two Latin words: ''pro'', meaning'' before'' or ''forward''; and '' pellere'', meaning ''to drive''. A propulsion system consists of a source of mechanical power, and a ''propulsor'' (means of converting this power into propulsive force). Plucking a guitar string to induce a vibratory translation is technically a form of propulsion of the guitar string; this is not commonly depicted in this vocabulary, even though human muscles are considered to propel the fingertips. The motion of an object moving through a gravitational field is affected by the field, and within some frames of reference physicists speak of the gravitational field generating a force upon the object, but for deep theoretic reasons, physicists now consider the curved p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fender (vehicle)
Fender is the American English term for the part of an automobile, motorcycle or other vehicle body that frames a wheel well (the fender underside). Its primary purpose is to prevent sand, mud, rocks, liquids, and other road spray from being thrown into the air by the rotating tire. Fenders are typically rigid and can be damaged by contact with the road surface. Sticky materials, such as mud, may adhere to the smooth outer tire surface, while smooth loose objects, such as stones, can become temporarily embedded in the tread grooves as the tire rolls over the ground. These materials can be ejected from the surface of the tire at high velocity as the tire imparts kinetic energy to the attached objects. For a vehicle moving forward, the top of the tire is rotating upward and forward, and can throw objects into the air at other vehicles or pedestrians in front of the vehicle. In British English, the fender is called the wing. (This may refer to either the front or rear fenders. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheet Steel
Sheet metal is metal formed into thin, flat pieces, usually by an industrial process. Sheet metal is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking, and it can be cut and bent into a variety of shapes. Thicknesses can vary significantly; extremely thin sheets are considered foil or leaf, and pieces thicker than 6 mm (0.25 in) are considered plate, such as plate steel, a class of structural steel. Sheet metal is available in flat pieces or coiled strips. The coils are formed by running a continuous sheet of metal through a roll slitter. In most of the world, sheet metal thickness is consistently specified in millimeters. In the U.S., the thickness of sheet metal is commonly specified by a traditional, non-linear measure known as its gauge. The larger the gauge number, the thinner the metal. Commonly used steel sheet metal ranges from 30 gauge to about 7 gauge. Gauge differs between ferrous ( iron-based) metals and nonferrous metals such as aluminum or copper. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trailer Hitch
A tow hitch (or tow bar or trailer hitch in North America) is a device attached to the chassis of a vehicle for towing, or a towbar to an aircraft nose gear. It can take the form of a tow ball to allow swiveling and articulation of a trailer, or a tow pin, or a tow hook with a trailer loop, often used for large or agricultural vehicles where slack in the pivot pin allows similar movements. Another category is the towing pintle used on military vehicles worldwide. To tow safely, the correct combination of vehicle and trailer must be combined with correct loading horizontally and vertically on the tow ball. Advice should be heeded (see references) to avoid problems. Regional variations North America Trailer hitches for conventional passenger cars, light-duty commercial vehicles, light trucks, and multipurpose passenger vehicles come in two main OEM or aftermarket types: receiver and bumper/fixed-drawbar. Receiver-type hitches consist of a portion with a rearward-facing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bumper (car)
A bumper is a structure attached to or integrated with the front and rear ends of a motor vehicle, to absorb impact in a minor collision, ideally minimizing repair costs. Stiff metal bumpers appeared on automobiles as early as 1904 that had a mainly ornamental function. Numerous developments, improvements in materials and technologies, as well as greater focus on functionality for protecting vehicle components and improving safety have changed bumpers over the years. Bumpers ideally minimize height mismatches between vehicles and protect pedestrians from injury. Regulatory measures have been enacted to reduce vehicle repair costs and, more recently, impact on pedestrians. History Bumpers were at first just rigid metal bars. George Albert Lyon invented the earliest car bumper. The first bumper appeared on a vehicle in 1897, and it was installed by Nesselsdorfer Wagenbau-Fabriksgesellschaft, a Czech carmaker. The construction of these bumpers was not reliable as they featured on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plexiglas
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) belongs to a group of materials called engineering plastics. It is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Astariglas, Lucite, Perclax, and Perspex, among several others ( see below). This plastic is often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It can also be used as a casting resin, in inks and coatings, and for many other purposes. Although not a type of familiar silica-based glass, the substance, like many thermoplastics, is often technically classified as a type of glass, in that it is a non-crystalline vitreous substance—hence its occasional historic designation as ''acrylic glass''. Chemically, it is the synthetic polymer Some familiar household synthetic polymers include: Nylons in textiles and fabrics, Teflon in non-stick pans, Bakelite for electrical switches, polyvinyl chloride (PVC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



_deLuxe_Two_door_1958_Bumper.jpg)
