|
Habenular Nuclei
The habenula (diminutive of Latin meaning rein) is a small bilateral neuronal structure in the brain of vertebrates, that has also been called a microstructure since it is no bigger than a pea. The naming as little rein describes its elongated shape in the epithalamus, where it borders the third ventricle, and lies in front of the pineal gland. Although it is a microstructure each habenular nucleus is divided into two distinct regions of nuclei, a medial habenula (MHb), and a lateral habenula (LHb) both having different neuronal populations, inputs, and outputs. The medial habenula can be subdivided into five subnuclei, the lateral habenula into four subnuclei. Research has shown morphological complexity in the MHb and LHb. Different inputs to the MHb are discriminated between the different subnuclei. In the two regions of nuclei there is a difference in gene expression giving different functions to each. The habenula is a conserved structure across vertebrates. In mammals it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the nervous system, and with the spinal cord, comprises the central nervous system. It consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. The brain controls most of the activities of the human body, body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sensory nervous system. The brain integrates sensory information and coordinates instructions sent to the rest of the body. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six Cerebral cortex#Layers of neocortex, neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes of the brain, lobes – the frontal lobe, frontal, pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nociception
In physiology, nociception , also nocioception; ) is the Somatosensory system, sensory nervous system's process of encoding Noxious stimulus, noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal to trigger an appropriate defensive response. In nociception, intense chemical (e.g., capsaicin present in chili pepper or cayenne pepper), mechanical (e.g., cutting, crushing), or thermal (heat and cold) stimulation of sensory neurons called nociceptors produces a signal that travels along a chain of nerve fibers to the brain. Nociception triggers a variety of physiological and behavioral responses to protect the organism against an aggression, and usually results in a subjective experience, or perception, of pain in Sentience, sentient beings. Detection of noxious stimuli Potentially damaging mechanical, thermal, and chemical stimuli are detecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preoptic Area
The preoptic area is a region of the hypothalamus. MeSH classifies it as part of the anterior hypothalamus. TA lists four nuclei in this region, (medial, median, lateral, and periventricular). Functions The preoptic area is responsible for thermoregulation and receives nervous stimulation from thermoreceptors in the skin, mucous membranes, and hypothalamus itself. Nuclei Median preoptic nucleus The median preoptic nucleus is located along the midline in a position significantly dorsal to the other three preoptic nuclei, at least in the crab-eating macaque brain. It wraps around the top (dorsal), front, and bottom (ventral) surfaces of the anterior commissure. The median preoptic nucleus generates thirst. Drinking decreases noradrenaline release in the median preoptic nucleus. Medial preoptic nucleus The medial preoptic nucleus is bounded laterally by the lateral preoptic nucleus, and medially by the preoptic periventricular nucleus. It releases gonadotropin-releasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions. Vesicles of the forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three primary brain vesicles during the early development of the nervous system. At the five-vesicle stage, the forebrain separates into the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, and epithalamus) and the telencephalon which develops into the cerebrum. The cerebrum consists of the cerebral cortex, underlying white matter, and the basal ganglia. In humans, by 5 weeks in utero it is visible as a single portion toward the front of the fetus. At 8 weeks in utero, the forebrain splits into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. When the embryonic forebrain fails to divide the brain into two lobes, it results i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindbrain
The hindbrain, rhombencephalon (shaped like a rhombus) is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes. Metencephalon Rhombomeres Rh3-Rh1 form the metencephalon. The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; it contains: * a portion of the fourth (IV) ventricle, * the trigeminal nerve (CN V), * abducens nerve (CN VI), * facial nerve (CN VII), * and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Myelencephalon Rhombomeres Rh8-Rh4 form the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon forms the medulla oblongata in the adult brain; it contains: * a portion of the fourth ventricle, * the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), * vagus nerve (CN X), * accessory nerve (CN XI), * hypoglossal nerve (CN XII), * and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Evolution The hindbrain is homologous to a part of the arthropod brain k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum. It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.Breedlove, Watson, & Rosenzweig. Biological Psychology, 6th Edition, 2010, pp. 45-46 The name ''mesencephalon'' comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The midbrain is the shortest segment of the brainstem, measuring less than 2cm in length. It is situated mostly in the posterior cranial fossa, with its superior part extending above the tentorial notch. The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostral and caudal, Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while Rostral and caudal, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Diencephalic Conduction System
The epithalamus (: epithalami) is a posterior (dorsal) segment of the diencephalon. The epithalamus includes the habenular nuclei, the stria medullaris, the anterior and posterior paraventricular nuclei, the posterior commissure, and the pineal gland. Functions The function of the epithalamus is to connect the limbic system to other parts of the brain. The epithalamus also serves as a connecting point for the dorsal diencephalic conduction system, which is responsible for carrying information from the limbic forebrain to limbic midbrain structures. Some functions of its components include the secretion of melatonin from the pineal gland (circadian rhythms), regulation of motor pathways and emotions, and how energy is conserved in the body. A study has shown that the lateral habenula, in the epithalamus, produces spontaneous theta oscillatory activity that was correlated with theta oscillation in the hippocampus. The same study also found that the increase in theta waves in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Pallidum
The ventral pallidum (VP) is a structure within the basal ganglia of the brain. It is an output nucleus whose fibres project to thalamic nuclei, such as the ventral anterior nucleus, the ventral lateral nucleus, and the medial dorsal nucleus. The VP is a core component of the reward system which forms part of the limbic loop of the basal ganglia, a pathway involved in the regulation of motivational salience, behavior, and emotions. It is involved in addiction. The VP contains one of the brain's pleasure centers, which mediates the subjective perception of pleasure that results from "consuming" certain rewarding stimuli (e.g., palatable food). Anatomy The ventral pallidum lies within the basal ganglia, a group of subcortical nuclei. Along with the external globus pallidus, it is separated from other basal ganglia nuclei by the anterior commissure. The ventral pallidum contains GABAergic neurons, glutamatergic neurons, and cholinergic neurons that are well conserved ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
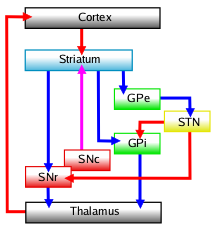
Internal Globus Pallidus
The internal globus pallidus (GPi or medial globus pallidus) is one of the two subcortical nuclei that provides inhibitory output in the basal ganglia, the other being the substantia nigra pars reticulata. Together with the external globus pallidus (GPe), it makes up one of the two segments of the globus pallidus, a structure that can decay with certain neurodegenerative disorders and is a target for medical and neurosurgical therapies. The GPi, along with the substantia nigra pars reticulata, comprise the primary output of the basal ganglia, with its outgoing GABAergic neurons having an inhibitory function in the thalamus, the centromedian complex and the pedunculopontine complex. Anatomy The efferent bundle is constituted first of the ansa and lenticular fasciculus, then crosses the internal capsule within and in parallel to the Edinger's comb system then arrives at the laterosuperior corner of the subthalamic nucleus and constitutes the field H2 of Forel, then H, and sudd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus Accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for ' nucleus adjacent to the septum') is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum, which is the main component of the basal ganglia. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. Each cerebral hemisphere has its own nucleus accumbens, which can be divided into two structures: the nucleus accumbens core and the nucleus accumbens shell. These substructures have different morphology and functions. Different NAcc subregions (core vs shell) and neuron subpopulations within each region ( D1-type vs D2-type medium spiny neurons) are responsible fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. It forms the Basal (anatomy), basal part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is about the size of an Almond#Nut, almond. The hypothalamus has the function of regulating certain metabolic biological process, processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It biosynthesis, synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls thermoregulation, body temperature, hunger (physiology), hunger, important aspects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagonal Band Of Broca
The diagonal band of Broca interconnects the amygdala and the septal area. It is one of the olfactory structures. It is situated upon the inferior aspect of the brain. It forms the medial margin of the anterior perforated substance. It was described by the French neuroanatomist Paul Broca. Structure It consists of fibers that are said to arise in the parolfactory area, the gyrus subcallosus and the anterior perforated substance, and course backward in the longitudinal striae to the dentate gyrus and the hippocampal region. This is a cholinergic bundle of nerve fibers posterior to the anterior perforated substance. It interconnects the subcallosal gyrus in the septal area with the hippocampus and lateral olfactory area. Nuclei Two structures are often described in this brain regions, namely the nuclei of the vertical and horizontal limbs of the diagonal band of Broca (nvlDBB and nhlDBB, respectively). nvlDBB projects to the hippocampal formation through the fornix and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |