|
HSN2
Hereditary sensory neuropathy, type II also known as HSN2 is a region of a parent protein which in humans in encoded by the ''WNK1'' gene. It is a transcript variant of the WNK1 gene that is selectively expressed in nervous system tissues, and during development. Mutations in this exon of the ''WNK1'' gene have been identified as causative in genetic neuropathy syndromes, and in inherited pain insensitivity. Function The HSN2-containing ''WNK1'' isoforms are expressed in the sensory transducing neurons of the peripheral nervous system, as well as in the central nervous system. The sensory afferent neurons expressing the HSN2 splice variant of ''WNK1'' are associated with the transmission of sensory and nociceptive signals. The novel protein product of the isoform is more plentiful in sensory neurons than motor neurons. It is proposed that this gene product may play a role in the development and/or maintenance of peripheral sensory neurons or their supporting Schwann cells. Clinica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Sensory Neuropathy
Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy (HSAN) or hereditary sensory neuropathy (HSN) is a condition used to describe any of the types of this disease which inhibit sensation. They are less common than Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Classification Eight different clinical entities have been described under hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies – all characterized by progressive loss of function that predominantly affects the peripheral sensory nerves. Their incidence has been estimated to be about 1 in 250,000. Type 1 Hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1 is a condition characterized by nerve abnormalities in the legs and feet (peripheral neuropathy). Many people with this condition have tingling, weakness, and a reduced ability to feel pain and sense hot and cold. Some affected individuals do not lose sensation, but instead feel shooting pains in their legs and feet. As the disorder progresses, the sensory abnormalities can affect the hands, arms, shoulders, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
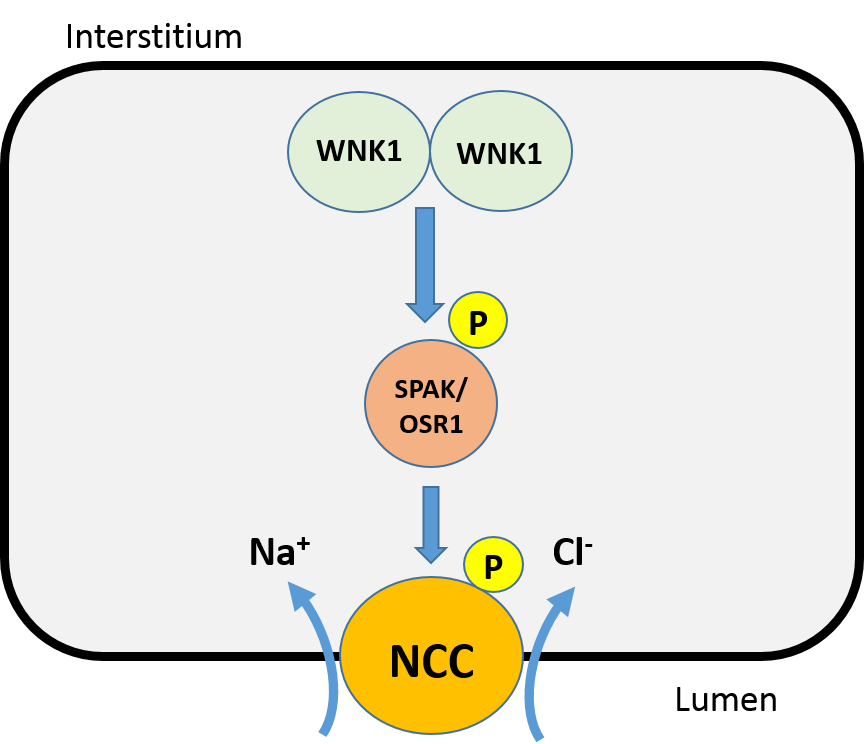
WNK1
WNK (lysine deficient protein kinase 1), also known as WNK1, is an enzyme that is encoded by the ''WNK1'' gene. WNK1 is serine-threonine protein kinase and part of the "with no lysine/K" kinase WNK family. The predominant role of WNK1 is the regulation of cation-Cl− cotransporters (CCCs) such as the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC), basolateral Na-K-Cl symporter ( NKCC1), and potassium chloride cotransporter (KCC1) located within the kidney. CCCs mediate ion homeostasis and modulate blood pressure by transporting ions in and out of the cell. ''WNK1'' mutations as a result have been implicated in blood pressure disorders/diseases; a prime example being familial hyperkalemic hypertension (FHHt). Structure The WNK1 protein is composed of 2382 amino acids (molecular weight 230 kDa). The protein contains a kinase domain located within its short N-terminaldomain and a long C-terminal tail. The kinase domain has some similarity to the MEKK protein kinase family. As a member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Shopping
Home shopping is the electronic retailing and home shopping channels industry, which includes such billion dollar television-based and e-commerce companies as Shop LC, HSN, Gemporia, TJC, QVC, eBay, ShopHQ, Buy.com and Amazon.com, as well as traditional mail order and brick and mortar retailers as Hammacher Schlemmer and Sears, Roebuck and Co. Home shopping allows consumers to shop for goods from the privacy of their own home, as opposed to traditional shopping, which requires one to visit brick and mortar stores and shopping malls. There are three main types of home shopping: mail or telephone ordering from catalogs; telephone ordering in response to advertisements in print and electronic media (such as periodicals, TV and radio); and online shopping. The study shows that home shopping are continuously preferred by the customers especially for those teleworkers and busy working class. History The possibility for merchants to show their goods through the world was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins. The peripheral nervous system can be divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, the cranial nerves are part of the PNS with the exception of the optic nerve (cranial nerve II), along with the retina. The second cranial nerve is not a true peripheral nerve but a tract of the diencephalon. Cranial nerve ganglia, as with all ganglia, are part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nociception
Nociception (also nocioception, from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal in order to trigger an appropriate defense response. In nociception, intense chemical (e.g., capsaicin present in Chili pepper or Cayenne pepper), mechanical (e.g., cutting, crushing), or thermal (heat and cold) stimulation of sensory neurons called nociceptors produces a signal that travels along a chain of nerve fibers via the spinal cord to the brain. Nociception triggers a variety of physiological and behavioral responses to protect the organism against an aggression and usually results in a subjective experience, or perception, of pain in sentient beings. Detection of noxious stimuli Potentially damaging mechanical, thermal, and chemical stimuli are det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. There are two types of motor neuron – upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons. Axons from upper motor neurons synapse onto interneurons in the spinal cord and occasionally directly onto lower motor neurons. The axons from the lower motor neurons are efferent nerve fibers that carry signals from the spinal cord to the effectors. Types of lower motor neurons are alpha motor neurons, beta motor neurons, and gamma motor neurons. A single motor neuron may innervate many muscle fibres and a muscle fibre can undergo many action potentials in the time taken for a single muscle twitch. Innervation takes place at a neuromuscular junction and twitches can become superimposed as a resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |