|
HProduct
hProduct is a microformat for publishing details of products, on web pages, using (X)HTML classes and ''rel'' attributes. On 12 May 2009, Google Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ... announced that they would be parsing the hProduct, hCard and hReview microformats, and using them to populate search result pages. References External links hProductat the Microformats Wiki Microformats {{Compu-prog-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microformat
Microformats (μF) are predefined HTML markup (like HTML classes) created to serve as descriptive and consistent metadata about elements, designating them as representing a certain type of data (such as contact information, geographic coordinates, events, products, recipes, etc.). They allow software to process the information reliably by having set classes refer to a specific type of data rather than being arbitrary. Microformats emerged around 2005 and were predominantly designed for use by search engines, web syndication and aggregators such as RSS. Google confirmed in 2020 that it still parses microformats for use in content indexing. Microformats are referenced in several W3C social web specifications, including IndieAuth and Webmention. Although the content of web pages has been capable of some "automated processing" since the inception of the web, such processing is difficult because the markup elements used to display information on the web do not describe what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HCard
hCard is a microformat for publishing the contact details (which might be no more than the name) of people, companies, organizations, and places, in HTML, Atom, RSS, or arbitrary XML. The hCard microformat does this using a 1:1 representation of vCard (RFC 2426) properties and values, identified using HTML classes and ''rel'' attributes. It allows parsing tools (for example other websites, or Firefox's Operator extension) to extract the details, and display them, using some other websites or mapping tools, index or search them, or to load them into an address-book program. In May 2009, Google announced that they would be parsing the hCard and hReview and hProduct microformats, and using them to populate search-result pages. In September 2010 Google announced their intention to surface hCard, hReview information in their local search results. In February 2011, Facebook began using hCard to mark up event venues. Example Consider the HTML: Joseph Doe Joe The Examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HReview
hReview is a microformat for publishing reviews of books, music, films, restaurants, businesses, holidays, etc.Microformats: Empowering Your Markup for Web 2.0 (2007) by John Allsopp p. 200 using (X)HTML on web pages, using HTML classes and ''rel'' attributes. On the 12th of May 2009, Google announced that they would be parsing the hReview, hCard hCard is a microformat for publishing the contact details (which might be no more than the name) of people, companies, organizations, and places, in HTML, Atom, RSS, or arbitrary XML. The hCard microformat does this using a 1:1 representation of v ... and hProduct microformats, and using them to populate search result pages. References External links hReviewat thMicroformats Wiki Microformats {{Compu-prog-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
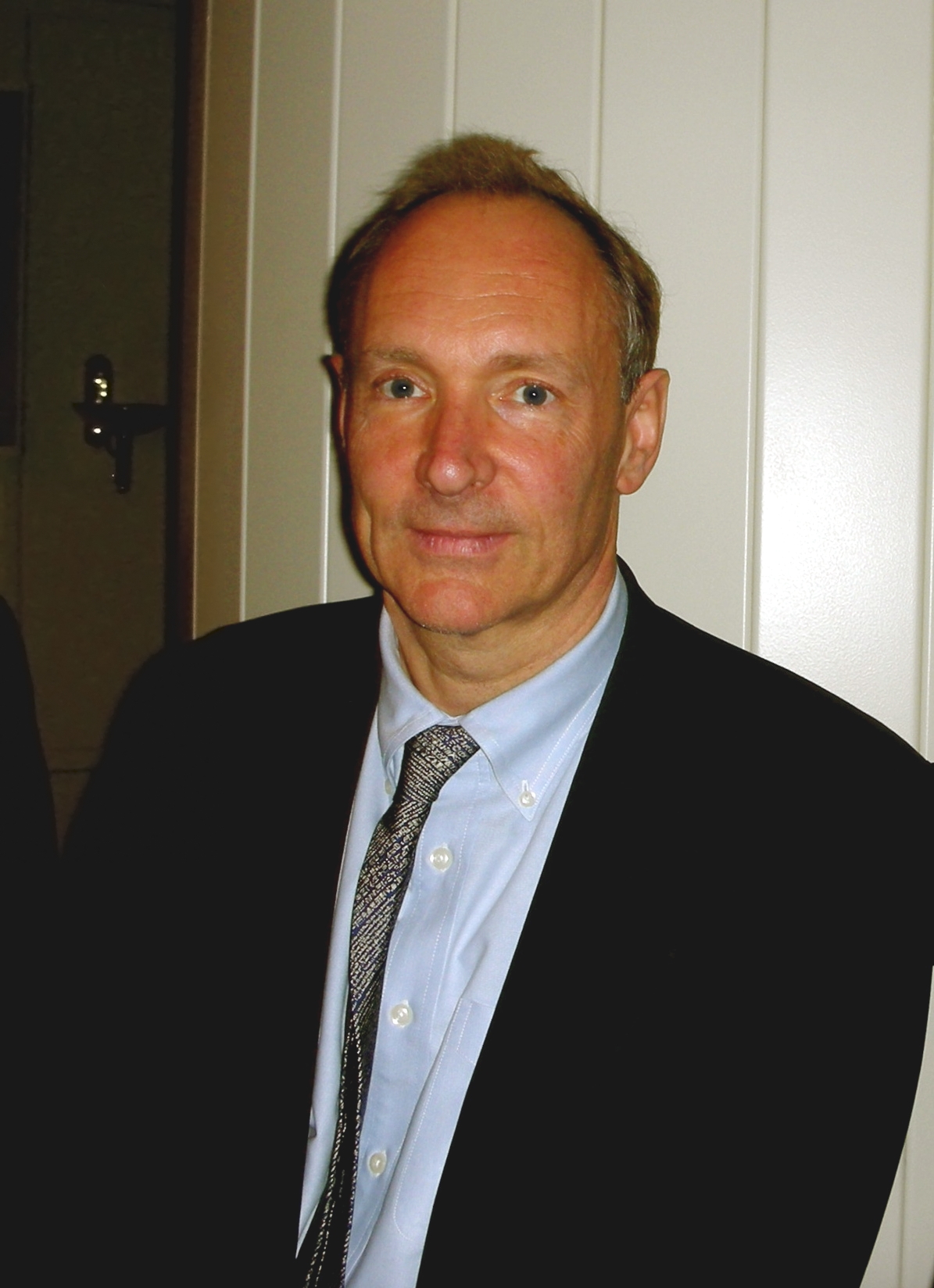
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the HTTP, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). The Web was invented by English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee while at CERN in 1989 and opened to the public in 1993. It was conceived as a "universal linked information system". Documents and other media content are made available to the network through web servers and can be accessed by programs such as web browsers. Servers and resources on the World Wide Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locators (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript, a programming language. Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and browser engine, render the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page Semantic Web, semantically and originally included cues for its appearance. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages. With HTML constructs, HTML element#Images and objects, images and other objects such as Fieldset, interactive forms may be embedded into the rendered page. HTML provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, Hyperlink, links, quotes, and other items. HTML elements are delineated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rel Attribute
A link relation is a descriptive attribute attached to a hyperlink in order to define the type of the link, or the relationship between the source and destination resources. The attribute can be used by automated systems, or can be presented to a user in a different way. In HTML these are designated with the attribute on , , or elements. Example uses include the standard way of referencing CSS, , which indicates that the external resource linked to with the attribute is a stylesheet, so a web browser will generally fetch this file to render the page. Another example is for the popular favicon icon. Link relations are used in some microformats (e.g. for tagging), in XHTML Friends Network (XFN), and in the Atom standard, in XLink, as well as in HTML. Standardized link relations are one of the foundations of HATEOAS as they allow the user agent to understand the meaning of the available state transitions in a Representational State Transfer system. The Internet Engineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Search
Google Search (also known simply as Google or Google.com) is a search engine operated by Google. It allows users to search for information on the World Wide Web, Web by entering keywords or phrases. Google Search uses algorithms to analyze and rank websites based on their relevance to the search query. It is the most popular search engine worldwide. Google Search is the List of most-visited websites, most-visited website in the world. As of 2025, Google Search has a 90% share of the global search engine market. Approximately 24.84% of Google's monthly global traffic comes from the United States, 5.51% from India, 4.7% from Brazil, 3.78% from the United Kingdom and 5.28% from Japan according to data provided by Similarweb. The order of search results returned by Google is based, in part, on a priority rank system called "PageRank". Google Search also provides many different options for customized searches, using symbols to include, exclude, specify or require certain search be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |