|
HMS Windsor Castle (1790)
HMS ''Windsor Castle'' was a 98-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 3 May 1790 at Deptford Dockyard. Dardanelles ''Windsor Castle'' was part of Robert Calder's fleet at the Battle of Cape Finisterre in 1805. She shared in the prize and head money for ''San Rafael'' and ''Firme'' captured on that day. On 25 September a French squadron of five frigates and two corvettes under Commodore Eleonore-Jean-Nicolas Soleil was escorting a convoy ferrying supplies and troops to the French West Indies. A British squadron intercepted the convoy, which led to the action of 25 September 1806, where the British captured four of the frigates: ''Armeide'', ''Minerva'', ''Indefatigable'', and ''Gloire''. The frigate and the corvette escaped, with managing to outrun ''Windsor Castle''. While in the Mediterranean she served during Vice Admiral Sir John Duckworth's unsuccessful 1807 Dardanelles Operation.Howard, pp.15-20. On 19 February, ''Windsor Castle'' s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of England (which included Wales) and Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems – English law and Scots law – remained in use. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the 1603 "Union of the Crowns" when James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland. Since James's reign, who had been the first to refer to himself as "king of Great Britain", a political union between the two mainland British kingdoms had been repeatedly attempted and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French West Indies
The French West Indies or French Antilles (french: Antilles françaises, ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Antiy fwansez) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean: * The two overseas departments of: ** Guadeloupe, including the islands of Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Les Saintes, Marie-Galante, and La Désirade. ** Martinique * The two overseas collectivities of: ** Saint Martin, the northern half of the island with the same name, the southern half is Sint Maarten, a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. ** Saint Barthélemy History Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc was a French trader and adventurer in the Caribbean, who established the first permanent French colony, Saint-Pierre, on the island of Martinique in 1635. Belain sailed to the Caribbean in 1625, hoping to establish a French settlement on the island of St. Christopher (St. Kitts). In 1626 he returned to France, where he won the support of Cardinal Richelieu to establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Of The Line Of The Royal Navy
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria Expedition Of 1807
The Alexandria expedition of 1807, also known as the Fraser expedition, ( ar, حملة فريزر) was a failed attempt by the British to capture the Egyptian city of Alexandria during the Anglo-Turkish War in order to secure a base of operations against the Ottoman Empire and the French Empire in the Mediterranean Sea. It was a part of a larger strategy against the Ottoman-French alliance of the Ottoman Sultan Selim III. Though Alexandria was briefly captured and occupied, attempts to proceed inland were rebuffed, with British forces being twice defeated in battles at Rosetta (Rashid, the port that guarded the entrance to the Nile), at a cost of over 900 officers and men killed, and many captured at the second siege of Rosetta alone. Captured British soldiers were marched to Cairo, and were marched there between rows of stakes whereon were displayed many hundreds of the severed heads of their slain comrades. British captives were then condemned to hard-labour or were sold into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
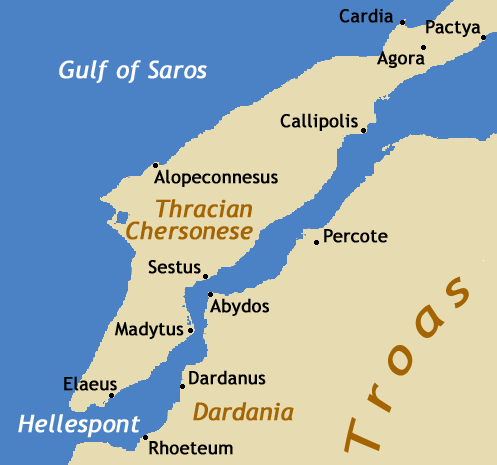
Abydos (Hellespont)
Abydos ( grc, Ἄβυδος, la, Abydus) was an ancient city and bishopric in Mysia. It was located at the Nara Burnu promontory on the Asian coast of the Hellespont (the straits of Dardanelles), opposite the ancient city of Sestos, and near the city of Çanakkale in Turkey. Abydos was founded in c. 670 BC at the most narrow point in the straits, and thus was one of the main crossing points between Europe and Asia, until its replacement by the crossing between Lampsacus and Kallipolis in the 13th century, and the abandonment of Abydos in the early 14th century. In Greek mythology, Abydos is presented in the myth of Hero and Leander as the home of Leander. The city is also mentioned in ''Rodanthe and Dosikles'', a novel written by Theodore Prodromos, a 12th-century writer, in which Dosikles kidnaps Rodanthe at Abydos. Archaeology In 1675, the site of Abydos was first identified, and was subsequently visited by numerous classicists and travellers, such as Robert Wood, Richa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Marine
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marines can trace their origins back to the formation of the "Duke of York and Albany's maritime regiment of Foot" on 28 October 1664, and can trace their commando origins to the formation of the 3rd Special Service Brigade, now known as 3 Commando Brigade on 14 February 1942, during the Second World War. As a specialised and adaptable light infantry and commando force, Royal Marine Commandos are trained for rapid deployment worldwide and capable of dealing with a wide range of threats. The Corps of Royal Marines is organised into 3 Commando Brigade and a number of separate units, including 47 Commando (Raiding Group) Royal Marines, and a company-strength commitment to the Special Forces Support Group. The Corps operates in all environments an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Pesquies
Nara Burnu (Turkish "Cape Nara"), formerly Nağara Burnu, in English Nagara Point, and in older sources Point Pesquies, is a headland on the Anatolian side of the Dardanelles Straits, north of Çanakkale. It is the narrowest and, with , the deepest, section of the Dardanelles Strait. As a result, it is also the point where the surface current from the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea is the strongest, with 1.5 to 2 times the normal rate, occasionally reaching the speed of per hour. The undercurrent is per hour, flowing in the opposite direction.Oceanography of the Turkish Straits - Volume 2, Issue 1 - Page 2-9, 1988. "The first two stations cover the northeastern part of the Strait from its Marmara end (Gelibolu-Çardak section) to the vicinity of the Nara Burnu where the channel is constricted and bends sharply. The profiles of the hydrographic properties are ..." The ancient and medieval city of Abydos is located at the Nara promontory. Due to the narrowness of the straits at this po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir John Duckworth, 1st Baronet
Sir John Thomas Duckworth, 1st Baronet, GCB (9 February 174831 August 1817) was an officer of the Royal Navy, serving during the Seven Years' War, the American War of Independence, the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic wars, as the Governor of Newfoundland during the War of 1812, and a member of the British House of Commons during his semi-retirement. Duckworth, a vicar's son, achieved much in a naval career that began at the age of 11. Serving with most of the great names of the Royal Navy during the later 18th and early 19th centuries, he fought almost all of Britain's enemies on the seas at one time or another, including a Dardanelles operation that would be remembered a century later during the First World War. He was in command at the Battle of San Domingo, the last great fleet action of the Napoleonic Wars. Early life Born in Leatherhead, Surrey, England, Duckworth was one of five sons of Sarah Johnson and the vicar Henry Duckworth A.M. of Stoke Poges, County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Of 25 September 1806
The action of 25 September 1806 was a naval battle fought during the Napoleonic Wars off the French Biscay port of Rochefort. A French squadron comprising five frigates and two corvettes, sailing to the French West Indies with supplies and reinforcements, was intercepted by a British squadron of six ships of the line that was keeping a close blockade of the port as part of the Atlantic campaign of 1806. The British ships, under the command of Commodore Sir Samuel Hood, spotted the French convoy early in the morning of 25 September, just a few hours after the French had left port, and immediately gave chase. Although the French ships tried to escape, they were heavily laden with troops and stores, and the strong winds favoured the larger ships of the line, which caught the French convoy after a five-hour pursuit, although they had become separated from one another during the chase. At 05:00 the leading British ship, HMS ''Monarch'', was within range and opened fire on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)