|
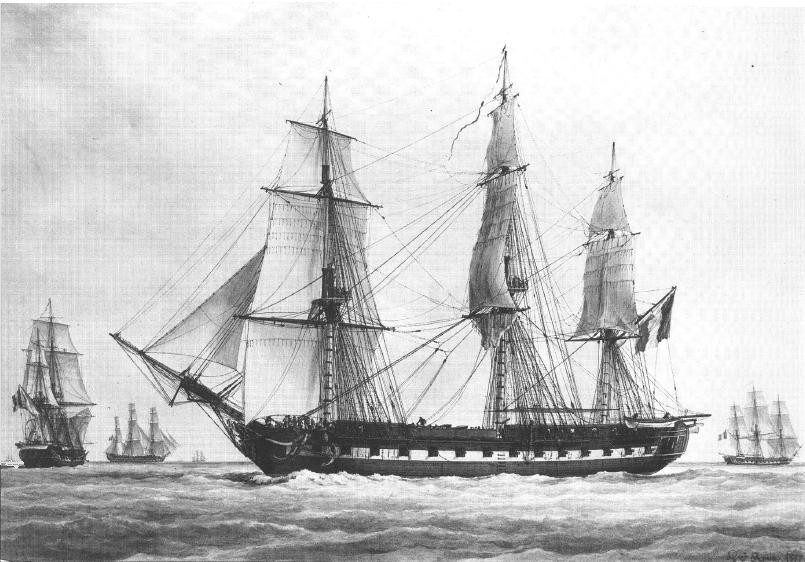
HMS Tweed (1823)
HMS ''Tweed'' may refer to any one of several Royal Navy ships named for the River Tweed, including: * *HMS ''Tweed'' was an ordered and laid down in 1795, but was renamed on 30 October 1795 before her launch in 1796. *, a ship-sloop wrecked in 1813. *, a 28-gun sixth-rate frigate built in 1823 at Portsmouth and sold in 1852. *, a torpedo gunboat In the late 19th century, torpedo gunboats were a form of gunboat armed with torpedoes and designed for hunting and destroying smaller torpedo boats. By the end of the 1890s torpedo gunboats were superseded by their more successful contemporaries, .... *, of 1,460 tons displacement launched about 1943 and sunk on 7 January 1944 during the Second World War. {{DEFAULTSORT:Tweed, Hms Royal Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early Middle Ages, medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the English Navy of the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the early 18th century until the World War II, Second World War, it was the world's most powerful navy. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Tweed
The River Tweed, or Tweed Water, is a river long that flows east across the Border region in Scotland and northern England. Tweed cloth derives its name from its association with the River Tweed. The Tweed is one of the great salmon rivers of Britain and the only river in England where an Environment Agency rod licence is not required for angling. The river generates a large income for the local borders region, attracting anglers from all around the world. Etymology ''Tweed'' may represent an Old Brittonic name meaning "border". A doubtful proposal is that the name is derived from a non-Celtic form of the Indo-European root ''*teuha-'' meaning "swell, grow powerful". Course The River Tweed flows primarily through the scenic Borders region of Scotland. Eastwards from the settlements on opposing banks of Birgham and Carham it forms the historic boundary between Scotland and England. It rises in the Lowther Hills at Tweed's Well near the rising points of the Clyde -- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship-sloop
During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all unrated warships, including gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fire ships were classed by the Royal Navy as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the role of a sloop-of-war when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of the First World War and the highly successful of the Second World War, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capabilities. They performed similar duties to the destroyer escorts of the United States Navy, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a sixth-rate was the designation for small warships mounting between 20 and 28 carriage-mounted guns on a single deck, sometimes with smaller guns on the upper works and sometimes without. It thus encompassed ships with up to 30 guns in all. In the first half of the 18th century the main battery guns were 6-pounders, but by mid-century these were supplanted by 9-pounders. 28-gun sixth-rates were classed as frigates, those smaller as 'post ships', indicating that they were still commanded by a full ('post') captain, as opposed to sloops of 18 guns and less, which were under commanders. Rating Sixth-rate ships typically had a crew of about 150–240 men, and measured between 450 and 550 tons. A 28-gun ship would have about 19 officers; commissioned officers would include the captain, and two lieutenants; warrant officers would include the master, ship's surgeon, and purser. The other quarterdeck off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailing Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Gunboat
In the late 19th century, torpedo gunboats were a form of gunboat armed with torpedoes and designed for hunting and destroying smaller torpedo boats. By the end of the 1890s torpedo gunboats were superseded by their more successful contemporaries, the torpedo boat destroyers. History A number of torpedo gunboats, the prototype ''Rattlesnake'' of 1886 followed by the ''Grasshopper'' class (of 3 vessels), the ''Sharpshooter'' class (13 vessels), the ''Alarm'' class (11 vessels) and the ''Dryad'' class (5 vessels), were built for the Royal Navy during the 1880s and the 1890s; similar vessels were also constructed or otherwise acquired by a number of European nations and Japan. Essentially very small cruisers, torpedo gunboats were typically fitted with locomotive boilers and were equipped with torpedo tubes and an adequate gun armament, intended for hunting down smaller enemy torpedo boats. In practice they failed in their primary objective, as they were not fast enough to k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |