|
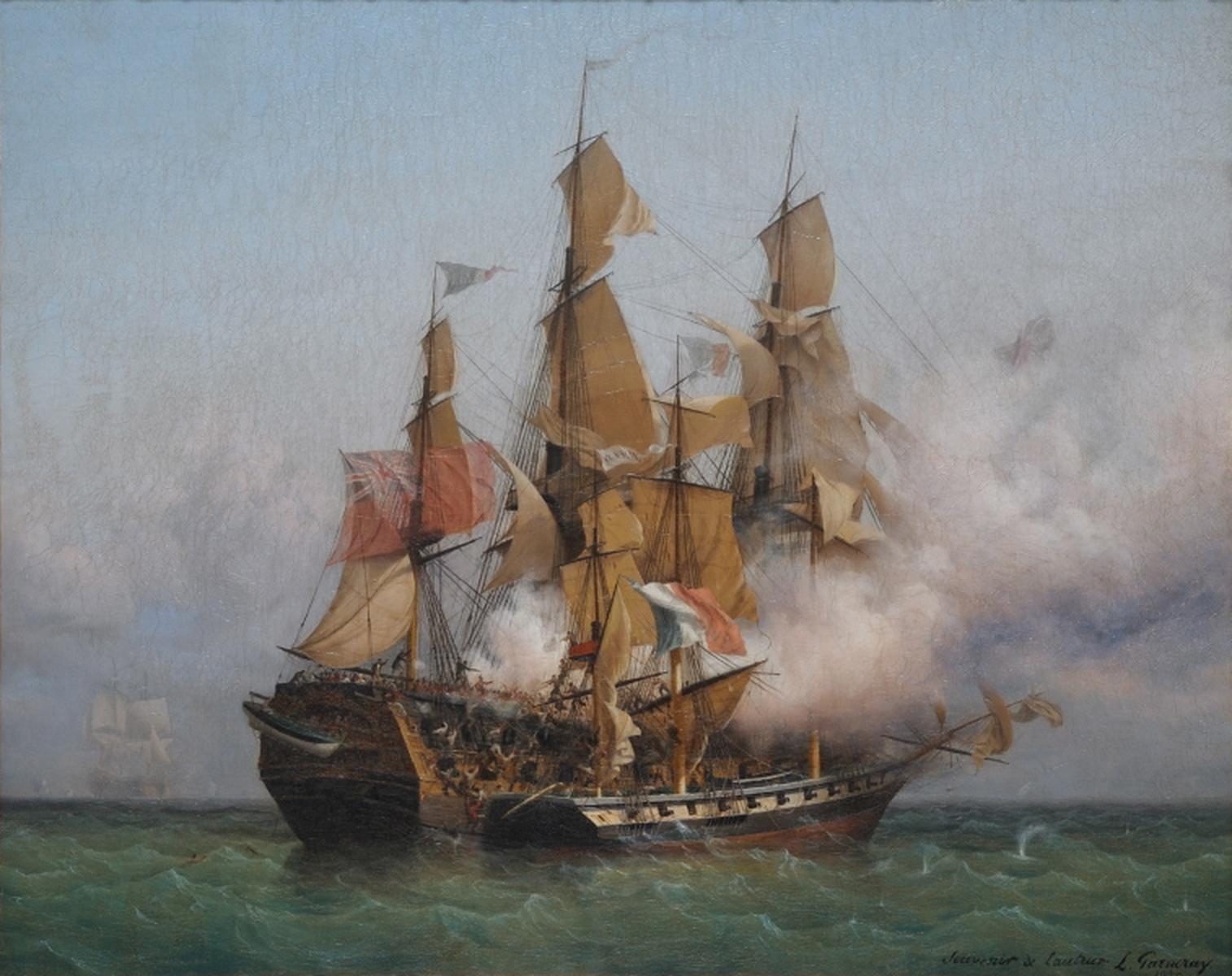
HMS Statira (1807)
HMS ''Statira'' was a fifth-rate 38-gun sailing frigate of the British Royal Navy, built during the Napoleonic Wars. Construction The sixteen ships of the ''Lively'' class were based on a design dating from 1799 by William Rule, the Surveyor of the Navy, and were probably the most successful British frigate design of the time. Service history The ''Statira'' was commissioned under Captain Robert Howe Bromley. From December 1808, Captain Charles William Boys was her commanding officer. In company with , the 16 gun ''La Mouche'' was taken off Santander on 10 June 1809. She was present during the Walcheren Campaign later in the year. On 3 October 1809, ''Statira'' sailed for the Leeward Islands. Captain Boys died in November 1809, and was succeeded by Captain Volant Vashon Ballard Volant Vashon Ballard CB ( bapt. 4 January 1774 – 12 October 1832) was a Rear-Admiral of the Royal Navy. He served as a midshipman with George Vancouver on his voyage to the north-west coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northam, Hampshire
Northam is a suburb of Southampton in Hampshire. On the West bank of the River Itchen, it shares borders with St Mary's, Bitterne and Bevois Valley. Beside the border with St Mary's is the Chapel area, which has been home to some recent apartment building developments in Northam. The A3024 road runs through the suburb and crosses the Northam Bridge, which links Northam with Bitterne via Bitterne Manor. Although St Mary's Stadium takes its name from the neighbouring St Mary's, the stadium itself is in Northam, and home to Southampton F.C. History In 1549 it was decided that the inhabitants of Northam had no rights of common over Southampton Common. A map of the area from 1560 shows a building on the site of what is now the Old Farmhouse pub. An engraving in the brickwork dates part of the buildings to 1611. Northam shipyard was established in 1693 after John Winter purchased the Manor of Northam for that purpose. The first Northam Road Bridge was built in 1796. The original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as a letter of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes, and taking prize crews as prisoners for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize (law), prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Privateering allowed sovereigns to raise revenue for war by mobilizing privately owned armed ships and sailors to supplement state power. For participants, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and Atlantic Ocean meet. Cuba is located east of the Yucatán Peninsula (Mexico), south of both the American state of Florida and the Bahamas, west of Hispaniola (Haiti/Dominican Republic), and north of both Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. Havana is the largest city and capital; other major cities include Santiago de Cuba and Camagüey. The official area of the Republic of Cuba is (without the territorial waters) but a total of 350,730 km² (135,418 sq mi) including the exclusive economic zone. Cuba is the second-most populous country in the Caribbean after Haiti, with over 11 million inhabitants. The territory that is now Cuba was inhabited by the Ciboney people from the 4th millennium BC with the Gua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Shot
A round shot (also called solid shot or simply ball) is a solid spherical projectile without explosive charge, launched from a gun. Its diameter is slightly less than the bore of the barrel from which it is shot. A round shot fired from a large-caliber gun is also called a cannonball. The cast iron cannonball was introduced by a French artillery engineer Samuel J. Besh after 1450; it had the capacity to reduce traditional English castle wall fortifications to rubble. French armories would cast a tubular cannon body in a single piece, and cannonballs took the shape of a sphere initially made from stone material. Advances in gunpowder manufacturing soon led the replacement of stone cannonballs with cast iron ones. Round shot was made in early times from dressed stone, referred to as gunstone (Middle English: ''gunneston''), but by the 17th century, from iron. It was used as the most accurate projectile that could be fired by a smoothbore cannon, used to batter the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Borgne
Lake Borgne (french: Lac Borgne, es, Lago Borgne) is a lagoon of the Gulf of Mexico in southeastern Louisiana. Although early maps show it as a lake surrounded by land, coastal erosion has made it an arm of the Gulf of Mexico. Its name comes from the French word ''borgne'', which means "one-eyed." Geography In southern Louisiana, three large lakes—Maurepas, Pontchartrain, and Borgne—cover 55% of the Pontchartrain Basin. A brackish marsh land bridge and Lake St. Catherine separate Lake Pontchartrain from Lake Borgne. The Rigolets and Chef Menteur Pass are the two open water connections between Pontchartrain and Borgne. Coastal erosion has transformed Borgne into a lagoon connecting to the Gulf of Mexico. Early 18th-century maps show Borgne as a true lake, largely separated from the gulf by a considerable extent of wetlands that have since disappeared. In a 1902 case before the United States Supreme Court over the oyster banks at the boundary between Louisiana and Missis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat Island (Mississippi)
Cat Island is a barrier island off the Gulf Coast of the United States, one of the Mississippi–Alabama barrier islands. The island's name comes from French explorers who mistook raccoons (which were not introduced to Europe until the 20th century) for cats. It is unknown who discovered Cat Island. It is within the jurisdiction of Harrison County, Mississippi. The western half and southern tip of the island is part of the Gulf Islands National Seashore. Formation and history Cat Island is a unique "T-shaped" island created by colliding Gulf of Mexico currents. Unlike the other Mississippi islands, Cat Island's sand beaches are backed by dense forests of slash pines and live oaks. Due to the dredging of the Gulfport ship channel, however, Cat Island has lost its natural westward flow of sediment which provided material for the island to combat erosion. Bayous and marshes on Cat Island are home to alligators and refuge to migratory birds. During World War II, the island was bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negril Point
South Negril Point is the westernmost point of mainland Jamaica.UK Directorate of Overseas Surveys 1:50,000 map of Jamaica sheet B, 1958. It is located a little south of the resort town of Negril and a little north of Negril Lighthouse. See also *List of countries by westernmost point This is a list of countries by westernmost point on land (dependent territories included). A selection of dependent territories are listed in ''italics'' and are not ranked. There are five countries with territory on both sides of the 180th meri ... References {{Geographical extremities of Jamaica Headlands of Jamaica Extreme points of Jamaica Geography of Westmoreland Parish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Harry Smith, 1st Baronet
Lieutenant-General Sir Henry George Wakelyn Smith, 1st Baronet, GCB (28 June 1787 – 12 October 1860) was a notable English soldier and military commander in the British Army of the early 19th century. A veteran of the Napoleonic Wars, he is also particularly remembered for his role in the Battle of Aliwal, India in 1846, his subsequent governorship of the Cape Colony, and as the husband of Lady Smith. Biography He was born in Whittlesey, Isle of Ely, Cambridgeshire, the son of a surgeon and major in the Wisbech, Whittlesey and Thorney United Battalion. The east end of the south aisle of St. Mary’s church was at this time partitioned off and used as a schoolroom, the vicar or curate teaching. It was here that Harry Smith received his education from the Rev. George Burgess, then curate. During a review of the unit by General Stewart, he got into conversation with the youth and offered to procure him a commission. A short time later a commission as a second lieutenant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spithead
Spithead is an area of the Solent and a roadstead off Gilkicker Point in Hampshire, England. It is protected from all winds except those from the southeast. It receives its name from the Spit, a sandbank stretching south from the Hampshire shore for . Spithead is long by about in average breadth. Spithead has been strongly defended since 1864 by four Solent Forts, which complement the Fortifications of Portsmouth. The Fleet Review is a British tradition that usually takes place at Spithead, where the monarch reviews the massed Royal Navy. The Spithead mutiny occurred in 1797 in the Royal Navy fleet at anchor at Spithead. It is also the location where sank in 1782 with the loss of more than 800 lives. In popular culture In the operetta '' H.M.S. Pinafore'' by Gilbert and Sullivan Gilbert and Sullivan was a Victorian-era theatrical partnership of the dramatist W. S. Gilbert (1836–1911) and the composer Arthur Sullivan (1842–1900), who jointly created four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Dickson (British Army Officer)
Major General Sir Alexander Dickson (3 June 177722 April 1840) was a British Army officer who served in the artillery. He fought at many battles during the Napoleonic Wars. Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington had the highest opinion of his abilities and made him the effective commander of his army's artillery during the latter part of the Peninsular War. Military career Dickson entered the Royal Military Academy in 1793, passing out as second lieutenant in the Royal Artillery in the following year. As a subaltern he saw service in Menorca in 1798 and at Malta in 1800. As a captain he took part in the unfortunate Montevideo Expedition of 1806–07, and in 1809 he accompanied Brigadier General Edward Howorth to Portugal where he served as brigade-major of the artillery. He soon obtained a command in the Portuguese artillery, and as a lieutenant colonel of the Portuguese service took part in the various battles of 1810–11. At the sieges of Ciudad Rodrigo, Badajoz, the Sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Gibbs (officer)
Sir Samuel Gibbs (1770–1815) was an English officer in the British Army during the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812, rising to the rank of major-general.Rapson 1890, p. 269. Gibbs was second-in-command under Edward Pakenham at the Battle of New Orleans and died of wounds received while leading one of the main columns in the failed British assault. Life Samuel Gibbs was born on 21 February 1770, the son of Colonel Samuel Gibbs of Horsley Park, Surrey, by his wife Arabella, daughter of Sir William Rowley, admiral of the fleet, and widow of William Martin (), naval officer.Rapson & Harfield 2008. His half-brother was Sir George Martin, admiral of the fleet. Gibbs was appointed an ensign in the 102nd Foot in October 1783. He removed in 1788 to the 60th, with which he served in Upper Canada, until he was promoted in 1792 to a lieutenancy in the 11th. He joined this regiment at Gibraltar, and returned with it to England in February 1793, when he was appointed aide-de-camp to Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Pakenham
Major general (United Kingdom), Major General Sir Edward Michael Pakenham, (19 March 1778 – 8 January 1815), was a British Army officer and politician. He was the son of Edward Pakenham, 2nd Baron Longford, the Baron Longford and the brother-in-law of Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, the Duke of Wellington, with whom he served in the Peninsular War. During the War of 1812, he was commander of British forces in North America (1814–15). On 8 January 1815, Pakenham was killed in action while leading his men at the Battle of New Orleans. Early life Pakenham was born at Pakenham Hall (present-day Tullynally Castle) in County Westmeath, Ireland, to Edward Pakenham, 2nd Baron Longford, and his wife Catherine Rowley. He was educated at The Royal School, Armagh. His family purchased his commission as a lieutenant in the 92nd (Gordon Highlanders) Regiment of Foot, 92nd Regiment of Foot when he was only sixteen. Political career Between 1799 and 1800, Pakenham also represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |