|
HMS Phoenix (1783)
HMS ''Phoenix'' was a 36-gun fifth-rate sailing frigate, frigate of the Royal Navy. The shipbuilder George Parsons (shipbuilder), George Parsons built her at Bursledon and launched her on 15 July 1783. She served in the French Revolutionary Wars, French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars and was instrumental in the events leading up to the battle of Trafalgar. ''Phoenix'' was involved in several single-ship actions, the most notable occurring on 10 August 1805 when she captured the French frigate ''Didon'', which was more heavily armed than her. She was wrecked, without loss of life, off Smyrna in 1816. Active service She was commissioned in October 1787 under Captain John W. Payne, and paid off in December. Recommissioned in October 1788, she sailed for the East Indies in November under Captain George A. Byron. East Indies In the beginning of November 1791, , Commodore William Cornwallis, ''Phoenix'', Captain Sir Sir Richard Strachan, 6th Baronet, Richard Strachan, and , Cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Parsons (shipbuilder)
George Parsons (baptised 21 September 1749 – 16 April 1812) was an English shipbuilder. Biography He was born in Poole, the son of George Parsons. His father moved to Portsmouth to take up a position as a shipwright in the Royal Dockyard in 1740. George junior began as a Quarter Boy entering 18 June 1744. He continued in the Royal Dockyard until, as a 2nd shipwright he was discharged 6 April 1763. His move to Bursledon therefore probably occurred later that year and certainly by 1764. His first employer there was a shipowner, Thomas Cooper, and a few years later, Philemon Ewer, a descendant of the pre-eminent local shipbuilder of the previous generation. He almost certainly moved into his own yard by 1774 at Bursledon Point on the Hamble, though the advertisement in 1776 for "a good burdensome well built Sloop, about 30 tons, just finished" suggested this might have been built in partnership with Ewer. By late 1778 he was ready to build on his own account when a Navy Board lett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassery
Thalassery (), formerly Tellicherry, is a municipality, Commercial City on the Malabar Coast in Kannur district, in the state of Kerala, India, bordered by the districts of Mahé (Pondicherry), Kozhikode, Wayanad, Kasaragod and Kodagu (Karnataka). Thalassery municipality has a population just under 100,000. Thalassery Heritage City has an area of . Thalassery is situated in an altitude ranging from 2.5m to 30m above mean sea-level. Tellicherry municipality was formed on 1 November 1866 according to the Madras Act 10 of 1865 (Amendment of the Improvements in City act 1850) of the British Indian Empire, making it the second oldest municipality in the state. At that time the municipality was known as Tellicherry Commission, and Tellicherry was the capital of North Malabar. G. M. Ballard, the Malabar collector, was the first President of the municipal commission. Later a European barrister, A. F. Lamaral, became the first Chairman of Thalassery municipality. Thalassery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striking The Colours
Striking the colors—meaning lowering the flag (the " colors") that signifies a ship's or garrison's allegiance—is a universally recognized indication of surrender, particularly for ships at sea. For a ship, surrender is dated from the time the ensign is struck. In international law "Colours. A national flag (or a battle ensign). The colours . . . are hauled down as a token of submission." International law absolutely requires a ship of war to fly its ensign at the commencement of any hostile acts, i.e., before firing on the enemy. During battle there is no purpose in striking the colors other than to indicate surrender. It was and is an offense to continue to fight after striking one's colors, and an offense to continue to fire on an enemy after she has struck her colors, unless she indicates by some other action, such as continuing to fire or seeking to escape, that she has not truly surrendered. For this reason, striking the colors is conclusive evidence of a surrende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Of 12 May 1796
The action of 12 May 1796 was a minor naval engagement during the French Revolutionary Wars between a squadron of British Royal Navy frigates and a frigate and four smaller ships of the Batavian Navy. The British squadron had been detached on the previous day from the British North Sea fleet under Admiral Adam Duncan, which was cruising off the Batavian fleet anchorage at the Texel, while the Batavian squadron was returning to the Netherlands from the Norwegian coast where it had been sheltering since suffering defeat at the action of 22 August 1795 the previous year. As the Batavian squadron neared the Batavian coast, the British squadron under Captain Lawrence Halstead attacked. In his frigate HMS ''Phoenix'', Halstead was able to cut the Batavian frigate ''Argo'' off from the shore and bring it to battle, forcing it to surrender in just 20 minutes as other British ships closed with the combat. The remainder of the Batavian squadron had dispersed eastwards away from the frig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
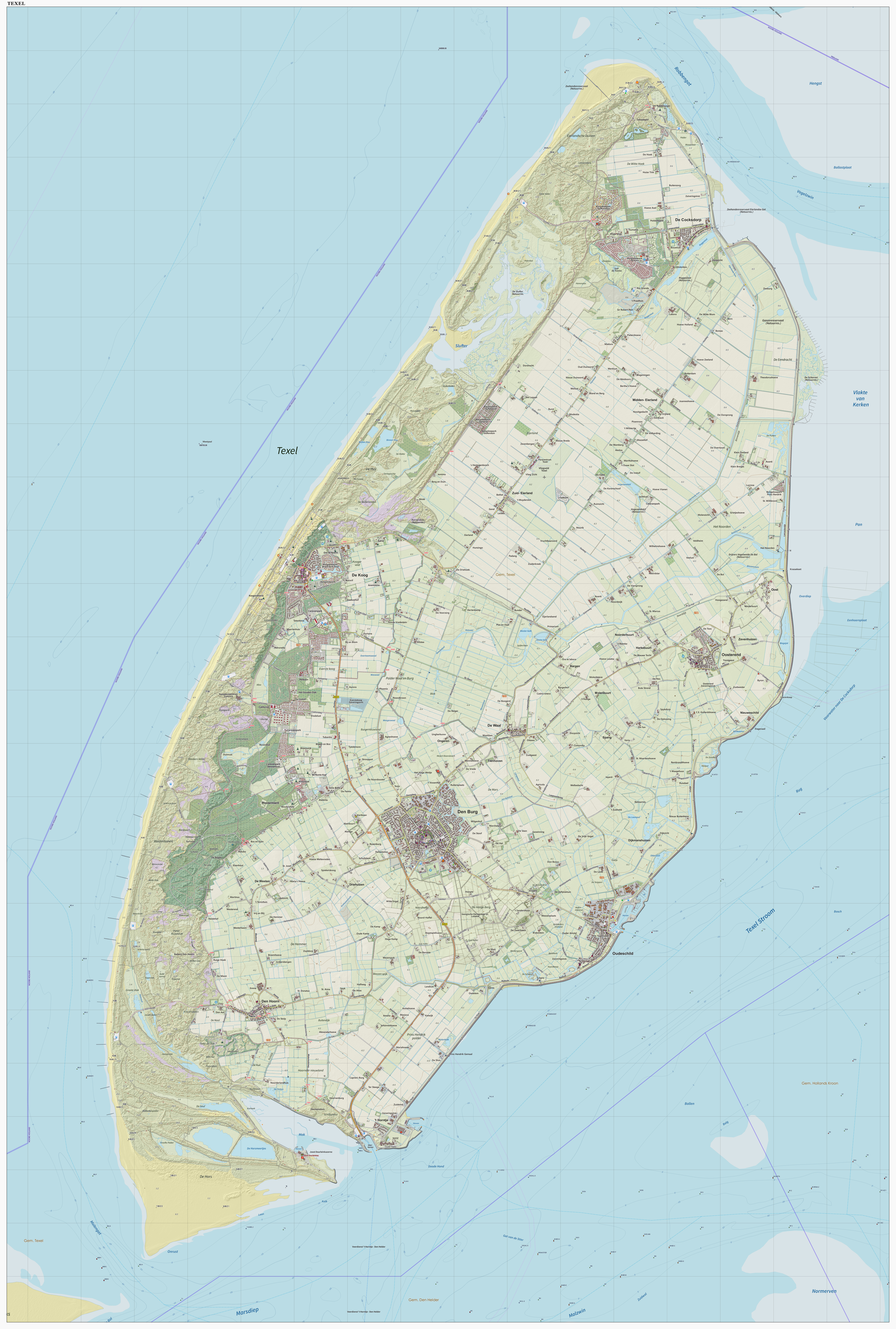
Texel
Texel (; Texels dialect: ) is a municipality and an island with a population of 13,643 in North Holland, Netherlands. It is the largest and most populated island of the West Frisian Islands in the Wadden Sea. The island is situated north of Den Helder, northeast of Noorderhaaks, and southwest of Vlieland. Name The name ''Texel'' is Frisian, but because of historical sound-changes in Dutch, where all -x- sounds have been replaced with -s- sounds (compare for instance English ''fox'', Frisian ''fokse'', German ''Fuchs'' with Dutch ''vos''), the name is typically pronounced ''Tessel'' in Dutch. History The All Saints' Flood (1170) created the islands of Texel and Wieringen from North Holland. In the 13th century Ada, Countess of Holland was held prisoner on Texel by her uncle, William I, Count of Holland. Texel received city rights in 1415. The first Dutch expedition to the Northwest Passage departed from the island on the 5th of June, 1594. Texel was involved i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flekkerøy
Flekkerøy or Flekkerøya is an island and residential district in Kristiansand municipality in Agder county, Norway. The district is located within the borough of Vågsbygd, and it consists of 4 main neighborhoods: Berge/Andås, Kjære, Lindebø/Skålevik, and Mæbø/Høyfjellet. The district covers all of the island of Flekkerøya which lies within the city of Kristiansand. Since 1989, the island (and district) has been connected to the mainland through the Flekkerøy Tunnel, a long subsea road tunnel. The island has 3,632 inhabitants (as of 23 October 2013). Flekkerøy Church is located on the island. History Since the 15th century, Flekkerøy was an important harbour along the Skagerrak, and since 1540 it has been considered as the most important outport in the whole region of Southern Norway. In 1555, the first fortifications were built, but it was torn down in 1561. Anne of Denmark and James VI of Scotland came to Flekkerøy in 1589. In the early 17th century, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brig
A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and were a common type of smaller merchant vessel or warship from then until the latter part of the 19th century. In commercial use, they were gradually replaced by fore-and-aft rigged vessels such as schooners, as owners sought to reduce crew costs by having rigs that could be handled by fewer men. In Royal Navy use, brigs were retained for training use when the battle fleets consisted almost entirely of iron-hulled steamships. Brigs were prominent in the coasting coal trade of British waters. 4,395 voyages to London with coal were recorded in 1795. With an average of eight or nine trips per year for one vessel, that is a fleet of over 500 colliers trading to London alone. Other ports and coastal communities were also be served by colliers trading to Britain's coal ports. In the first half of the 19th century, the vast majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brig-sloop
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' encompassed all the unrated combat vessels, including the very small gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fireships were classed as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the sloop role when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of World War I and the highly successful of World War II, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capability. They performed similar duties to the American destroyer escort class ships, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different from a civilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Duncan, 1st Viscount Duncan
Admiral Adam Duncan, 1st Viscount Duncan, KB (1 July 17314 August 1804) was a British admiral who defeated the Dutch fleet off Camperdown on 11 October 1797. This victory is considered one of the most significant actions in naval history. Life Adam was the second son of Alexander Duncan, Baron of Lundie, Angus, (d. May 1777) Provost of Dundee, and his wife (and first cousin once removed) Helen, daughter of John Haldane of Gleneagles. He was born at Dundee. In 1746, after receiving his education in Dundee, he entered the Royal Navy on board the sloop ''Trial'', under Captain Robert Haldane, with whom, in and afterwards in , he continued until the peace in 1748. In 1749 he was appointed to , then commissioned for service in the Mediterranean, by the Hon. Augustus Keppel (afterwards Viscount Keppel), with whom he was afterwards in on the coast of North America, and was confirmed in the rank of lieutenant on 10 January 1755. Seven Years War In August 1755 he followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Halsted
Admiral Sir Lawrence William Halsted GCB (2 April 1764 – 22 April 1841) was an officer of the Royal Navy who served during the American War of Independence and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Halsted was the son of a naval officer and served with his father during the first years of the war in America. After his father's death he served under Captain Richard Onslow and was present at the engagements with the Comte d'Estaing and the Comte de Grasse in the West Indies and off the coast of North America. He survived various battles and a hurricane in the Atlantic in 1782, and by the end of the wars had risen to lieutenant. He received his first independent commands while serving in the East Indies in the inter-war years, and after spending time as a flag captain during the early years of the French Revolutionary Wars, moved on to command a number of frigates. Halsted went on to achieve particular success aboard , and was rewarded with command of a squa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahé, India
Mahé, also known as Mayyazhi, is a small town in the Mahé district of the Puducherry Union Territory. It is situated at the mouth of the Mahé River and is surrounded by the State of Kerala. The Kannur District surrounds Mahé on three sides and Kozhikode District from one side. Formerly part of French India, Mahé now forms a municipality in Mahé district, one of the four districts of the Union Territory of Puducherry. Mahé has one representative in the Puducherry Legislative Assembly. Etymology The name ''Mahé'' derives from ''Mayyazhi'', the name given to the local river and region in the Malayalam language.The original spelling found on French documents from the early 1720s is ''Mayé'', with ''Mahé'' and ''Mahié'' also found on documents, maps and geographical dictionaries until the early 19th century when the spelling Mahé became the norm. Therefore, the belief that the name of the town was given in honour of Bertrand François Mahé de La Bourdonnais (16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striking The Colours
Striking the colors—meaning lowering the flag (the " colors") that signifies a ship's or garrison's allegiance—is a universally recognized indication of surrender, particularly for ships at sea. For a ship, surrender is dated from the time the ensign is struck. In international law "Colours. A national flag (or a battle ensign). The colours . . . are hauled down as a token of submission." International law absolutely requires a ship of war to fly its ensign at the commencement of any hostile acts, i.e., before firing on the enemy. During battle there is no purpose in striking the colors other than to indicate surrender. It was and is an offense to continue to fight after striking one's colors, and an offense to continue to fire on an enemy after she has struck her colors, unless she indicates by some other action, such as continuing to fire or seeking to escape, that she has not truly surrendered. For this reason, striking the colors is conclusive evidence of a surrende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |