|
HMS Pearl (1708)
HMS ''Pearl'' was a 42-gun fifth-rate of the Royal Navy. Her crew was involved in the hunt and death of Blackbeard in 1718. Early career The ''Pearl'' was launched by Richard Burchett of Rotherhithe on 5 August 1708. She was commissioned in July 1708 under the command of Captain Henry Lawson, who commanded her at first in the Bristol Channel in 1709, moving to the Channel Islands in 1710, and then into the English Channel in 1711. She went on to cruise off the coast of Portugal, where she captured two French privateers, the ''Bizarre'' on 8 September 1711, and the ''Victorieuse'' on 18 September 1711. Captain Caesar Brookes took over command in 1712, serving in the North Sea, before ''Pearl'' was paid off in December that year. She recommissioned in July 1715 under the command of Captain Charles Poole, and served with Admiral George Byng's fleet in the English Channel, and then on the coast of Scotland during the Jacobite rising of 1715. In 1716 she commissioned under Captain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of England (which included Wales) and Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems – English law and Scots law – remained in use. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the 1603 "Union of the Crowns" when James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland. Since James's reign, who had been the first to refer to himself as "king of Great Britain", a political union between the two mainland British kingdoms had been repeatedly attempted and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Byng, 1st Viscount Torrington
Admiral of the Fleet (Royal Navy), Admiral of the Fleet George Byng, 1st Viscount Torrington, (27 January 1663 – 17 January 1733), of Southill Park in Bedfordshire, was a Royal Navy officer and statesman. While still a lieutenant, he delivered a letter from various captains to William III of England, Prince William of Orange, who had just landed at Torbay, assuring the Prince of the captains' support; the Prince gave Byng a response which ultimately led to the Royal Navy switching allegiance to the Prince and the Glorious Revolution of November 1688. As a captain, Byng saw action at the Battle of Vigo Bay, when the French fleet were defeated, during the War of the Spanish Succession. As a flag officer, he led the bombardment squadron while serving under Admiral George Rooke, Sir George Rooke at the Capture of Gibraltar and then took part in the Battle of Málaga (1704), Battle of Málaga at a later stage in the same war. Byng was sent to the Mediterranean to thwart any attemp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1700s Ships
Seventeen or 17 may refer to: *17 (number), the natural number following 16 and preceding 18 * one of the years 17 BC, AD 17, 1917, 2017 Literature Magazines * ''Seventeen'' (American magazine), an American magazine * ''Seventeen'' (Japanese magazine), a Japanese magazine Novels * ''Seventeen'' (Tarkington novel), a 1916 novel by Booth Tarkington *''Seventeen'' (''Sebuntiin''), a 1961 novel by Kenzaburō Ōe * ''Seventeen'' (Serafin novel), a 2004 novel by Shan Serafin Stage and screen Film * ''Seventeen'' (1916 film), an American silent comedy film *'' Number Seventeen'', a 1932 film directed by Alfred Hitchcock * ''Seventeen'' (1940 film), an American comedy film *'' Eric Soya's '17''' (Danish: ''Sytten''), a 1965 Danish comedy film * ''Seventeen'' (1985 film), a documentary film * ''17 Again'' (film), a 2009 film whose working title was ''17'' * ''Seventeen'' (2019 film), a Spanish drama film Television * ''Seventeen'' (TV drama), a 1994 UK dramatic short starring Chri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Of The Royal Navy
''Ships of the Royal Navy'' is a naval history reference work by J. J. Colledge (1908–1997); it provides brief entries on all recorded ships in commission in the Royal Navy from the 15th century, giving location of constructions, date of launch, tonnage, specification and fate. It was published in two volumes by Greenhill Books. Volume 1, first published in 1969, covers major ships; Volume 2, first published in 1970, covers Navy-built naval trawler, trawlers, Naval drifter, drifters, Tugboat, tugs and requisitioned ships including Auxiliary cruiser, Armed Merchant Cruisers. The book is the standard single-volume reference work on ships of the Royal Navy, and Colledge's conventions and spellings of names are used by museums, libraries and archives. For more data on ships of the pre-1863 Royal Navy, see ''British Warships in the Age of Sail''. A revised third version of the Volume 1 work was published in 2003 which added the ships of the late 20th century. The revision was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deptford Dockyard
Deptford Dockyard was an important naval dockyard and base at Deptford on the River Thames, operated by the Royal Navy from the sixteenth to the nineteenth centuries. It built and maintained warships for 350 years, and many significant events and ships have been associated with it. Founded by Henry VIII in 1513, the dockyard was the most significant royal dockyard of the Tudor period and remained one of the principal naval yards for three hundred years. Important new technological and organisational developments were trialled here, and Deptford came to be associated with the great mariners of the time, including Francis Drake and Walter Raleigh. The yard expanded rapidly throughout the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, encompassing a large area and serving for a time as the headquarters of naval administration, and the associated Victualling Yard became the Victualling Board's main depot. Tsar Peter the Great visited the yard officially incognito in 1698 to learn shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wiley & Sons
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company founded in 1807 that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son John (born in Flatbush, New York, October 4, 1808; died in East Orange, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Lyme (1695)
HMS ''Lyme'' was a 32-gun fifth rate built by Mr. Flint of Plymouth Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymout ... in 1694/95. She spent her career on counter piracy patrols and trade protection duties in Home Waters, the Mediterranean and in North America and the West Indies. She was rebuilt to the 1719 Establishment as a sixth rate in 1720/21. Her breaking was completed in January 1739. She was the fourth vessel to bear the name ''Lyme'' since it was used for a 52-gun ship built at Portsmouth in 1654, renamed ''Montagu in May 1660 rebuilt Chatham 1675, rebuilt Woolwich 1698, rebuilt Portsmouth 1716 and broken in September 1749. Construction and Specifications She was ordered on 16 February 1694 to be built under contract by Mr. Flint of Plymouth. She was launched on 20 Apr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
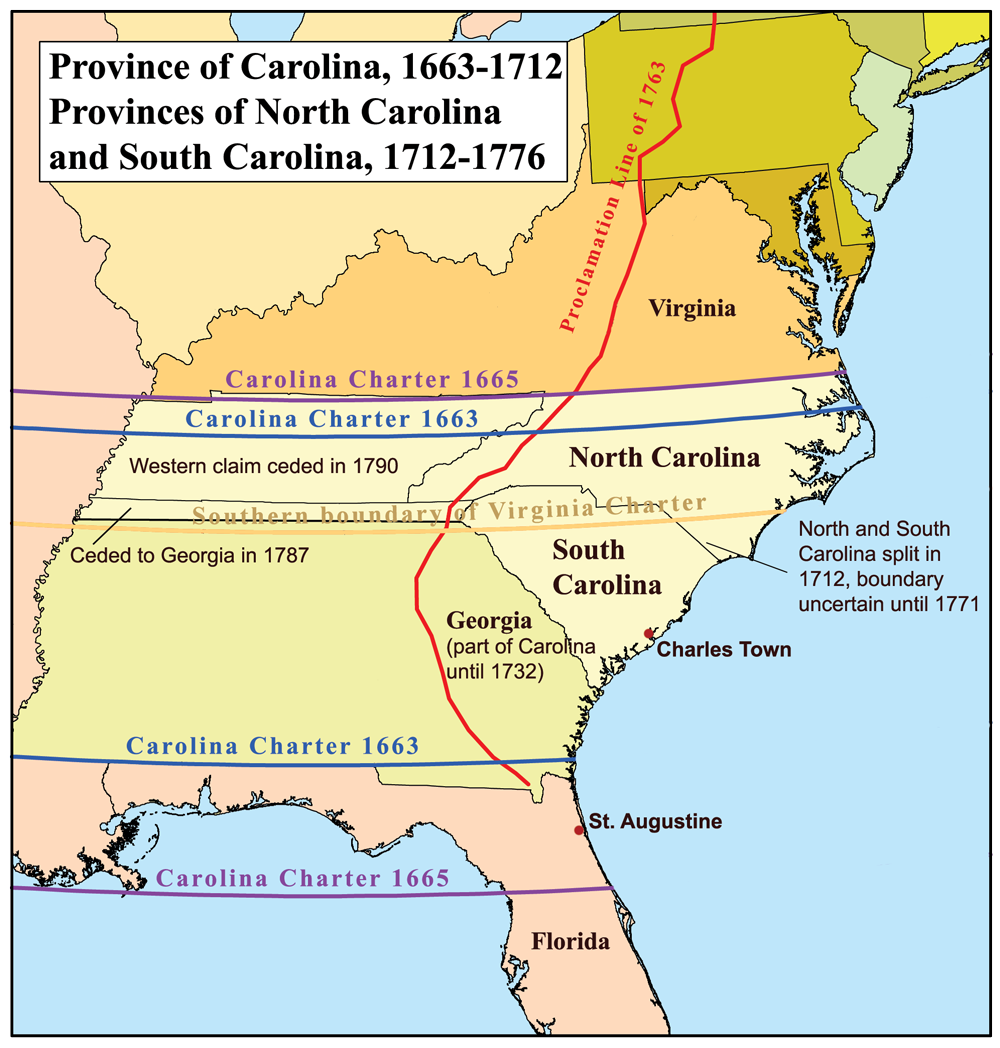
Province Of North Carolina
Province of North Carolina was a province of Great Britain that existed in North America from 1712(p. 80) to 1776. It was one of the five Southern colonies and one of the thirteen American colonies. The monarch of Great Britain was represented by the Governor of North Carolina, until the colonies declared independence on July 4, 1776. Etymology "Carolina" is taken from the Latin word for "Charles" ( Carolus), honoring King Charles II, and was first named in the 1663 Royal Charter granting to Edward, Earl of Clarendon; George, Duke of Albemarle; William, Lord Craven; John, Lord Berkeley; Anthony, Lord Ashley; Sir George Carteret, Sir William Berkeley, and Sir John Colleton the right to settle lands in the present-day U.S. states of North Carolina, Tennessee, South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and Florida. History King Charles II granted the Charter of Carolina in 1663 for land south of the British Colony of Virginia and north of Spanish Fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Spotswood
Alexander Spotswood (12 December 1676 – 7 June 1740) was a British Army officer, explorer and lieutenant governor of Colonial Virginia; he is regarded as one of the most significant historical figures in British North American colonial history. After a brilliant but unsatisfactory military career, in 1710 he was nominated colonial governor of Virginia, a post which he held for twelve years. During that period, Spotswood engaged in the exploration of the territories beyond the western border, of which he was the first to see the economic potentials. In 1716 he organised and led an expedition west of the mountains, known as Knights of the Golden Horseshoe Expedition, with which he established the Crown's dominion over the territory between the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Shenandoah Valley, thus taking a decisive step for the future British expansion to the West. As the governor of Virginia, Spotswood's first preoccupation was to make sea routes safe and fight against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Maynard
Robert Maynard (19 September 1684 – 4 January 1751) was a British lieutenant, and later captain, in the Royal Navy. Little is known about Maynard's early life, other than he was born in England in 1684 and then later joined the English Navy. He was made a lieutenant in January 1707, and by 1709 was the third lieutenant on . In November 1718, Maynard was tasked with hunting down and killing the notorious pirate Blackbeard. While leading , Maynard lured Blackbeard into attacking his ship off the coast of North Carolina, and in the ensuing struggle Maynard and his crew killed Blackbeard. Expecting to be rewarded for his actions, Maynard was never fully compensated or paid for the expedition. He was eventually promoted to commander in 1739, and to captain in 1740, before dying at the age of 66 in his home county of Kent, England. Early life Maynard was born in Dartford, Kent, England on 19 September 1684. Naval commands and battles Governor Alexander Spotswood of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colonial empire, English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (history), ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography'' Online, University of Toronto, May 2, 2005 in 1583 and the colony of Roanoke (further south, in modern eastern North Carolina) by Sir Walter Raleigh in the late 1580s. The founder of the new colony was the Virginia Company, with the first two settlements in Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown on the north bank of the James River and Popham Colony on the Kennebec River in modern-day Maine, both in 1607. The Popham colony quickly failed due to Starving Time, a famine, disease, and conflicts with local Native American tribes in the first two years. Jamestown occupied land belonging to the Powhatan Confederacy, and was also at the brink of failure before the arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A marginal sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two water bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The "Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula. The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea–Baltic Canal and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |