|
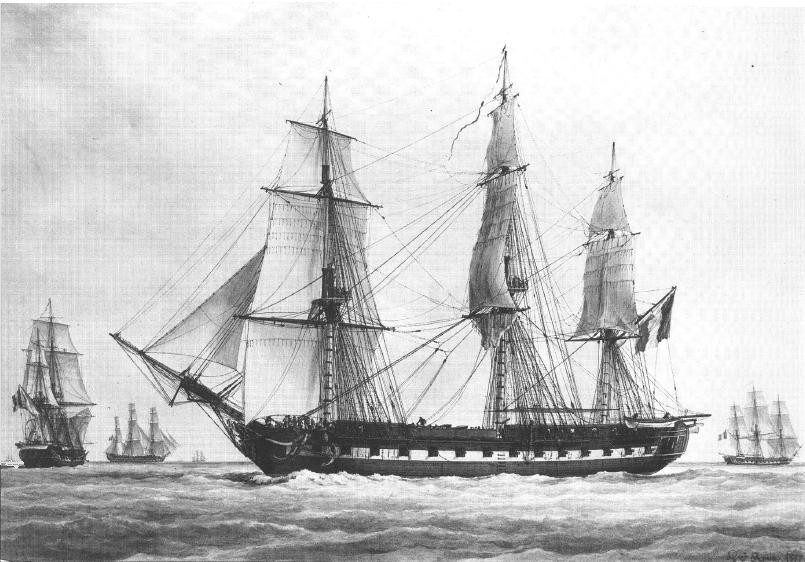
HMS Lowestoffe (1723)
HMS ''Lowestoffe'' was a 32-gun fifth rate built at Chatham Dockyard in 1696/97. She spent her career on counter piracy patrols and trade Protection duties. She participated in the capture of Port Royal in Nova Scotia. She was rebuilt in 1722/24 as a 20-gun sixth rate. She was sold in July 1744. She was the first vessel to bear the name ''Lowestoffe'' or ''Lowestoft'' in the English and Royal Navy. Construction and specifications She was ordered on 24 December 1696 to be built at Chatham Dockyard under the guidance of Master Shipwright Robert Lee. She was launched on 7 August 1697. Her dimensions were a gundeck of with a keel of for tonnage calculation with a breadth of and a depth of hold of . Her builder's measure tonnage was calculated as 356 tons ( burthen).Winfred 2009, Ch 5, The Fifth Rates, Vessels acquired from 16 December 1688, Fifth Rates of 32 and 36 guns, 1694 Programme, Lowestoffe The gun armament initially was four demi-culverinsA demi-culverin was a gun of 3, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of England
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from the late 9th century, when it was unified from various Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, which would later become the United Kingdom. The Kingdom of England was among the most powerful states in Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern period, early modern periods. Beginning in the year 886 Alfred the Great reoccupied London from the Danish Vikings and after this event he declared himself King of the Anglo-Saxons, until his death in 899. During the course of the early tenth century, the various Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms were united by Alfred's descendants Edward the Elder (reigned 899–924) and Æthelstan (reigned 924–939) to form the Kingdom of the English. In 927, Æthelstan conquered the last remaining Viking kingdom, Scandinavian York, York, making him the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Red Ensign 1620
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Culture, language and peoples * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity * English studies, the study of English language and literature Media * English (2013 film), ''English'' (2013 film), a Malayalam-language film * English (novel), ''English'' (novel), a Chinese book by Wang Gang ** English (2018 film), ''English'' (2018 film), a Chinese adaptation * The English (TV series), ''The English'' (TV series), a 2022 Western-genre miniseries * English (play), ''English'' (play), a 2022 play by Sanaz Toossi People and fictional characters * English (surname), a list of people and fictional characters * English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach * English Gardner (born 1992), American track and field sprinter * English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer * Aid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chatham Dockyard
Chatham Dockyard was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the River Medway in Kent. Established in Chatham, Kent, Chatham in the mid-16th century, the dockyard subsequently expanded into neighbouring Gillingham, Kent, Gillingham; at its most extensive (in the early 20th century) two-thirds of the dockyard lay in Gillingham, one-third in Chatham. It came into existence at the time when, following the English Reformation, Reformation, relations with the Catholic countries of Europe had worsened, leading to a requirement for additional defences. Over 414 years Chatham Royal Dockyard provided more than 500 ships for the Royal Navy, and was at the forefront of shipbuilding, Industrial technology, industrial and British industrial architecture, architectural technology. At its height, it employed over 10,000 skilled artisans and covered . Chatham dockyard closed in 1984, and of the Georgian dockyard is now managed as the Chatham Historic Dockyard visitor attraction by the Chatham Histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fifth Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a fifth rate was the second-smallest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six " ratings" based on size and firepower. Rating The rating system in the Royal Navy as originally devised had just four rates, but early in the reign of Charles I, the original fourth rate (derived from the "Small Ships" category under his father, James I) was divided into new classifications of fourth, fifth, and sixth rates. While a fourth-rate ship was defined as a ship of the line, fifth and the smaller sixth-rate ships were never included among ships-of-the-line. Nevertheless, during the Anglo-Dutch Wars of the 17th century, fifth rates often found themselves involved among the battle fleet in major actions. Structurally, these were two-deckers, with a complete battery on the lower deck, and fewer guns on the upper deck (below the forecastle and quarter decks, usually with no guns in the waist on this deck). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Builder's Old Measurement
Builder's Old Measurement (BOM, bm, OM, and o.m.) is the method used in England from approximately 1650 to 1849 for calculating the cargo capacity of a ship. It is a volumetric measurement of cubic capacity. It estimated the tonnage of a ship based on length and maximum beam. It is expressed in "tons burden" (, ), and abbreviated "tons bm". The formula is: : \text = \frac where: * ''Length'' is the length, in feet, from the stem to the sternpost; * '' Beam'' is the maximum beam, in feet. The Builder's Old Measurement formula remained in effect until the advent of steam propulsion. Steamships required a different method of estimating tonnage, because the ratio of length to beam was larger and a significant volume of internal space was used for boilers and machinery. In 1849, the Moorsom System was created in the United Kingdom. The Moorsom system calculates the cargo-carrying capacity in cubic feet, another method of volumetric measurement. The capacity in cubic feet i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full-rigged Ship
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing ship, sailing vessel with a sail plan of three or more mast (sailing), masts, all of them square rig, square-rigged. Such a vessel is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged, with each mast stepped in three segments: lower, top, and topgallant. Masts The Mast (sailing), masts of a full-rigged ship, from Bow (ship), bow to stern, are: * Foremast, which is the second tallest mast * Mainmast, the tallest * Mizzenmast, the third tallest * Jiggermast, which may not be present but will be fourth tallest if so If the masts are of wood, each mast is in three or more pieces. They are (in order, from bottom up): * Th''e mast or the lower.'' * Topmast * Topgallant mast * Royal mast, if fitted On steel-masted vessels, the masts are not constructed in the same way, but the corresponding sections of the mast are still named after the traditional wooden sections. Sails The lowest and normally largest sail on a mast is the course ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a sixth-rate was the designation for small warships mounting between 20 and 28 carriage-mounted guns on a single deck, sometimes with smaller guns on the upper works and sometimes without. It thus encompassed ships with up to 30 guns in all. In the first half of the 18th century the main battery guns were 6-pounders, but by mid-century these were supplanted by 9-pounders. 28-gun sixth-rates were classed as frigates, those smaller as 'post ships', indicating that they were still commanded by a full Post-captain, ('post') captain, as opposed to Sloop-of-war, sloops of 18 guns and less, which were under Commander (Royal Navy), commanders. Rating Sixth-rate ships typically had a crew of about 150–240 men, and measured between 450 and 550 tons. A 28-gun ship would have about 19 officers; commissioned officers would include the Captain (Royal Navy), captain, and two Lieutenant (navy), lieutenants; warrant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Cotterell (Royal Navy Officer)
Rear Admiral Charles Cotterell (died 1754) was a Royal Navy officer who served as Commander-in-Chief, The Nore from 1744 to 1745. Naval career Cotterell became commanding officer of the sloop in 1722. Promoted to captain in June 1726, he commanded, successively, the fifth-rate , the fourth-rate , the fifth-rate , the sixth-rate , the fifth-rate , the fourth-rate , the fourth-rate , the fourth-rate and the fourth-rate . He saw action at the battle of Cartagena de Indias in May 1741. After that he commanded the first-rate and served as Commander-in-Chief, The Nore The Commander-in-Chief, The Nore, was an operational commander of the Royal Navy. His subordinate units, establishments, and staff were sometimes informally known as the Nore Station or Nore Command. Nore, The Nore is a sandbank at the mouth of t ... from 1744 to 1745. He died in 1754. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Cotterell, Charles 1754 deaths Royal Navy rear admirals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigates Of The Royal Navy
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Of The Royal Navy
''Ships of the Royal Navy'' is a naval history reference work by J. J. Colledge (1908–1997); it provides brief entries on all recorded ships in commission in the Royal Navy from the 15th century, giving location of constructions, date of launch, tonnage, specification and fate. It was published in two volumes by Greenhill Books. Volume 1, first published in 1969, covers major ships; Volume 2, first published in 1970, covers Navy-built naval trawler, trawlers, Naval drifter, drifters, Tugboat, tugs and requisitioned ships including Auxiliary cruiser, Armed Merchant Cruisers. The book is the standard single-volume reference work on ships of the Royal Navy, and Colledge's conventions and spellings of names are used by museums, libraries and archives. For more data on ships of the pre-1863 Royal Navy, see ''British Warships in the Age of Sail''. A revised third version of the Volume 1 work was published in 2003 which added the ships of the late 20th century. The revision was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |