|
HMS Lark (1794)
HMS ''Lark'' was a 16-gun ship sloop of the , launched in 1794 at Northfleet. She served primarily in the Caribbean, where she took a number of prizes, some after quite intensive action. ''Lark'' foundered off San Domingo in August 1809, with the loss of her captain and almost all her crew. French Revolutionary Wars ''Lark'' was commissioned in March 1794 under Commander Josias Rowley. Later that year Commander Francis Austen, who would go on to rise to the rank of admiral of the fleet, served on her when she was part of a fleet that evacuated British troops from Ostend and Nieuwpoort after the French captured the Netherlands. In 1795, the ''Lark'' was part of the squadron under Commodore Payne that escorted Princess Caroline of Brunswick to England. That same year she was part of the British naval force that supported the invasion of France by a force of French '' émigrés''. In January 1795 Commander William Ogilvy recommissioned her. On 21 March 1796, ''Lark'' joined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northfleet
Northfleet is a town in the borough of Gravesham in Kent, England. It is located immediately west of Gravesend, and on the border with the Borough of Dartford. Northfleet has its own railway station on the North Kent Line, just east of Ebbsfleet International railway station on the High Speed 1 line. The area Northfleet's name is derived from being situated on the northern reach of what was once called the River Fleet (today known as the Ebbsfleet River). There is a village at the other end of the river named Southfleet. It has been the site of a settlement on the shore of the River Thames adjacent to Gravesend since Roman times. It was known as ''Fleote'' by the Saxons c. 600 AD, ''Flyote'' c. 900 AD, and ''Flete'' c. 1000 AD. It was recorded as ''Norfluet'' in the Domesday Book, and ''Northflet'' in 1201. By 1610 the name of Northfleet had become established. A battle took place during the Civil War at the Stonebridge over the Ebbsfleet river. Northfleet became a town in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Newman-Newman
Captain James Newman-Newman (1767–1811) of the British Royal Navy was an officer who served in numerous actions with distinction during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars before his death in the wreck of his ship of the line HMS ''Hero'', which was lost with two other battleships off the Northern European coast during a storm in December 1811. Over 2,000 sailors lost their lives. Career Newman-Newman was born in 1767, and joined the Royal Navy at a young age, serving as a lieutenant aboard the flagship of Sir Alexander Hood, HMS ''Royal George'' during the battle of the Glorious First of June, when a French fleet was defeated deep in the Atlantic by the British Channel Fleet under Lord Howe. Due to good service in this action, Newman-Newman was promoted to captain and took command of a succession of frigates in the Mediterranean and home waters, beginning with HMS ''Ceres'' in 1795. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polacca
A polacca (or ''polacre'') is a type of seventeenth- to nineteenth-century sailing vessel, similar to the xebec. The name is the feminine of "Polish" in the Italian language. The polacca was frequently seen in the Mediterranean. It had two or three single-pole masts, the three-masted vessels often with a lateen hoisted on the foremast (which was slanted forward to accommodate the large lateen yard) and a gaff or lateen on the mizzen mast. The mainmast was square-rigged after the European style. Special polaccas were used by Murat Reis, whose ships had lateen sails in front and fore-and-aft rig behind. Some polacca pictures show what appears to be a ship-rigged vessel (sometimes with a lateen on the mizzen) with a galley-like hull and single-pole masts. Thus, the term "polacca" seems to refer primarily to the masting and possibly the hull type as opposed to the type of rig used for the sails. Two-masted polaccas were referred to as brig-polaccas with square sails on both mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabo Catoche
Cabo Catoche or Cape Catoche, in the Mexican state of Quintana Roo, is the northernmost point on the Yucatán Peninsula. It lies in the municipality of Isla Mujeres, about north of the city of Cancún. According to the International Hydrographic Organization, it marks the division point between the Caribbean Sea to the east and Gulf of Mexico to the west. The name is believed to be a corruption of the Mayan word ''cotoch'', meaning "our houses, our homeland". "Cotoch" is the name used by Diego de Landa to refer to the region in 1566.Landa, Diego "Relación de Yucatán". Linkgua, s.l., 2008, p. 11. Catoche was the location of the first intentional landing by Europeans in the territory of modern-day Mexico, during the Córdoba expedition, on 4 March 1517. The Spanish were invited into the native town with "''Cones catoche, cones catoche'', which means: 'Come to our houses'." On the way, the Spaniards were ambushed, suffering thirteen wounded to the native's fifteen killed. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cane Sugar Mill
A sugar cane mill is a factory that processes sugar cane to produce raw or white sugar. The term is also used to refer to the equipment that crushes the sticks of sugar cane to extract the juice. Processing There are a number of steps in producing raw sugar from cane: # Cane receiving and unloading (receive the cane at the factory and unload it from the transport vehicles) # Cane preparation (cutting and shredding cane to prepare it for juice extraction) # Juice extraction (two technologies are in common use; milling or diffusion) # Juice clarification (remove suspended solids from the juice, typically mud, waxes, fibres) # Juice evaporation (to concentrate the juice to a thick syrup of about 65°brix) # Syrup clarification (remove suspended solids from the syrup, typically colloid size of mud, waxes, fibres, etc.) # Crystallisation # Centrifugation (Separation of the sugar crystals from the mother liquor, done by centrifugal machines) # Sugar drying # Packaging and delivery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Turk Island
Grand Turk Island is an island in the Turks and Caicos Islands. It is the largest island in the Turks Islands (the smaller of the two archipelagos that make up the island territory) with . Grand Turk contains the territory's capital, Cockburn Town, and the JAGS McCartney International Airport. The island is the administrative, historic, cultural and financial center of the territory and has the second-largest population of the islands at approximately 4,831 people in 2012. The name comes from a species of cactus on the island, the Turk's Cap Cactus ('' Melocactus intortus''), which has a distinctive cap, reminiscent of an Ottoman fez. History The Lucayan people were the indigenous people of the island, who called it ''Abawana,'' meaning "the First Small Land"''.'' The Spanish later called it Amuana. Grand Turk was first colonised in 1681 by Bermudians, who set up the salt industry in the islands. In 1766 it became the capital of the country. For some time, at least until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
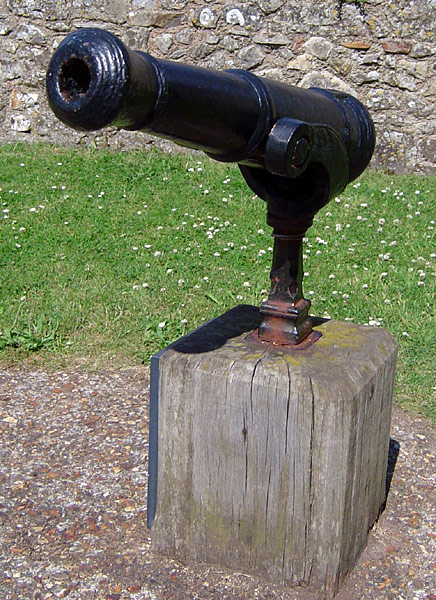
Swivel Guns
The term swivel gun (or simply swivel) usually refers to a small cannon, mounted on a swiveling stand or fork which allows a very wide arc of movement. Another type of firearm referred to as a swivel gun was an early flintlock combination gun with two barrels that rotated along their axes to allow the shooter to switch between rifled and smoothbore barrels. Swivel guns should not be confused with pivot guns, which were far larger weapons mounted on a horizontal pivot, or screw guns, which are a mountain gun with a segmented barrel. An older term for the type is peterero (alternative spellings include "paterero" and "pederero"). The name was taken from the Spanish name for the gun, pedrero, a combination of the word piedra (stone) and the suffix -ero (-er), because stone was the first type of ammunition fired. Configuration Swivel guns are among the smallest types of cannon, typically measuring less than in length and with a bore diameter of up to . They can fire a variety of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
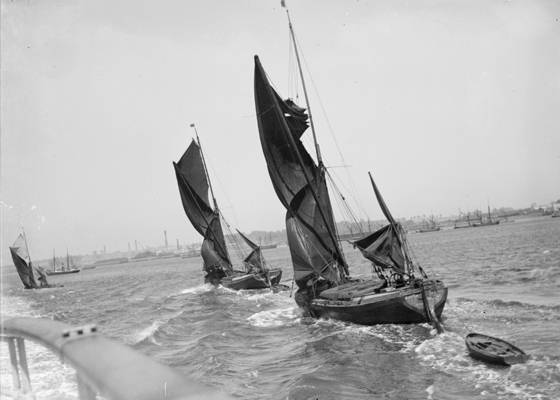
Lateen
A lateen (from French ''latine'', meaning "Latin") or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same overall category of sail. The lateen originated in the Mediterranean as early as the 2nd century CE, during Roman times, and became common there by the 5th century. The wider introduction of lateen rig at this time coincided with a reduction in the use of the Mediterranean square rig of the classical era. Since the performance of these two rigs is broadly similar, it is suggested that the change from one to the other was on cost grounds, since lateen used fewer components and had less cordage to be replaced when it wore out. Arab seafarers adopted the lateen rig at a later datethere is some limited archaeological evidence of lateen rig in the Indian Ocean in the 13th century CE and iconographic evidence from the 16th century. It has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wentworth Loring
Admiral Sir John Wentworth Loring, KCB, KCH (13 October 1775 – 29 July 1852) was a Royal Navy officer of the early nineteenth century who is best known for his service in the Napoleonic Wars as a frigate commander. Born in the Thirteen Colonies at the outbreak of the American War of Independence, Loring's family fled to Britain and he subsequently joined the Royal Navy aged 13. In 1793, aged 17, Loring was badly wounded in combat at the start of the French Revolutionary Wars. He subsequently served throughout the following 23 years of warfare between Britain and France, achieving success in command of the frigate HMS ''Niobe''. After the war he served in an influential position at the Royal Naval College, Portsmouth and eventually became a full admiral. Life John Loring was born in October 1775 at the start of the American War of Independence to Joshua Loring, High Sheriff of Massachusetts. John's grandfather, Joshua Loring, had served in the navy in the Seven Yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Corvette Perçante (1795)
''Perçante'' was a 20-gun ship-corvette of the French Navy, built at Bayonne and launched in 1795. The British captured her in 1796 and took her into the Royal Navy under the name HMS ''Jamaica''. They rated her as a sixth-rate 26-gun frigate. She served during both the French Revolutionary Wars and part of the Napoleonic Wars, during which she captured some privateers and participated in a boat attack. The Admiralty had her laid up in 1810 and sold her in 1814. Design ''Perçante'' was one of four ''Bonne Citoyenne''-class corvettes launched between 1794 and 1796, all four of which the Royal Navy captured between 1796 and 1798. The class was built to a design by Raymond-Antoine Haran. All members of the class were flush-decked, but with a long topgallant forecastle. French service ''Perçante'' was stationed at Bayonne and Rochefort. Initially she was under the command of ''enseigne de vaisseau'' Laporte, who commanded her from 13 June 1795 to 17 August.''Fonds'', Vol. 1, 158. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
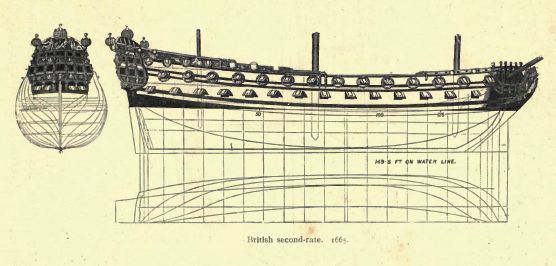
Second Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns and were originally two-deckers or had only partially armed third gun decks. A "second rate" was the second largest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six "ratings" based on size and firepower. They were essentially smaller and hence cheaper versions of the three-decker first rates. Like the first rates, they fought in the line of battle, but unlike the first rates, which were considered too valuable to risk in distant stations, the second rates often served also in major overseas stations as flagships. They had a reputation for poor handling and slow sailing. They were popular as flagships of admirals commanding the Windward and/or Leeward Islands station, which was usually a Rear-admiral of the red. Rating Typically measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaica Station (Royal Navy)
The Jamaica Station was a formation or command of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy stationed at Port Royal in Jamaica from 1655 to 1830. History The station was formed, following the capture of Jamaica, by assembling about a dozen frigates in 1655. The first "Admiral and General-at-Sea" was Sir William Penn.Cundall, p. xx Its main objectives in the early years were to defend Jamaica and to harass Spanish ports and shipping. In the late 1720s three successive commanders of the station lost their lives to tropical diseases while undertaking a Blockade of Porto Bello during the Anglo-Spanish War. The general ill-health associated with the station continued throughout the century. An assessment of Navy strength at the Jamaica station in 1742 found around 3,000 men were fit to serve out of a total Navy complement of 6,620. A Navy hospital was constructed in 1745 but its location was poor and many patients brought in for shipboard diseases developed additional tropical illnesses while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |