|
HMS Cydnus (1813)
HMS ''Cydnus'' was one of eight Royal Navy 38-gun ''Cydnus''-class fifth-rates. This frigate was built in 1813 at Blackwall Yard, London, and broken up in 1816. Design, construction and armament The entire class was a version of the frigates, but built of red fir (pine), which was cheaper and more abundant than oak. Most importantly, it permitted noticeably faster construction, but at a cost of reduced durability. To enable the new frigate to meet the American frigates on less unequal terms, ''Cydnus'', and her sister received medium 24-pounders and an increased complement of men. ''Cydnus''s 24-pounders were of a design by General Sir Thomas Blomefield, 1st Baronet and measured 7 ft. 6 in. in length while weighing about 40 cwt. The 24-pounders on ''Eurotas'' were to a design by Colonel Congreve. During December 1813 and January 1814, ''Cyndus'' and ''Eurotas'' actually temporarily exchanged six 24-pounders, presumably to enable both vessels to test the designs agains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Of Great Britain And Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into a unified state. The establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922 led to the remainder later being renamed the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in 1927. The United Kingdom, having financed the European coalition that defeated France during the Napoleonic Wars, developed a large Royal Navy that enabled the British Empire to become the foremost world power for the next century. For nearly a century from the final defeat of Napoleon following the Battle of Waterloo to the outbreak of World War I, Britain was almost continuously at peace with Great Powers. The most notable exception was the Crimean War with the Russian Empire, in which actual hostilities were relatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 12 pence or one-twentieth of a pound before being phased out during the 20th century. Currently the shilling is used as a currency in five east African countries: Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Somalia, as well as the ''de facto'' country of Somaliland. The East African Community additionally plans to introduce an East African shilling. History The word ''shilling'' comes from Old English "Scilling", a monetary term meaning twentieth of a pound, from the Proto-Germanic root skiljaną meaning 'to separate, split, divide', from (s)kelH- meaning 'to cut, split.' The word "Scilling" is mentioned in the earliest recorded Germanic law codes, those of Æthelberht of Kent. There is evidence that it may alternatively be an early borrowing of Phoeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
£sd
£sd (occasionally written Lsd, spoken as "pounds, shillings and pence" or pronounced ) is the popular name for the pre-decimal currencies once common throughout Europe, especially in the British Isles and hence in several countries of the British Empire and subsequently the Commonwealth. The abbreviation originates from the Latin currency denominations '' librae'', '' solidi'', and '' denarii''. In the United Kingdom, these were referred to as '' pounds'', '' shillings'', and '' pence'' (''pence'' being the plural of ''penny''). Although the names originated from popular coins in the classical Roman Empire, their definitions and the ratios between them were introduced and imposed across Western Europe by the Emperor Charlemagne. The £sd system was the standard across much of the European continent (France, Italy, Germany, etc.) for nearly a thousand years, until the decimalisations of the 18th and 19th centuries. As the United Kingdom remained one of the few countries r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Starr (1805)
HMS ''Starr'' was a 16-gun ''Merlin''-class ship sloop of the Royal Navy. She was built by Tanner, of Dartmouth, to plans by Sir William Rule, and launched in July 1805. As a sloop she served on convoy duty, though she also participated in the invasion of Martinique in early 1809. She was rebuilt as a bomb vessel in May 1812 and renamed ''Meteor''. As ''Meteor'' she served in the Baltic and then off the United States, participating in attacks on up the Potomac and on Baltimore and New Orleans. She was sold in October 1816. Napoleonic Wars She was commissioned in October 1805 under Commander John Simpson. On 3 January 1806 she recaptured the ships ''Argo'' and ''Adventure'', and shared in the recapture of the ''Good Intent''. ''Starr'' was off Villa de Conde, Portugal, when she intercepted the vessels, which had been taken from a convoy that had been escorting from Newfoundland to Portugal, and both of which had been carrying cargoes of fish. ''Starr'' sighted ''Good Inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third rate ships embodied the best compromise between sailing ability (speed, handling), firepower, and cost. So, while first-rates and second-rates were both larger and more powerful, third-rate ships were the optimal configuration. Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
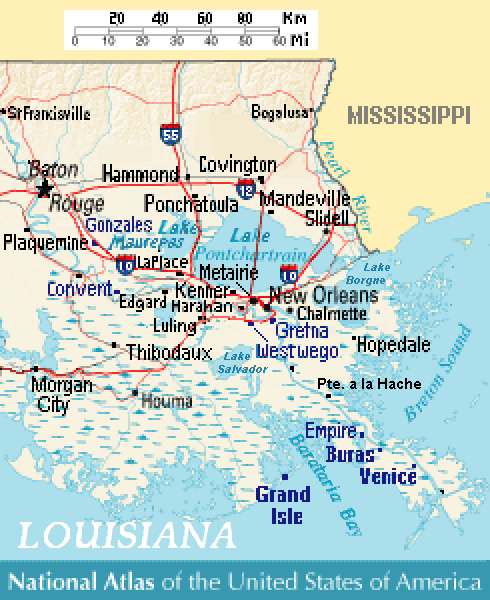
Lake Borgne
Lake Borgne (french: Lac Borgne, es, Lago Borgne) is a lagoon of the Gulf of Mexico in southeastern Louisiana. Although early maps show it as a lake surrounded by land, coastal erosion has made it an arm of the Gulf of Mexico. Its name comes from the French word ''borgne'', which means "one-eyed." Geography In southern Louisiana, three large lakes—Maurepas, Pontchartrain, and Borgne—cover 55% of the Pontchartrain Basin. A brackish marsh land bridge and Lake St. Catherine separate Lake Pontchartrain from Lake Borgne. The Rigolets and Chef Menteur Pass are the two open water connections between Pontchartrain and Borgne. Coastal erosion has transformed Borgne into a lagoon connecting to the Gulf of Mexico. Early 18th-century maps show Borgne as a true lake, largely separated from the gulf by a considerable extent of wetlands that have since disappeared. In a 1902 case before the United States Supreme Court over the oyster banks at the boundary between Louisiana and Missis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a sixth-rate was the designation for small warships mounting between 20 and 28 carriage-mounted guns on a single deck, sometimes with smaller guns on the upper works and sometimes without. It thus encompassed ships with up to 30 guns in all. In the first half of the 18th century the main battery guns were 6-pounders, but by mid-century these were supplanted by 9-pounders. 28-gun sixth rates were classed as frigates, those smaller as ' post ships', indicating that they were still commanded by a full ('post') captain, as opposed to sloops of 18 guns and less under commanders. Rating Sixth-rate ships typically had a crew of about 150–240 men, and measured between 450 and 550 tons. A 28-gun ship would have about 19 officers; commissioned officers would include the captain, and two lieutenants; warrant officers would include the master, ship's surgeon, and purser. The other quarterdeck officers were t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lake Borgne
The Battle of Lake Borgne was a coastal engagement between the Royal Navy and the U.S. Navy in the American South theatre of the War of 1812. It occurred on December 14, 1814 on Lake Borgne. The British victory allowed them to disembark their troops unhindered nine days later and to launch an offensive upon New Orleans on land. Background In August 1814, Vice Admiral Cochrane had convinced the Admiralty that a campaign against New Orleans would weaken American resolve against Canada, and hasten a successful end to the war. In the winter of 1814, the British had the objective of gaining control of the entrance of the Mississippi, and to challenge the legality of the Louisiana Purchase. To this end, an expeditionary force of about 8,000 troops under General Edward Pakenham had arrived in the Gulf Coast, to attack New Orleans. An anonymous letter sent from Pensacola, dated December 5 and addressed to Commodore Daniel Patterson warned him of this imminent threat, and was received o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans . ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nueva Orleans) is a consolidated city-parish located along the in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 according to the 2020 U.S. census, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around the Indian Ocean by Portuguese explorers, soon after the Cape route was discovered. Nowadays, this term is broadly used to refer to the Malay Archipelago, which today comprises the Philippine Archipelago, Indonesian Archipelago, Malaysian Borneo, and New Guinea. Historically, the term was used in the Age of Discovery to refer to the coasts of the landmasses comprising the Indian subcontinent and the Indochinese Peninsula along with the Malay Archipelago. Overview During the era of European colonization, territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia were known as the Spanish East Indies for 333 years before the American conquest. Dutch occupied colonies in the area were known for about 300 years as the Dutch East Indies till ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madeira
) , anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira") , song_type = Regional anthem , image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg , map_alt=Location of Madeira , map_caption=Location of Madeira , subdivision_type=Sovereign state , subdivision_name=Portugal , established_title= Discovery , established_date=1418-1419 , established_title2=Settlement , established_date2=c. 1425 , established_title3=Autonomous status , established_date3=30 April 1976 , named_for = en, wood ( pt, madeira) , official_languages= Portuguese , demonym= en, Madeiran ( pt, Madeirense) , capital = Funchal , government_type= Autonomous Region , leader_title1=Representative of the Republic , leader_name1=Irineu Barreto , leader_title2= President of the Regional Government of Madeira , leader_name2= Miguel Albuquerque , leader_title3=President of the Legislative Assembly , leader_name3=José Manuel Rodrigues , legislature= Legislative Assembly , national_representation=Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Gloire (1803)
''Gloire'' was a 44-gun frigate of the French Navy, lead ship of her class. She took part in Allemand's expedition of 1805. On 18 July, she captured and burnt a Prussian cutter to maintain the secrecy of the movements of the fleet, in spite of the neutrality of Prussia at the time. The next day, along with , she captured and burnt her. In the action of 25 September 1806 The action of 25 September 1806 was a naval battle fought during the Napoleonic Wars off the French Biscay port of Rochefort. A French squadron comprising five frigates and two corvettes, sailing to the French West Indies with supplies and rei ..., , ''Gloire'', and were captured by a four-ship squadron under Samuel Hood. She was brought into British service as HMS ''Gloire'' and broken up in 1812.Winfield & Roberts p.145 Citations References * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Gloire (1803) Frigates of the Royal Navy Ships built in France Age of Sail frigates of France 1803 ships Frigates of the French Navy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |