|
HMS Corso (1796)
''El Corso'' was launched in Spain in 1791 as a naval brig. the British Royal Navy captured her in 1796 and took her into service as HMS ''Corso''. She then served in the Mediterranean where she captured numerous small vessels, the great majority of which were merchant vessels. In 1802 she sailed to England. From July 1802 to her sale in September 1814 she served as a receiving ship. Capture On 2 December 1796 encountered the Spanish naval brig ''El Corso'' off Monaco as ''El Corso'' was on her way from Genoa to Barcelona. ''Southampton'' captured ''El Corso'' by boarding. She was armed with eighteen 6-pounder guns and had a crew of 136 men under the command of Don Antonio Oacaro. The Royal Navy took the brig into service as HMS ''Corso''. Royal Navy Commander Bartholomew James commissioned ''Corso'' in the Mediterranean in December 1796. On 6 August 1798 ''Corso'' and captured ''Liguria''. On 24 August ''Corso'' captured the French privateer ''Francois'' near Corf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
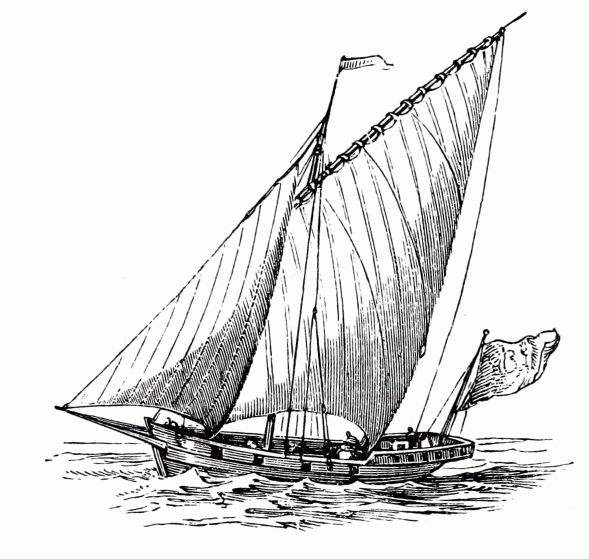
Tartane
A tartane (also tartan, tartana) was a small ship used both as a fishing ship and for coastal trading in the Mediterranean. They were in use for over 300 years until the late 19th century. A tartane had a single mast on which was rigged a large lateen sail, and with a bowsprit and fore-sail. When the wind was aft a square sail Square rig is a generic type of sail and rigging arrangement in which a sailing vessel's primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spars that are perpendicular (or square) to the median plane of the keel and masts of the vessel. These sp ... was generally hoisted like a cross jack. References * * * Merchant sailing ship types {{ship-type-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Settee (sail)
The settee sail was a lateen sail with the front corner cut off, giving it a quadrilateral shape. The settee sail requires a shorter yard than does the lateen, and both settee and lateen have shorter masts than square-rigged sails. History of the sail form It can be traced back to navigation in the Mediterranean Sea in late antiquity; the oldest evidence is from a late 5th-century ship in a Roman mosaic at Kelenderis in Cilicia on the southern coast of Anatolia (now Aydıncık, Mersin). It lasted well into the 20th century as a common sail on Arab dhows and on the Gozo boat of Malta Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two .... Model of a sambuk with two settee sails Settee (boat) Settees (or ''saëtia'') then were a sharp-prowed, single-decked merchant sailing vess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Genoa (1800)
The siege of Genoa saw an Austrian army led by Michael von Melas besiege the port of Genoa, which was occupied by a French garrison under the command of André Massena, from 19 April to 4 June 1800. It formed part of the larger Marengo campaign during the War of the Second Coalition. The Austrian army isolated Massena and half of the French army in Genoa, while driving the other half from the area. Once Genoa was under siege, Massena conducted a very active defense with frequent sorties. Besieged on land by 24,000 troops led by Peter Karl Ott von Bátorkéz and at sea by a Royal Navy squadron under Lord Keith, famine reduced the defenders to starvation. By the time Massena surrendered the city on 4 June, 30,000 of Genoa's 160,000 inhabitants had died of starvation and disease. While the Austrian army was focused on the siege, a French army under Napoleon invaded Italy from the northwest, winning a close affair at the Battle of Marengo. Background In early 1799, the Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasha
Pasha (; ; ) was a high rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitary, dignitaries, and others. ''Pasha'' was also one of the highest titles in the 20th-century Kingdom of Egypt and it was also used in Morocco in the 20th century, where it denoted a regional official or governor of a district. Etymology The English word ''pasha'' comes from Turkish language, Turkish ('; also ()). The Oxford English Dictionary attributes the origin of the English borrowing to the mid-17th century. The etymology of the Turkish word itself has been a matter of debate. Contrary to titles like emir (''amīr'') and bey (sir), which were established in usage much earlier, the title ''pasha'' came into Ottoman Empire, Ottoman usage right after the reign of Osman I (d. 1324), though it had been used before the Ottomans by some Anatolian beyliks, Anatolian Turkish rulers of the same era. Old Turkish had no fixed distinction betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
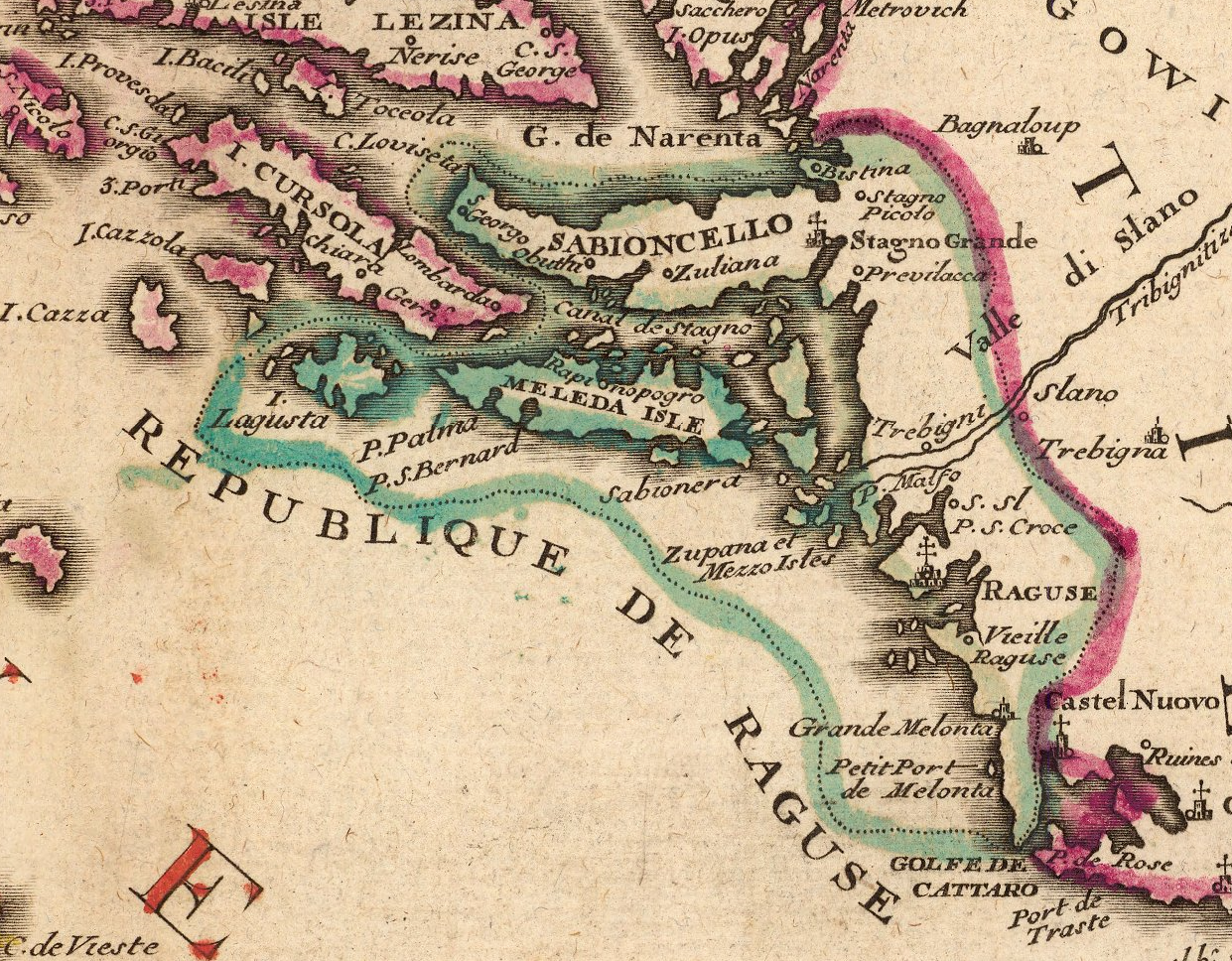
Republic Of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost Croatia) that carried that name from 1358 until 1808. It reached its commercial peak in the 15th and the 16th centuries, before being conquered by Napoleon's First French Empire, French Empire and formally annexed by the Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1808. It had a population of about 30,000 people, of whom 5,000 lived within the city walls. Its motto was "'", a Latin phrase which can be translated as "Liberty is not well sold for all the gold". Names Originally named ' (Latin for "Ragusan municipality" or "community"), in the 14th century it was renamed ' (Latin for ''Ragusan Republic''), first mentioned in 1385. It was nevertheless a Republic under its previous name, although its Rector was appointed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochineal
The cochineal ( , ; ''Dactylopius coccus'') is a scale insect in the suborder Sternorrhyncha, from which the natural dye carmine is derived. A primarily sessility (motility), sessile parasitism, parasite native to tropical and subtropical South America through North America (Mexico and the Southwest United States), this insect lives on Cactus, cacti in the genus ''Opuntia'', feeding on plant moisture and nutrients. The insects are found on the pads of prickly pear cacti, collected by brushing them off the plants, and dried. The insect produces carminic acid that deters predation by other insects. Carminic acid, typically 17–24% of dried insects' weight, can be extracted from the body and eggs, then mixed with aluminium or calcium salts to make carmine dye, also known as cochineal. Today, carmine is primarily used as a Food coloring, colorant in food and in lipstick (Carmine, E120 or Carminic acid, Natural Red 4). Carmine dye was used in the Americas for coloring fabrics and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
En Flûte
''En flûte'' (French: "as a fluyt") is a French naval expression of the Age of Sail to designate the use of a warship as a transport with reduced armament.Willaumez, p. 294 Some warships, ships of the line or frigates, were occasionally used with limited artillery, by reducing the number and calibre of their guns. Since ships have a limited amount of cargo space, they may be armed ''en flûte'' to make room for other cargo, such as troops and ammunition, reducing the ship's ability to defend herself if attacked. The term emerged from the French name for a type of ship – the cargo-carrying ''flûte'' used extensively as a mercantile ship or as a naval auxiliary vessel. In turn this derived from the Dutch name ''fluyt'', probably the most common type of cargo-carrier during the seventeenth century – when in English usage it was commonly rendered as a flyboat. This tactic was most relevant in the Age of Sail, when gun decks took up most of the space on a warship above the wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
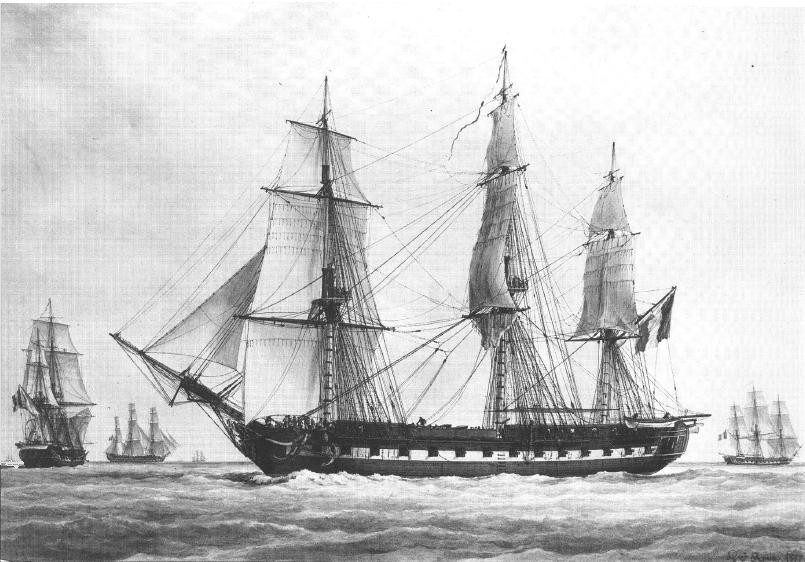
French Ship Généreux (1785)
''Généreux'' was a French 74-gun ship of the line. After capture she completed her career as part of the Royal Navy as HMS ''Généreux''. History She was launched in 1785 at Rochefort. Under Louis-Jean-Nicolas Lejoille, she was one of only two ships to escape the British attack at the Battle of the Nile in August 1798, along with . Shortly after the battle of the Nile, on 18 August 1798, she fell in with a smaller British ship of the line, of 50 guns. After a long battle, the ''Généreux'' captured the ''Leander'', with the ''Leander'' suffering 35 killed and 57 wounded and the ''Généreux'' suffered around 100 killed and 180 wounded. In March 1799, ''Généreux'' escorted a convoy to Corfu, which was being besieged by a joint Russo-Ottoman fleet. En route, her captain, Lejoille, decided to bombard Brindisi. He was killed in the ensuing exchange of fire, and lieutenant Claude Touffet took over. The city fell on 3 March after a two-hour battle. On 6 February 1800, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Perrée
Counter-Admiral Jean-Baptiste Perrée (19 December 1761Levot, p. 394 in 1866 write 19 April 1761 – 18 February 1800Levot, p. 395) was a French Navy officer who served in the French Revolutionary Wars. Career Born to a family of sailors in Saint-Valery-sur-Somme, Perrée started sailing in 1773 at the age of twelve as a boy on the merchantman ''Glorieuse'', under his father. In the course of the following twenty years, he steadily rose in rank in the merchant navy, took part in a campaign on the fluyt ''Boulonnaise'' in the French Navy as an aid-pilot, and earned his commission of Sea captain in 1785.Granier, p. 162 Commerce raiding on ''Proserpine'' In 1793, when France declared war on Britain during the War of the First Coalition, Perrée enlisted in the Navy as an acting Ensign.''Enseigne non entretenu'' (Granier, p. 162) In September 1793, he was reported to be commanding a frigate squadron in the Western Mediterranean, fighting the inconclusive action of 22 October 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contre-amiral
Counter admiral is a military rank used for high-ranking officers in several navies around the world, though the rank is not used in the English-speaking world, where its equivalent rank is rear admiral. The term derives from the French . Depending on the country, it is either a one-star or two-star rank. In modern navies that use it, counter admiral is generally, although not always, the lowest flag officer rank. In the German Navy, for instance, ranks below ; in the Royal Canadian Navy, (rear admiral in English) ranks above . French speaking countries In France and other French speaking countries' navies the rank of is used as the lowest flag officer. It is usually placed above ship-of-the-line captain () and below vice admiral (). Germany is a NATO OF-7 (two-star rank) of the (German Navy), equivalent to the ("major general") in the German Army and the German Air Force. Nordic countries The rank of counter admiral is used in all the Nordic countries. Denmark and No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |