|
HMS Cherub (1806)
HMS ''Cherub'' was an 18-gun Royal Navy sloop built in Dover in 1806. She participated in two major campaigns in the West Indies during the Napoleonic Wars, and one major engagement in the Pacific during the War of 1812, all each of which earned her crews clasps to the Naval General Service Medal. The Navy sold her in 1820. Career Commander John Ravenshaw commissioned ''Cherub'' in April for the North Sea. ''Cherub'' is listed among the vessels qualifying for prize money arising out of the battle of Copenhagen. On the way there, ''Cherub'' and detained the Danish ship ''Neptunus'' on 30 August. ''Cherub'' sent ''Neptune'' (or ''Neptunus''), which had been sailing from Stockholm to Holstein, into Sheerness. Slightly earlier, she supported the Swedes at the defence of Stralsund and Rügen. On 29 February 1808 ''Cherub'' sailed for the Leeward Islands. From April to mid-June 1808 ''Cherub'' and cruised in company, and agreed to share any prizes they captured. Around 9 May '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
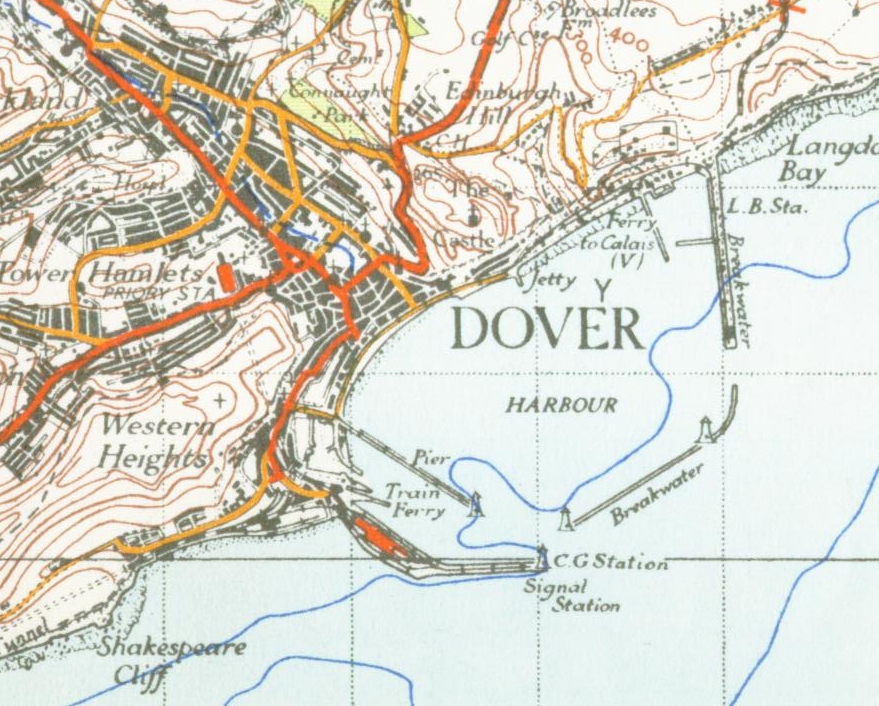
Dover
Dover ( ) is a town and major ferry port in Kent, southeast England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies southeast of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover. Archaeological finds have revealed that the area has always been a focus for peoples entering and leaving Great Britain, Britain. The name derives from the River Dour that flows through it. In recent times the town has undergone transformations with a high-speed rail link to London, new retail in town with St James' area opened in 2018, and a revamped promenade and beachfront. This followed in 2019, with a new 500m Pier to the west of the Harbour, and new Marina unveiled as part of a £330m investment in the area. It has also been a point of destination for many English Channel migrant crossings (2018-present), illegal migrant crossings. The Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Guayra
La Guaira () is the capital city of the Venezuelan state of the same name (formerly named Vargas) and the country's main port, founded in 1577 as an outlet for nearby Caracas. The city hosts its own professional baseball team in the Venezuelan Professional Baseball League, the Tiburones de La Guaira. They have won eight national championships since their founding in 1962 and won the Caribbean Series in 2023-24 History After the founding of Caracas by Spanish in 1567, toward the turn of the 16th century, the Port of La Guaira emerged on the coast and, since that time, has been the gateway to Caracas. This coastal city, almost without land to develop and bathed by the Caribbean Sea, became an important harbour during the 18th century. Attacked by buccaneers and by the English, Dutch, and French armadas, La Guaira was transformed into a fortified, walled city. During the War of Jenkins' Ear (1739–1748), the first attack of the Royal Navy took place on La Guaira. In March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinique
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼnja. A part of the French West Indies (Antilles), Martinique is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region and a single territorial collectivity of France. It is a part of the European Union as an outermost region within the special territories of members of the European Economic Area, and an associate member of the Caribbean Community, CARICOM, the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS), the Association of Caribbean States (ACS), and the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) but is not part of the Schengen Area or the European Union Customs Union. The currency in use is the euro. It has been a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve since 2021 for its entire land and sea territory. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Pierre, Martinique
Saint-Pierre (, ; ; Martinican Creole: ) is a town and commune of France's Caribbean overseas department of Martinique, founded in 1635 by Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc. Before the total destruction of Saint-Pierre by a volcanic eruption in 1902, it was the most important city of Martinique culturally and economically, being known as "the Paris of the Caribbean". While Fort-de-France was the official administrative capital, Saint-Pierre was the cultural capital of Martinique. After the disaster, Fort-de-France grew in economic importance. History Saint-Pierre was founded in 1635 by Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc, a French trader and adventurer, as the first permanent French colony on the island of Martinique. The Great Hurricane of 1780 produced a storm-surge of which "inundated the city, destroying all houses" and killed 9,000 people. Eruption of Mount Pelée The town was again destroyed in 1902, when the volcano Mount Pelée erupted, killing 28,000 people. The entire populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
63rd (West Suffolk) Regiment Of Foot
The 63rd Regiment of Foot was a British Army regiment raised in 1756. Under the Childers Reforms, it amalgamated with the 96th Regiment of Foot to form the Manchester Regiment in 1881. History Formation and service in the Seven Years' War The formation of the regiment was prompted by the expansion of the army as a result of the commencement of the Seven Years' War. On 25 August 1756 it was ordered that a number of existing regiments should raise a second battalion; among those chosen was the 8th (The King's) Regiment of Foot, 8th Regiment of Foot. The 2nd Battalion of the 8th Regiment of Foot was formed on 10 December 1756 and renumbered as the 63rd Regiment of Foot on 21 April 1758. Later that year, the newly created 63rd, along with a number of other regiments and various other assets, set off for the West Indies. In January 1759 the regiment took part in the unsuccessful Invasion of Martinique (1759), invasion of Martinique. Later that month the regiment took part in the Invasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Beckwith (British Army Officer)
General Sir George Beckwith GCB (1753 – 20 March 1823) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator who served as governor of Barbados from 1810 to 1815. Military career Beckwith was commissioned into the 37th Regiment of Foot in 1771. He distinguished himself as a regimental officer in the American Revolutionary War, where he was assistant to Major Oliver Delancey responsible for British Intelligence. In July 1782, he replaced Delancey and after the war he worked for Sir Guy Carleton in Canada. His efforts were aimed at stirring up trouble in Vermont, Florida, Kentucky and Tennessee. At the time Britain thought the weak American government might ask for British help. He was then appointed Governor and Commander-in-Chief of Bermuda in 1797, when a colonel. His baggage and furniture left England on 23 September 1797, aboard the ''Caledonia'', travelling in a convoy bound for Halifax, Nova Scotia, but was lost when the ''Caledonia'' was captured by the French. Bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Cochrane
Admiral Sir Alexander Inglis Cochrane, GCB (born Alexander Forrester Cochrane; 23 April 1758 – 26 January 1832) was a Royal Navy officer and politician who served in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars and achieved the rank of admiral of the blue. He captained off Alexandria, Egypt during the French invasion of Egypt and Syria. Cochrane was knighted into the Order of the Bath for his services in 1806. In 1814 he became vice admiral and commander-in-chief of the North American Station, led British naval forces during the attacks on Washington and New Orleans, and was promoted to admiral in 1819 and became commander-in-chief of the Plymouth naval base. Naval career Alexander Inglis Cochrane was a younger son of the Scottish peer Thomas Cochrane, 8th Earl of Dundonald, and his second wife, Jane Stuart. He joined the Royal Navy as a boy and served with British naval forces in North America. He served during the American War of Independence. Cochrane also partici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Martinique (1809)
The British invaded and captured the French colony of Martinique between 30 January and 24 February 1809 during the West Indies campaign of 1804–1810 of the Napoleonic Wars. Martinique, like the nearby island of Guadeloupe, was a major threat to Britain's trade in the West Indies, providing a sheltered base from which privateers and French Navy warships could raid British merchant shipping and disrupt the trade routes that maintained the economy of the United Kingdom. Both islands also provided a focus for larger-scale French operations in the region and in the autumn of 1808, following the Spanish alliance with Britain, the Admiralty decided to order a British squadron to neutralise the threat, beginning with Martinique. The British mustered a large expeditionary force under Vice-Admiral Sir Alexander Cochrane and Lieutenant-General George Beckwith, commanding 29 ships and 10,000 men – almost four times the number of French regular troops garrisoning Martinique. Landing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basse-Terre Island
Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and two Îles des Saintes—as well as many uninhabited islands and outcroppings. It is south of Antigua and Barbuda and Montserrat and north of Dominica. The capital city is Basse-Terre, on the southern west coast of Basse-Terre Island; the most populous city is Les Abymes and the main centre of business is neighbouring Pointe-à-Pitre, both on Grande-Terre Island. It had a population of 395,726 in 2024. Like the other overseas departments, it is an integral part of France. As a constituent territory of the European Union and the eurozone, the euro is its official currency and any European Union citizen is free to settle and work there indefinitely, but is not part of the Schengen Area. It included Saint Barthélemy and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Tudor Tucker (Royal Navy Officer)
Thomas Tudor Tucker, C.B. (1775–1852) was a British sailor from Bermuda. He was a Rear Admiral in the British Navy. Life He was named for an uncle, Thomas Tudor Tucker, who served as Treasurer of the United States. The third of the eight sons (all in the public service) of Henry Tucker, secretary of the council of the Bermudas, he was born on 29 June 1775; Henry St George Tucker was his eldest brother. After two voyages in the service of the East India Company, Tucker entered the Royal Navy in 1793 as master's mate of , with Captain William Clark, whom he followed to , and , in which he was present at the reduction of the Cape of Good Hope. On 21 March 1796 he was appointed acting lieutenant of on the East India station, in which and afterwards in the sloop , again in ''Victorious'' and in , he served as acting lieutenant for nearly four years. On her way homewards ''Sceptre'' was lost in Table Bay, on 5 November 1799. Many of her crew perished, and Tucker was left to find h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pence
A penny is a coin (: pennies) or a unit of currency (: pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. At present, it is the formal name of the British penny ( p) and the '' de facto'' name of the American one-cent coin (abbr. ¢). ''Penny'' is also the informal name of the cent unit of account in Canada, although the production of one-cent coins was ended in 2012. The name ''penny'' is also used in reference to various historical currencies, also derived from the Carolingian system, such as the French denier and the German pfennig. It may also be informally used to refer to any similar smallest-denomination coin, such as the euro cent or Chinese fen. The Carolingian penny was originally a 0.940-fine silver coin, weighing pound. It was adopted by Offa of Mercia and other English kings and remained the principal currency in Europe over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Netley (1798)
HMS ''Netley'' was launched in 1798 with an experimental design. During the French Revolutionary Wars she spent some years on the Oporto station, where she captured many small privateers. The French captured her in 1806, early in the Napoleonic Wars. They lengthened her and she became the 17-gun privateer ''Duquesne''. In 1807 the British recaptured her and the Royal Navy returned her to service as the 12-gun gun-brig HMS ''Unique''. She was expended in an unsuccessful fire ship attack at Guadeloupe in 1809. Design ''Netley'' was built to a design by Sir Samuel Bentham. She was a modified and somewhat enlarged version of , a smaller version of his ''Dart''-class vessels. Bentham's designs featured little sheer, negative tumblehome, a large-breadth to length ratio with structural bulkheads, and sliding keels. They were also virtually double-ended. French Revolutionary Wars ''Netley'' was commissioned in 1798 under the command of Lieutenant Francis Godolphin Bond. Her first rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |