|
HMS Asia (1919)
Five ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Asia'', after the continent of Asia: * was a hulk purchased in 1694 and foundered in 1701. * was a 64-gun third rate launched in 1764 and broken up in 1804. * was a 74-gun third rate launched in 1811. She was renamed HMS ''Alfred'' in 1819, reduced to 50-guns in 1828 and broken up in 1865. * was an 84-gun second rate launched in 1824. She was used as a guardship from 1858 and was sold in 1908. * was an auxiliary cruiser of the British Caspian Flotilla The British Caspian Flotilla was a naval force of the Royal Navy established in the Caspian Sea in 1918. It was part of the allied intervention in the Russian Civil War. The flotilla initially reported to the Rear-Admiral Commanding, Black Sea, ... from 1918 to 1919. {{DEFAULTSORT:Asia, Hms Royal Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the World War II, Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
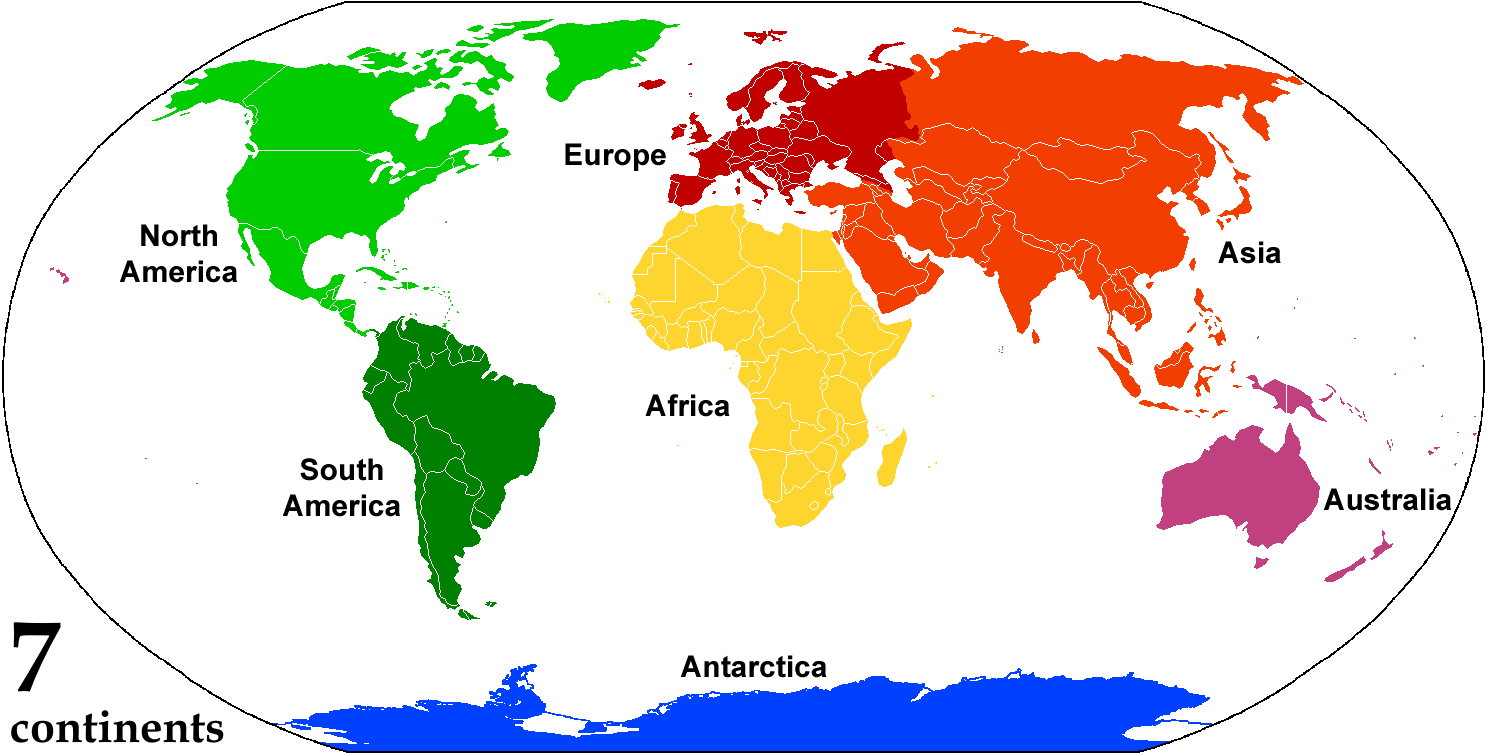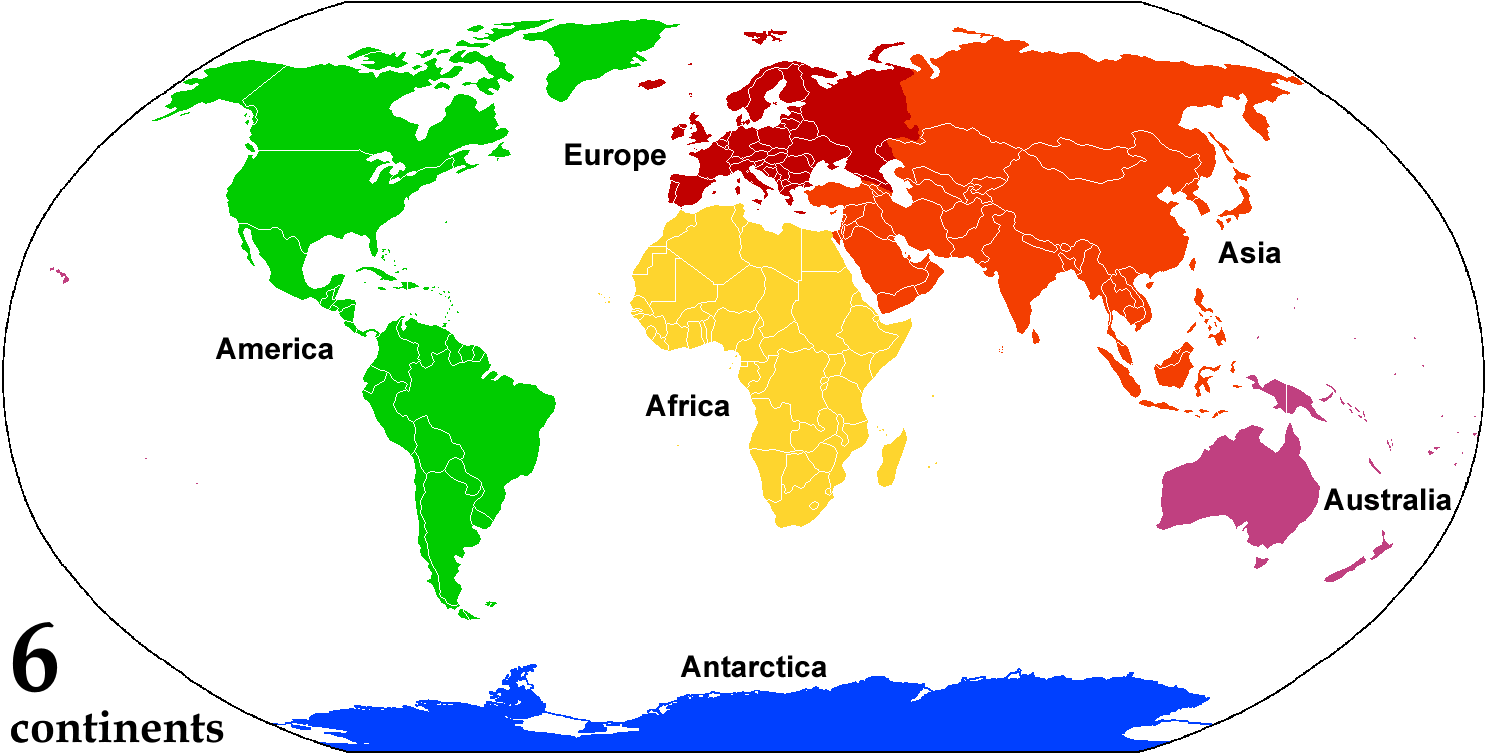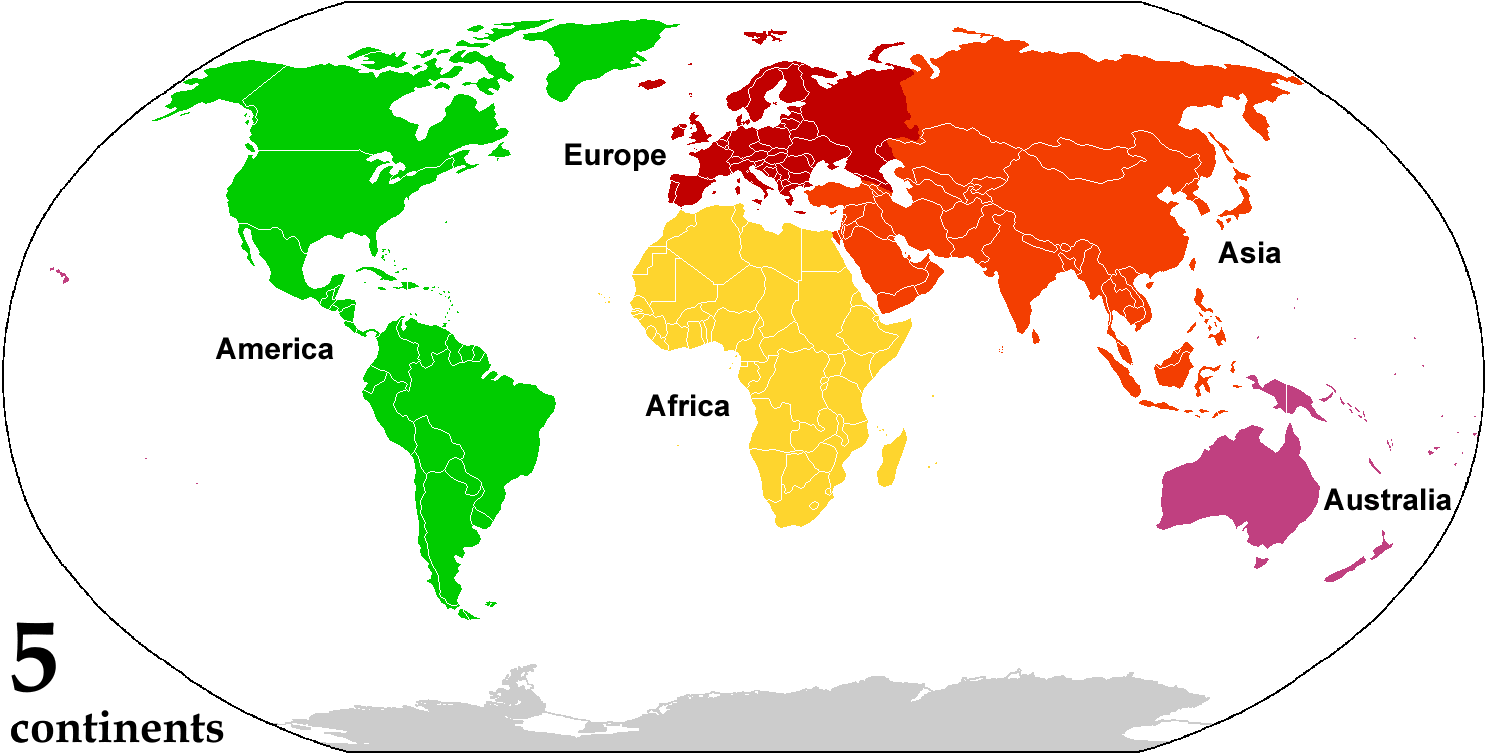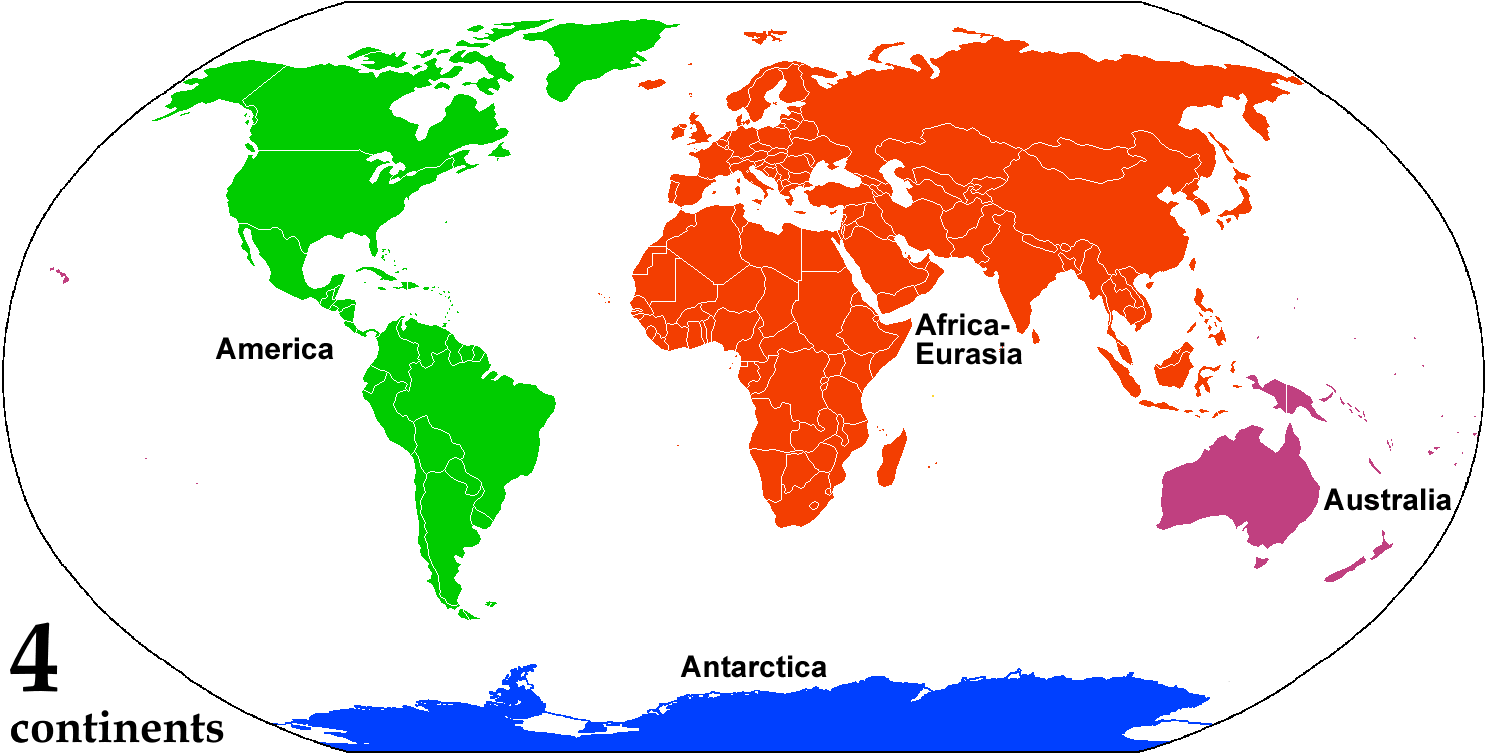
Continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven regions are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia, from largest to smallest—although sometimes Asia and Europe are considered a single continent, Eurasia." Variations with fewer continents may merge some of these, for example America, Eurasia, or Afro-Eurasia are sometimes treated as single continents, which can bring the total number as low as four. Zealandia, a largely submerged mass of continental crust, has also been described as a continent. Oceanic islands are frequently grouped with a nearby continent to divide all the world's land into geographical regions. Unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area of , about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8.7% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. In general terms, Asia is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, ling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third rate ships embodied the best compromise between sailing ability (speed, handling), firepower, and cost. So, while first-rates and second-rates were both larger and more powerful, third-rate ships were the optimal configuration. Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
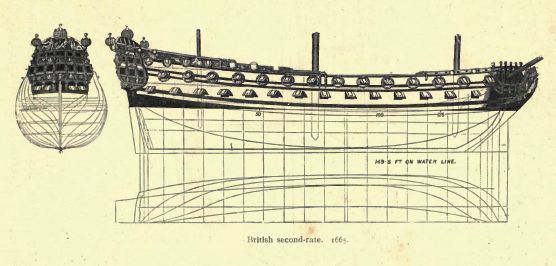
Second Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns and were originally two-deckers or had only partially armed third gun decks. A "second rate" was the second largest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six "ratings" based on size and firepower. They were essentially smaller and hence cheaper versions of the three-decker first rates. Like the first rates, they fought in the line of battle, but unlike the first rates, which were considered too valuable to risk in distant stations, the second rates often served also in major overseas stations as flagships. They had a reputation for poor handling and slow sailing. They were popular as flagships of admirals commanding the Windward and/or Leeward Islands station, which was usually a Rear-admiral of the red. Rating Typically measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Caspian Flotilla
The British Caspian Flotilla was a naval force of the Royal Navy established in the Caspian Sea in 1918. It was part of the allied intervention in the Russian Civil War. The flotilla initially reported to the Rear-Admiral Commanding, Black Sea, Caspian Sea and Sea of Marmora until 1919. History The decision to form the force was made on 11 July 1918 at the British military HQ in Baghdad. Its purpose was twofold: # To seize Krasnovodsk, the east coast terminal of the Trans-Caspian railway, and hence support the British Malleson Mission which was intervening in Turkmenistan. # To prevent Baku and the oilfields around it from falling onto the hands of the Germans or the Ottoman Empire. The force was established under the command of Commodore David Norris in September 1918. Norris traveled by road from Baghdad to Enzeli with a convoy of lorries transporting naval guns. In January 1919 he was reinforced by 12 Coastal Motor Boats sent by train from Batumi the Black Sea."The Roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |