|
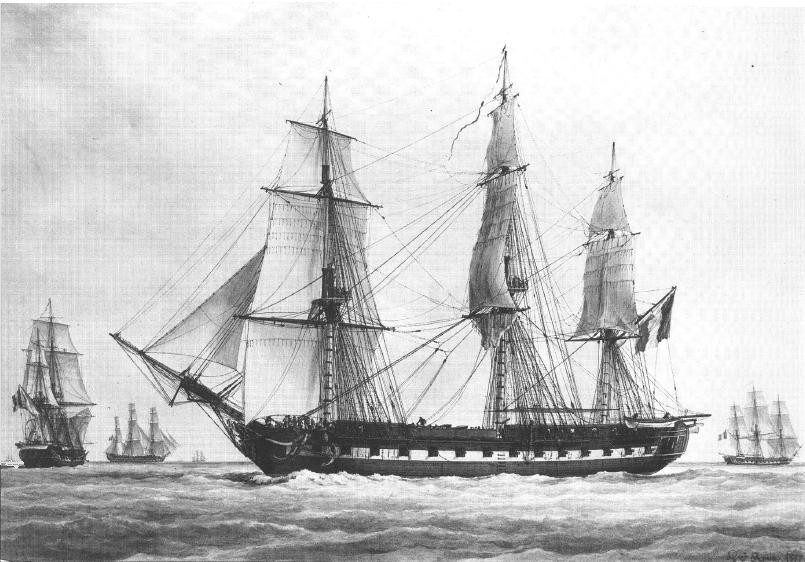
HMS Aquilon
Three ships of the Royal Navy have been named HMS ''Aquilon'', to commemorate the destruction of the French ship ''Aquilon'' by HMS ''Antelope'' in 1757. Aquilon was originally the Roman name for the North Wind. * of 1758 was a sixth-rate frigate which served in the navy until 1776. * of 1786 was a fifth-rate frigate during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars {{Infobox military conflict , conflict = Napoleonic Wars , partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars , image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg , caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ..., broken up in 1815. * HMS ''Aquilon'' was a small warship which was renamed before commissioning. Another ''Aquilon'' was captured in Havana in 1762 and commissioned into the Royal Navy, serving until 1770. {{DEFAULTSORT:Aquilon, Hms Royal Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship
A ship is a large watercraft, vessel that travels the world's oceans and other Waterway, navigable waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity and purpose. Ships have supported Geographic exploration, exploration, Global trade, trade, Naval warfare, warfare, Human migration, migration, colonization, and science. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a Full-rigged ship, ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is Square rig, square-rigged. The earliest historical evidence of boats is found in Egypt during the 4th millennium BCE. In 2024, ships had a global cargo capacity of 2.4 billion tons, with the three largest classes being ships carrying dry bulk (43%), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early Middle Ages, medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the English Navy of the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the early 18th century until the World War II, Second World War, it was the world's most powerful navy. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Aquilon
At least three ships of the French Navy have been named ''Aquilon'' *, a fifth rate In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a fifth rate was the second-smallest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six " ratings" based on size and firepower. Rating The rating system in the Royal N ... ship, sunk by HMS ''Antelope'' in 1757 *, a ''Téméraire''-class ship of the line. *, a ''Téméraire''-class ship of the line. {{DEFAULTSORT:Aquilon, French Ship French Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Antelope (1741)
HMS ''Antelope'' was a 50-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Rotherhithe on 13 March 1703. She was rebuilt once during her career, and served in the Seven Years' War and the American Revolutionary War. Orders were issued on 9 January 1738 for ''Antelope'' to be taken to pieces and rebuilt according to the 1733 proposals of the 1719 Establishment at Woolwich, from where she was relaunched on 27 January 1741. Career On 16 June 1756, she sailed from England for Gibraltar with Vice Admiral Sir Edward Hawke, 1st Baron Hawke and Rear Admiral Charles Saunders. She arrived there on 3 July with an order to supersede Admiral John Byng. ''Antelope'' returned to England with Byng, sailing on 9 July and arriving at Spithead on 26 July, where Byng was arrested before being landed on 19 August. His trial started on board ''St George'' on 27 December. On 30 April 1757, Captain Samuel Hood took command of ''Antelope''. On 15 May, after a short action off Bres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquilo (god)
Boreas (, , , , ; also , ) is the Greek god of the cold north wind, storms, and winter. Although he was normally taken as the north wind, the Roman writers Aulus Gellius and Pliny the Elder both took Boreas as a northeast wind, equivalent to the Roman god Aquilo or Septentrio. Boreas is depicted as being very strong, with a violent temper to match. He was frequently shown as a winged old man or sometimes as a young man with shaggy hair and beard, holding a conch shell and wearing a billowing cloak. Boreas's most known myth is his abduction of the Athenian princess Orithyia of Athens, Oreithyia. Description Boreas, like the rest of the wind gods, was said to be the son of Eos, the goddess of the dawn, by her husband Astraeus, a minor star-god. He is thus brother to the rest of the Anemoi (the wind gods), the five star-gods and the justice goddess Astraea. Boreas was closely associated with horses, storms, and winter. He was said to have fathered twelve colts, after taking th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a sixth-rate was the designation for small warships mounting between 20 and 28 carriage-mounted guns on a single deck, sometimes with smaller guns on the upper works and sometimes without. It thus encompassed ships with up to 30 guns in all. In the first half of the 18th century the main battery guns were 6-pounders, but by mid-century these were supplanted by 9-pounders. 28-gun sixth-rates were classed as frigates, those smaller as 'post ships', indicating that they were still commanded by a full ('post') captain, as opposed to sloops of 18 guns and less, which were under commanders. Rating Sixth-rate ships typically had a crew of about 150–240 men, and measured between 450 and 550 tons. A 28-gun ship would have about 19 officers; commissioned officers would include the captain, and two lieutenants; warrant officers would include the master, ship's surgeon, and purser. The other quarterdeck off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fifth-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a fifth rate was the second-smallest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six " ratings" based on size and firepower. Rating The rating system in the Royal Navy as originally devised had just four rates, but early in the reign of Charles I, the original fourth rate (derived from the "Small Ships" category under his father, James I) was divided into new classifications of fourth, fifth, and sixth rates. While a fourth-rate ship was defined as a ship of the line, fifth and the smaller sixth-rate ships were never included among ships-of-the-line. Nevertheless, during the Anglo-Dutch Wars of the 17th century, fifth rates often found themselves involved among the battle fleet in major actions. Structurally, these were two-deckers, with a complete battery on the lower deck, and fewer guns on the upper deck (below the forecastle and quarter decks, usually with no guns in the waist on this deck). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars () were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Habsburg monarchy, Austria, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, Russian Empire, Russia, and several other countries. The wars are divided into two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered territories in the Italian peninsula, the Low Countries, and the Rhineland with its very large and powerful military which had been totally mobilized for war against most of Europe with mass conscription of the vast French population. French success in these conflicts ensured military occupation and the spread of revolutionary principles over mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict , conflict = Napoleonic Wars , partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars , image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg , caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battles of Battle of Austerlitz, Austerlitz, Fall of Berlin (1806), Berlin, Battle of Friedland, Friedland, Battle of Aspern-Essling, Aspern-Essling, French occupation of Moscow, Moscow, Battle of Leipzig, Leipzig and Battle of Paris (1814), Paris , date = {{start and end dates, 1803, 5, 18, 1815, 11, 20, df=yes({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=05, day1=18, year1=1803, month2=11, day2=20, year2=1815) , place = Atlantic Ocean, Caucasus, Europe, French Guiana, Mediterranean Sea, North Sea, West Indies, Ottoman Egypt, Egypt, East Indies. , result = Coalition victory , combatant1 = Coalition forces of the Napoleonic Wars, Coalition forces:{{flagcountry, United Kingdom of Great Britain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Ship Aquilon (1754)
''Aquilón'' was a 68-gun ship of the line of the Spanish Navy. History She and her 11 sister ships were ordered on 15 June 1752 and their keels laid later that year at the Reales Astilleros de Esteiro. She belonged to the series popularly known as the 12 apostles or the Apostolate, all constructed simultaneously in the same shipyard by the British shipwright Rooth between 1753 and 1755 using the English method or by Jorge Juan y Santacilia. She was launched on 10 March 1754, entering service with 68 guns like the other 11 ships (some of the others later expanded to 74 guns). In mid-1754, under the command of Captain Francisco Lastarría, she sailed from Ferrol to Cadiz until December of that year. In April 1755 she was anchored in ordinary at the Arsenal de la Carraca, where it was found that she leaked and her wood rotted easily as with other ships built using the Gaztañeta method. From August 1755 onwards she underwent several modifications before being stationed at Cartagena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |