|
HMGCoA Reductase
β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A, is an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase. The research of Minor J. Coon and Bimal Kumar Bachhawat in the 1950s at University of Illinois led to its discovery. HMG-CoA is a metabolic intermediate in the metabolism of the branched-chain amino acids, which include leucine, isoleucine, and valine. Its immediate precursors are β-methylglutaconyl-CoA (MG-CoA) and β-hydroxy β-methylbutyryl-CoA (HMB-CoA). HMG-CoA reductase catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Biosynthesis Mevalonate pathway Mevalonate synthesis begins with the beta-ketothiolase-catalyzed Claisen condensation of two molecules of acetyl-CoA to produce acetoacetyl CoA. The following reaction involves the joining of acetyl-CoA and acetoacet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mevalonate Pathway
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones. The mevalonate pathway begins with acetyl-CoA and ends with the production of IPP and DMAPP. It is best known as the target of statins, a class of cholesterol lowering drugs. Statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase within the mevalonate pathway. Upper mevalonate pathway The mevalonate pathway of eukaryotes, archaea, and eubacteria all begin the same way. The sole carbon feed stock of the pathway is acetyl-CoA. The first step condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules to yield acetoacetyl-CoA. This is followed by a second condensation to form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mevalonic Acid
Mevalonic acid (MVA) is a key organic compound in biochemistry; the name is a contraction of dihydroxymethylvalerolactone. The carboxylate anion of mevalonic acid, which is the predominant form in biological environments, is known as ''mevalonate'' and is of major pharmaceutical importance. Drugs like statins (which lower levels of cholesterol) stop the production of mevalonate by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Chemistry Mevalonic acid is very soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It exists in equilibrium with its lactone form, called mevalonolactone, that is formed by internal condensation of its terminal alcohol and carboxylic acid functional groups. Mevalonolactone acts to correct statin linked myopathy and limb girdle muscular disease caused by HMG CoA reductase mutation. Biology Mevalonic acid is a precursor in the biosynthetic pathway known as the mevalonate pathway that produces terpenes and steroids. Mevalonic acid is the primary precursor of isopentenyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMG-CoA Lyase
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase (or HMG-CoA lyase) is an enzyme ( that in human is encoded by the HMGCL gene located on chromosome 1. It is a key enzyme in ketogenesis (ketone body formation). It is a ketogenic enzyme in the liver that catalyzes the formation of acetoacetate from HMG-CoA within the mitochondria. It also plays a prominent role in the catabolism of the amino acid leucine. Structure The HMGCL gene encodes a 34.5-kDa protein that is localized to the mitochondrion and peroxisome. Multible isoforms of the proteins are known due to alternative splicing. The major isoform (isoform 1) is most highly expressed in the liver whereas isoform 2 is found in energy-demanding tissues including the brain, heart, and skeletal muscle. Structure of the HMGCL protein has been resolved by X-ray crystallography at 2.1-Å resolution, and reveals that the protein may function as a dimer. Substrate access to the active site of the HMGCL enzyme involves substrate binding across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mevalonate Pathway
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones. The mevalonate pathway begins with acetyl-CoA and ends with the production of IPP and DMAPP. It is best known as the target of statins, a class of cholesterol lowering drugs. Statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase within the mevalonate pathway. Upper mevalonate pathway The mevalonate pathway of eukaryotes, archaea, and eubacteria all begin the same way. The sole carbon feed stock of the pathway is acetyl-CoA. The first step condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules to yield acetoacetyl-CoA. This is followed by a second condensation to form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils. Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all animal Cell (biology)#Eukaryotic cells, cells and is an essential structural and cholesterol signaling, signaling component of animal cell membranes. In vertebrates, hepatocyte, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. In the brain, astrocytes produce cholesterol and transport it to neurons. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as ''Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. Cholesterol also serves as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood, especially when bound to low-density lipoprotein (LDL, often referred to as "bad cholesterol"), may increase the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoprenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes", terpenoids contain additional functional groups, usually containing oxygen. When combined with the hydrocarbon terpenes, terpenoids comprise about 80,000 compounds. They are the largest class of plant secondary metabolites, representing about 60% of known natural products. Many terpenoids have substantial pharmacological bioactivity and are therefore of interest to medicinal chemists. Plant terpenoids are used for their aromatic qualities and play a role in traditional herbal remedies. Terpenoids contribute to the scent of eucalyptus, the flavors of cinnamon, cloves, and ginger, the yellow color in sunflowers, and the red color in tomatoes. Well-known terpenoids include citral, menthol, camphor, salvinorin A in the plant '' S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP+ or NAD+ as cofactors. Transmembrane oxidoreductases create electron transport chains in bacteria, chloroplasts and mitochondria, including respiratory complexes I, II and III. Some others can associate with biological membranes as peripheral membrane proteins or be anchored to the membranes through a single transmembrane helix. in Membranome database Reactions For e ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). NADPH is the reduced form, whereas NADP is the oxidized form. NADP is used by all forms of cellular life. NADP is essential for life because it is needed for cellular respiration. NADP differs from NAD by the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine moiety. This extra phosphate is added by NAD+ kinase and removed by NADP+ phosphatase. Biosynthesis NADP In general, NADP+ is synthesized before NADPH is. Such a reaction usually starts with NAD+ from either the de-novo or the salvage pathway, with NAD+ kinase adding the extra phosphate group. ADP-ribosyl cyclase allows for synthesis from nicotinamide in the salvage pathway, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mevalonate
Mevalonic acid (MVA) is a key organic compound in biochemistry; the name is a contraction of dihydroxymethylvalerolactone. The carboxylate anion of mevalonic acid, which is the predominant form in biological environments, is known as ''mevalonate'' and is of major pharmaceutical importance. Drugs like statins (which lower levels of cholesterol) stop the production of mevalonate by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Chemistry Mevalonic acid is very soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It exists in equilibrium with its lactone form, called mevalonolactone, that is formed by internal condensation of its terminal alcohol and carboxylic acid functional groups. Mevalonolactone acts to correct statin linked myopathy and limb girdle muscular disease caused by HMG CoA reductase mutation. Biology Mevalonic acid is a precursor in the biosynthetic pathway known as the mevalonate pathway that produces terpenes and steroids. Mevalonic acid is the primary precursor of isopentenyl pyroph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
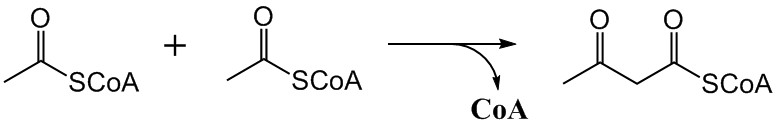
Acetoacetyl-CoA
Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis ( ketogenesis) pathway of the liver. In the ketone bodies digestion pathway (in the tissue), it is no longer associated with having HMG-CoA as a product or as a reactant. It is created from acetyl-CoA, a thioester, which reacts with the enolate of a second molecule of acetyl-CoA in a Claisen condensation reaction, and it is acted upon by HMG-CoA synthase to form HMG-CoA. During the metabolism of leucine, this last reaction is reversed. Some individuals may experience Acetoacetyl-CoA deficiency. This deficiency is classified as a disorder ketone body and isoleucine metabolism that can be inherited. Additional mutations include those with the enzymes within pathways related to Acetoacetyl CoA, including Beta-Ketothiolase deficiency and Mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase mutation. Add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, oxidized for energy production. Coenzyme A (CoASH or CoA) consists of a cysteamine, β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) through an amide linkage and 3'-phosphorylated ADP. The acetyl group (indicated in blue in the structural diagram on the right) of acetyl-CoA is linked to the sulfhydryl substituent of the β-mercaptoethylamine group. This thioester linkage is a "high energy" bond, which is particularly reactive. Hydrolysis of the thioester bond is exergonic (−31.5 kJ/mol). CoA is acetylated to acetyl-CoA by the breakdown of carbohydrates through glycolysis and by the breakdown of fatty acids through Beta oxidation, β-oxidation. Acetyl-CoA then enters the citric acid cycle, where the acetyl group is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |