|
HIPO
HIPO model (hierarchical input process output model) is a systems analysis design aid and documentation technique from the 1970s, used for representing the modules of a system as a hierarchy and for documenting each module.Sandia National Laboratories (1992)Sandia Software Guidelines Volume 5 Tools, Techniques, and Methodologies SANDIA REPORTS 85–2348qUC–32 History It was used to develop requirements, construct the design, and support implementation of an expert system to demonstrate automated rendezvous. Verification was then conducted systematically because of the method of design and implementation.Mary Ann Goodwin and Charles C. Robertson (1986)EXPERT SYSTEM VERIFICATION CONCERNS IN AN OPERATIONS ENVIRONMENT NASA paper N88-17234. The overall design of the system is documented using HIPO charts or structure charts. The structure chart is similar in appearance to an organizational chart, but has been modified to show additional detail. Structure charts can be used to displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure Chart
A structure chart (SC) in software engineering and organizational theory is a chart which shows the smallest of a system to its lowest manageable levels.IRS (2008) "Configuration Management" In: ''IRS Resources Part 2. Information Technol Chapter 27. Configuration Management''. Accessed aIRS.GOV14 November 2008. No longer online 8 November 2009. They are used in structured programming to arrange program modules into a tree. Each module is represented by a box, which contains the module's name. The tree structure visualizes the relationships between modules. Overview A structure chart is a top-down modular design tool, constructed of squares representing the different modules in the system, and lines that connect them. The lines represent the connection and or ownership between activities and subactivities as they are used in organization charts.H. Fujita & V. Gruhn (2004). ''New Trends in Software Methodologies, Tools and Techniques''. Page 6. In structured analysis structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stencil IBM-HIPO
Stencilling produces an image or pattern on a surface by applying pigment to a surface through an intermediate object, with designed holes in the intermediate object. The holes allow the pigment to reach only some parts of the surface creating the design. The stencil is both the resulting image or pattern and the intermediate object; the context in which ''stencil'' is used makes clear which meaning is intended. In practice, the (object) stencil is usually a thin sheet of material, such as paper, plastic, wood or metal, with letters or a design cut from it, used to produce the letters or design on an underlying surface by applying pigment through the cut-out holes in the material. The key advantage of a stencil is that it can be reused to repeatedly and rapidly produce the same letters or design. Although aerosol or painting stencils can be made for one-time use, typically they are made with the intention of being reused. To be reusable, they must remain intact after a design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Analysis
Systems analysis is "the process of studying a procedure or business to identify its goal and purposes and create systems and procedures that will efficiently achieve them". Another view sees systems analysis as a problem-solving technique that breaks a system down into its component pieces and analyses how well those parts work and interact to accomplish their purpose. The field of system analysis relates closely to requirements analysis or to operations research. It is also "an explicit formal inquiry carried out to help a decision maker identify a better course of action and make a better decision than they might otherwise have made." The terms analysis and synthesis stem from Greek, meaning "to take apart" and "to put together", respectively. These terms are used in many scientific disciplines, from mathematics and logic to economics and psychology, to denote similar investigative procedures. The analysis is defined as "the procedure by which we break down an intellectual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Documentation
Documentation is any communicable material that is used to describe, explain or instruct regarding some attributes of an object, system or procedure, such as its parts, assembly, installation, maintenance, and use. As a form of knowledge management and knowledge organization, documentation can be provided on paper, online, or on digital or analog media, such as audio tape or CDs. Examples are user guides, white papers, online help, and quick-reference guides. Paper or hard-copy documentation has become less common. Documentation is often distributed via websites, software products, and other online applications. Documentation as a set of instructional materials shouldn't be confused with documentation science, the study of the recording and retrieval of information. Principles for producing documentation While associated International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards are not easily available publicly, a guide from other sources for this topic may serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and is expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek language, Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchy
A hierarchy (from Ancient Greek, Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important concept in a wide variety of fields, such as architecture, philosophy, design, mathematics, computer science, organizational theory, systems theory, systematic biology, and the social sciences (especially political science). A hierarchy can link entities either directly or indirectly, and either vertically or diagonally. The only direct links in a hierarchy, insofar as they are hierarchical, are to one's immediate superior or to one of one's subordinates, although a system that is largely hierarchical can also incorporate alternative hierarchies. Hierarchical links can extend "vertically" upwards or downwards via multiple links in the same direction, following a path (graph theory), path. All parts of the hierarchy that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Structure
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization and storage format that is usually chosen for Efficiency, efficient Data access, access to data. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the Function (computer programming), functions or Operator (computer programming), operations that can be applied to the data, i.e., it is an algebraic structure about data. Usage Data structures serve as the basis for abstract data types (ADT). The ADT defines the logical form of the data type. The data structure implements the physical form of the data type. Different types of data structures are suited to different kinds of applications, and some are highly specialized to specific tasks. For example, Relational database, relational databases commonly use B-tree indexes for data retrieval, while compiler Implementation, implementations usually use hash tables to look up Identifier (computer languages), identifiers. Data s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
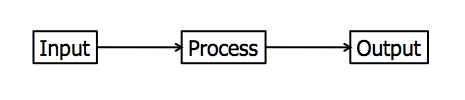
IPO Model
The input–process–output (IPO) model, or input-process-output pattern, is a widely used approach in systems analysis and software engineering for describing the structure of an information processing program or other process. Many introductory Computer programming, programming and systems analysis texts introduce this as the most basic structure for describing a process.Grady, J. O., "System Engineering Planning and Enterprise Identity", Taylor & Francis, 1995 .Zelle, J., "Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science, 2nd edition", Franklin, Beedle, & Associates, 2010.Curry, A. and Flett, P. and Hollingsworth, I., "Managing Information and Systems: The Business Perspective", Routledge, 2006. Overview A Computer Program, computer program is useful for another sort of process using the input-process-output model receives inputs from a user or other source, does some computations on the inputs, and returns the results of the computations. In essence the system sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIPOC
In process improvement, SIPOC or suppliers, inputs, process, outputs and customers (sometimes in the reversed order: COPIS) is a tool that summarizes the inputs and outputs of one or more business processes in table form, with each of the words forming a column in the table used in the analysis. It is used to define a business process from beginning to end before work on process improvement begins. History It was in use at least as early as the total quality management programs of the late 1980s and continues to be used today in Six Sigma, lean manufacturing, and business process management. COPIS variant To emphasize putting the needs of the customer foremost, the tool is sometimes called COPIS and the process information is filled out in reverse order by starting with the customer and working upstream to the supplier. Use The SIPOC is often presented at the outset of process improvement efforts such as kaizen events or during the "define" phase of the DMAIC process. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |