|
HBeAg
HBeAg is a hepatitis B viral protein, produced by the HBcAg reading frame. It is an indicator of active viral replication; this means the person infected with Hepatitis B can likely transmit the virus on to another person (i.e. the person is infectious). HBeAg is considered a marker for cccDNA replication. Structure HBeAg is an antigen that can be found between the icosahedral nucleocapsid core and the lipid envelope (the outer most layer of the hepatitis b virus). However, HBeAg is considered "nonparticulate" or "secretory". While both HBeAg and HBcAg are made from the same reading frame (multiple protein products can be produced from the same DNA sequence and when the genes "ORF Core" and "Pre C" are translated together, the result is HBeAg), HBeAg is secreted and accumulates in serum as an immunologically distinct soluble antigen. Hence the reason why the presence of both proteins together acts as a marker of viral replication, and why antibodies to these antigens are a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection. Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. For others, symptoms may appear 30 to 180 days after becoming infected and can include a rapid onset of sickness with nausea, vomiting, yellowish skin, fatigue, dark urine, and abdominal pain. Symptoms during acute infection typically last for a few weeks, though some people may feel sick for up to six months. Deaths resulting from acute stage HBV infections are rare. An HBV infection lasting longer than six months is usually considered chronic. The likelihood of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for those who are infected with HBV at a younger age. About 90% of those infected during or shortly after birth develop chronic hepatitis B, while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five develop chronic cases. Most of those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
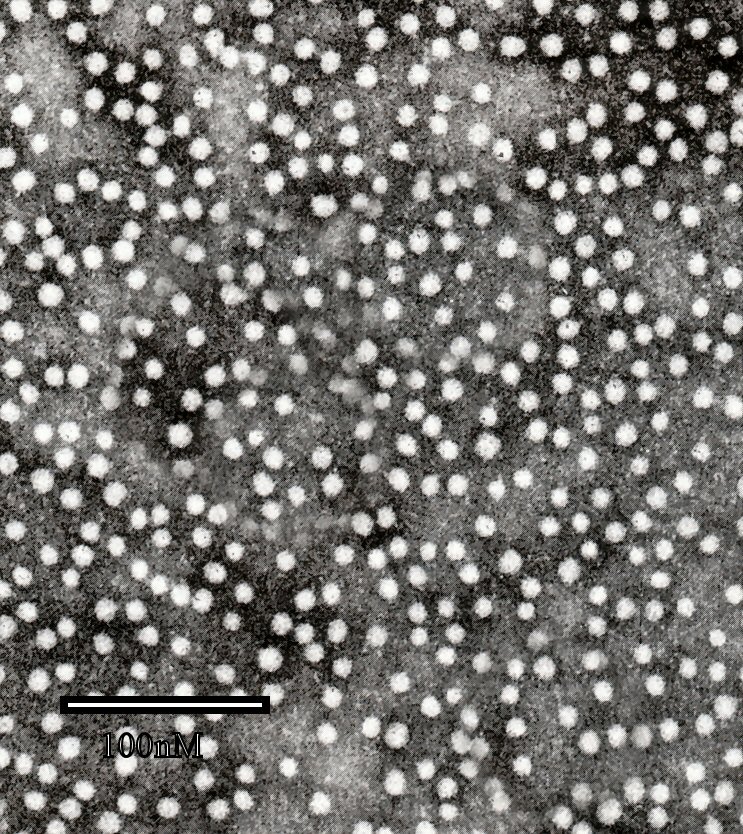
Hepatitis B Virus
''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus '' Orthohepadnavirus'' and a member of the '' Hepadnaviridae'' family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B. Disease Despite there being a vaccine to prevent Hepatitis B, HBV remains a global health problem. Hepatitis B can be acute and later become chronic, leading to other diseases and health conditions. In addition to causing hepatitis, infection with HBV can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. It has also been suggested that it may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Roles in disease Viral infection by ''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) causes many hepatocyte changes due to the direct action of a protein encoded by the virus, HBx, and to indirect changes due to a large increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) after infection. HBx appears to dysregulate a number of cellular pathways. HBx causes dysregulation in part by binding to genomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B Virus V2
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis is ''acute'' if it resolves within six months, and '' chronic'' if it lasts longer than six months. Acute hepatitis can resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer. Hepatitis is most commonly caused by the virus ''hepatovirus A'', '' B'', '' C'', '' D'', and '' E''. Other viruses can also cause liver inflammation, including cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, and yellow fever virus. Other common causes of hepatitis include heavy alcohol use, certain medications, toxins, other infections, autoimmune diseases, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Hepatitis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HBcAg
HBcAg (core antigen) is a hepatitis B viral protein. It is an indicator of active viral replication; this means the person infected with Hepatitis B can likely transmit the virus on to another person (i.e. the person is infectious). Structure and function HBcAg is an antigen that can be found on the surface of the nucleocapsid core (the inner most layer of the hepatitis B virus). While both HBcAg and HBeAg are made from the same open reading frame, HBcAg is not secreted. HBcAg is considered "particulate" and it does not circulate in the blood but recent study show it can be detected in serum by Radioimmunoassay. However, it is readily detected in hepatocytes after biopsy. The presence of both HBcAg and HBeAg proteins together act as a marker of viral replication, and antibodies to these antigens are a marker of declining replication. Interactions Tapasin can interact with HBcAg18-27 and enhance cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response against HBV. See also *HBeAg *HBsAg HBsAg (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HBsAg
HBsAg (also known as the Australia antigen) is the surface antigen of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Its presence in blood indicates current hepatitis B infection. Structure and function The viral envelope of an enveloped virus has different surface proteins from the rest of the virus which act as antigens. These antigens are recognized by antibody proteins that bind specifically to one of these surface proteins. Immunoassay Today, these antigen- proteins can be genetically manufactured (e.g. transgene '' E. coli'') to produce material for a simple antigen test, which detects the presence of HBV. It is present in the sera of patients with viral hepatitis B (with or without clinical symptoms). Patients who developed antibodies against HBsAg (anti-HBsAg seroconversion) are usually considered non-infectious. HBsAg detection by immunoassay is used in blood screening, to establish a diagnosis of hepatitis B infection in the clinical setting (in combination with other disease mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toll-like Receptor
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane-spanning receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from microbes. Once these microbes have reached physical barriers such as the skin or intestinal tract mucosa, they are recognized by TLRs, which activate immune cell responses. The TLRs include TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, TLR10, TLR11, TLR12, and TLR13. Humans lack genes for TLR11, TLR12 and TLR13 and mice lack a functional gene for TLR10. TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, and TLR10 are located on the cell membrane, whereas TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 are located in intracellular vesicles (because they are sensors of nucleic acids). TLRs received their name from their similarity to the protein coded by the toll gene. Function The ability of the immune s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-reactivity, cross-react and bind more tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunological
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there is a difference of human immunology and comparative immunology in veterinary medicine and animal biosciences. Immunology measures, uses charts and differentiate in context in medicine the studies of immunity on cell and molecular level, and the immune system as part of the physiological level as its functioning is of major importance. In the different states of both health, occurring symptoms and diseases; the functioning of the immune system and immunological responses such as autoimmune diseases, allergic hypersensitivities, or in some cases malfunctioning of immune system as for example in immunological disorders or in immune deficiency, and the specific transplant rejection) Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequence
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encased in lipid bilayers, and they infect their target cells by causing the viral envelope and cell membrane to fuse. Although there are effective vaccines against some of these viruses, there is no preventative or curative medicine for the majority of them. In most cases, the known vaccines operate by inducing antibodies that prevent the pathogen from entering cells. This happens in the case of enveloped viruses when the antibodies bind to the viral envelope proteins. The membrane fusion event that triggers viral entrance is caused by the viral fusion protein. Many enveloped viruses only have one protein visible on the surface of the particle, which is required for both mediating adhesion to the cell surface and for the subsequent membrane fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading Frame
In molecular biology, a reading frame is a way of dividing the sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid ( DNA or RNA) molecule into a set of consecutive, non-overlapping triplets. Where these triplets equate to amino acids or stop signals during translation, they are called codons. A single strand of a nucleic acid molecule has a phosphoryl end, called the 5′-end, and a hydroxyl or 3′-end. These define the 5′→3′ direction. There are three reading frames that can be read in this 5′→3′ direction, each beginning from a different nucleotide in a triplet. In a double stranded nucleic acid, an additional three reading frames may be read from the other, complementary strand in the 5′→3′ direction along this strand. As the two strands of a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule are antiparallel, the 5′→3′ direction on the second strand corresponds to the 3′→5′ direction along the first strand. In general, at the most, one reading frame in a given se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |