|
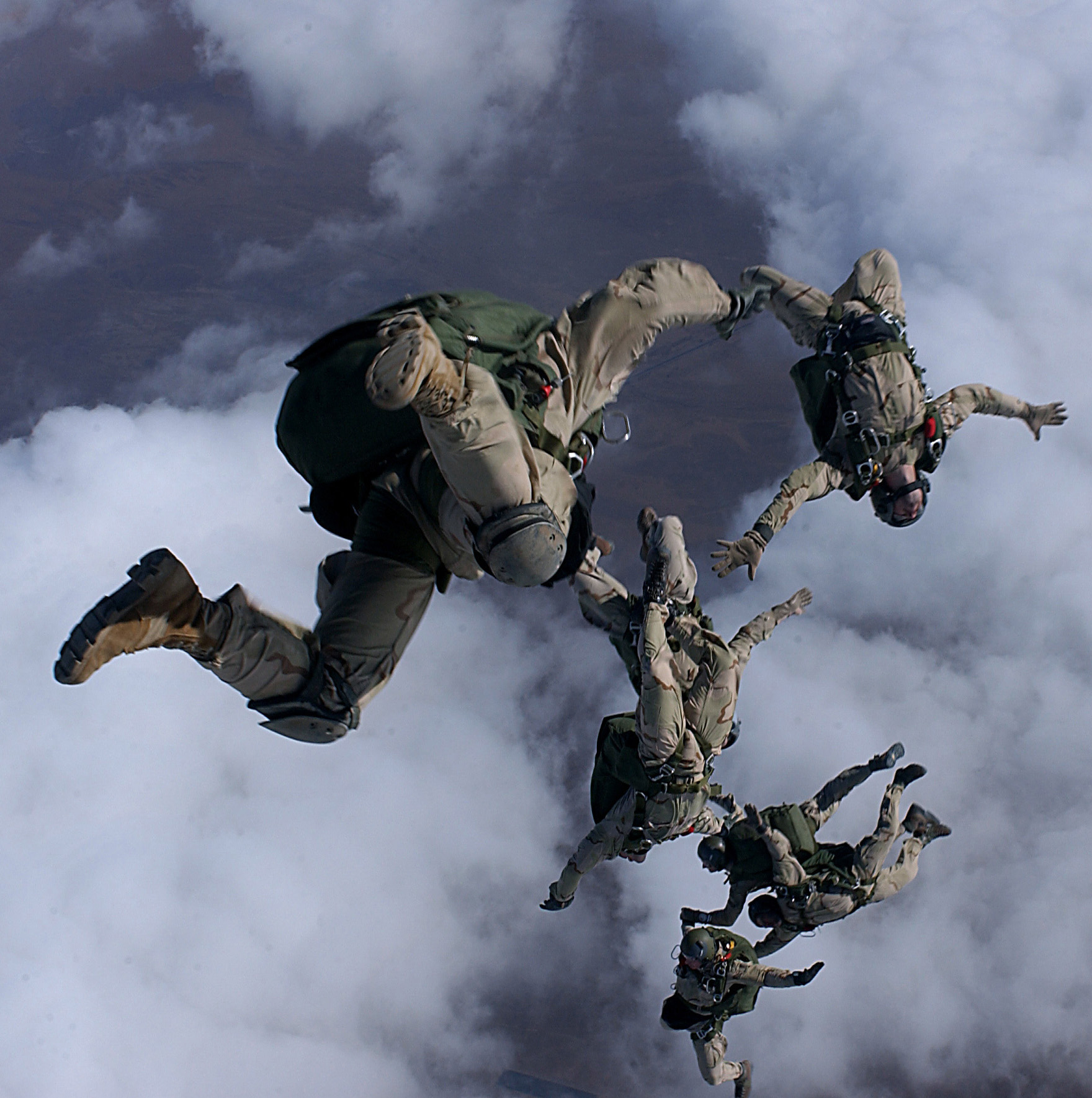
HALO Jump
High-altitude military parachuting is a style of parachuting in which personnel, equipment, or supplies are airdropped from an aircraft flying at a high altitude. The technique is often used in covert operations. High-altitude military parachuting is generally categorised as either High-altitude high-opening (HAHO) or High-altitude low-opening (HALO), depending upon the altitude at which parachutes are deployed after exiting the aircraft. In the HALO technique, the parachutist opens the parachute at a low altitude after free-falling for a period of time, while in the HAHO technique, the parachutist opens the parachute at a high altitude just a few seconds after jumping from the aircraft. In military operations, HALO is used for delivering equipment, supplies, or personnel, while HAHO is generally used exclusively for personnel. In typical HALO/HAHO insertions the troops jump from altitudes between . Military parachutists will often reach a terminal velocity of , allowing for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PJ HALO Drop
PJ most often refers to Pajamas. It can also refer to: Arts and entertainment * P.J. (film), ''P.J.'' (film), a 1968 film starring George Peppard * P.J. (comics), a character in ''The Family Circus'' comic strip * P.J. (Disney), Pete Junior, a Disney cartoon character * PJ (singer), singer and songwriter * PJ (song), "PJ" (song), by BossMan Dlow featuring Lil Baby, 2024 * P.J. (TV series), ''P.J.'' (TV series) (''Police judiciaire'') a French TV series starring Bruno Wolkowitch (1997–2009) Businesses * Peach John, a Japanese lingerie retailer with "pj" logo * PJ Media, originally known as Pajamas Media * PJ Trailers, an American trailer manufacturer Organisations * PJ, Central Directorate of the Judicial Police, Police Judiciaire, a higher branch of the French police services * PJ, Justicialist Party, (Partido Justicialista), a major Argentine political party * PJ, * PJ, Polícia Judiciária, Portuguese criminal investigation police People * P. J. (given name), including a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stapp
John Paul Stapp (July 11, 1910 – November 13, 1999) was an American career U.S. Air Force officer, flight surgeon, physician, biophysicist, and pioneer in studying the effects of acceleration forces on humans. He was a colleague and contemporary of Chuck Yeager, and became known as "the fastest man on earth". His work on Project Manhigh pioneered many developments for the US space program. Early years Born in Salvador de Bahia, Brazil, Stapp was the eldest of four sons of Reverend Charles Franklin Stapp and Mrs. Mary Louise Shannon, Baptist missionaries. He studied in Texas at Brownwood High School in Brownwood and San Marcos Baptist Academy in San Marcos. In 1931, Stapp received a bachelor's degree from Baylor University in Waco, an MA from Baylor in 1932, a PhD in Biophysics from the University of Texas at Austin in 1940, and an MD from the University of Minnesota, Twin Cities, in 1944. He interned for one year at St. Mary's Hospital in Duluth, Minnesota. Stapp w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-to-air Missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground or the sea to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft warfare, anti-aircraft system; in modern armed forces, missiles have replaced most other forms of dedicated anti-aircraft weapons, with anti-aircraft guns pushed into specialized roles. The first attempt at SAM development took place during World War II, but no operational systems were introduced. Further development in the 1940s and 1950s led to operational systems being introduced by most major forces during the second half of the 1950s. Smaller systems, suitable for close-range work, evolved through the 1960s and 1970s, to modern systems that are man-portable. Shipborne systems followed the evolution of land-based models, starting with long-range weapons and steadily evolving toward smaller designs to provide a layered defence. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with List of aircraft carriers in service, eleven in service, one undergoing trials, two new carriers under construction, and six other carriers planned as of 2024. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the U.S. Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 299 deployable combat vessels and about 4,012 operational aircraft as of 18 July 2023. The U.S. Navy is one of six United States Armed Forces, armed forces of the United States and one of eight uniformed services of the United States. The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEAL Teams
The United States Navy Sea, Air, and Land (SEAL) Teams, commonly known as Navy SEALs, are the United States Navy's primary special operations force and a component of the United States Naval Special Warfare Command. Among the SEALs' main functions are conducting small-unit special operation missions in maritime, jungle, urban, arctic, mountainous, and desert environments. SEALs are typically ordered to capture or kill high-level targets, or to gather intelligence behind enemy lines. SEAL team personnel are hand-selected, highly trained, and highly proficient in unconventional warfare (UW), direct action (DA), and special reconnaissance (SR), among other tasks like sabotage, demolition, intelligence gathering, and hydrographic reconnaissance, training, and advising friendly militaries or other forces. All active SEALs are members of the U.S. Navy. History Origins Although not formally founded until 1962, the modern-day U.S. Navy SEALs trace their roots to World War II. The Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
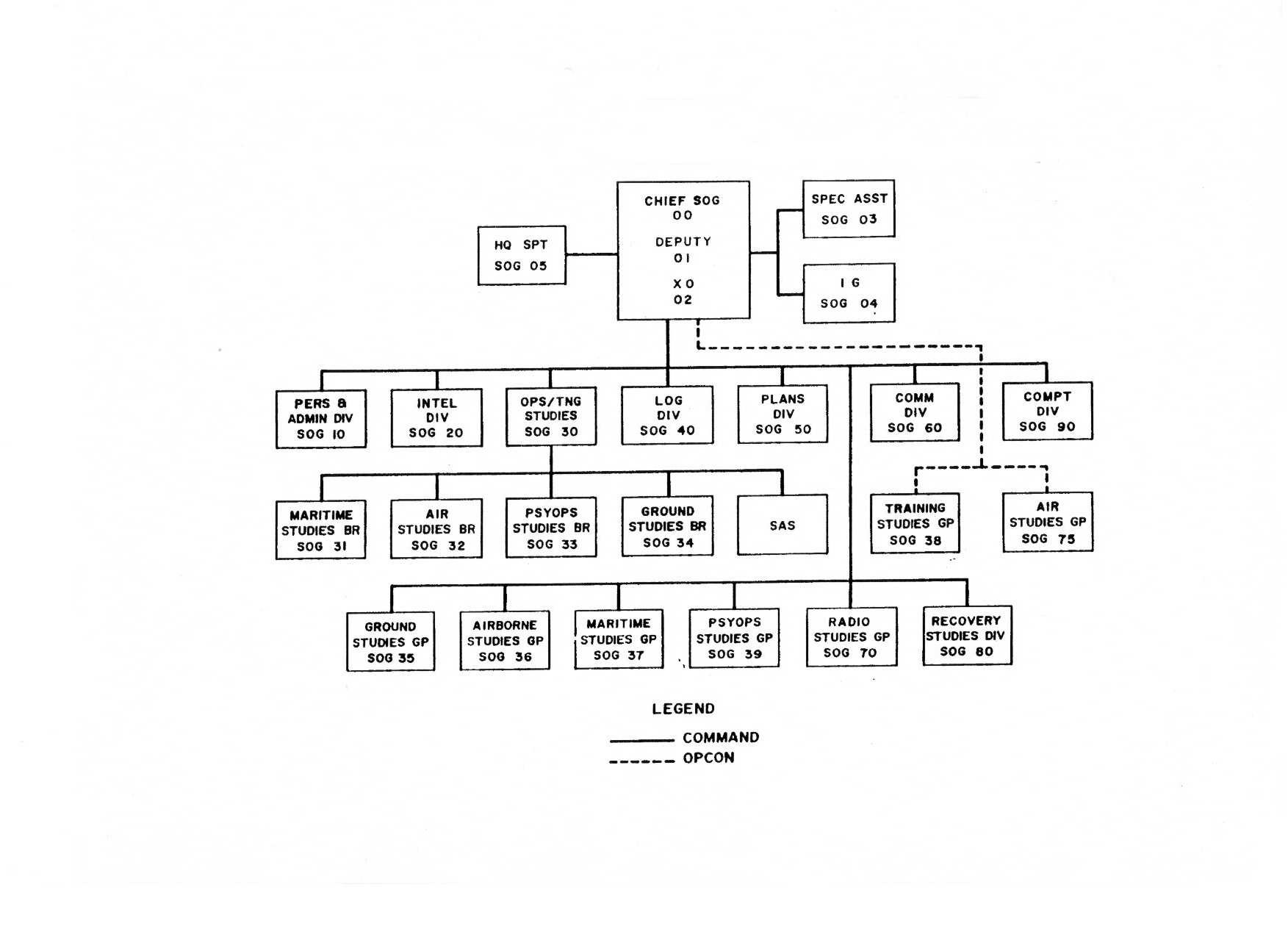
Military Assistance Command, Vietnam – Studies And Observations Group
Military Assistance Command, Vietnam – Studies and Observations Group (MACV-SOG) was a highly classified, multi-service United States special operations unit which conducted covert unconventional warfare operations before and during the Vietnam War. Established on 24 January 1964, it conducted strategic reconnaissance missions in the Republic of Vietnam (South Vietnam), the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North Vietnam), Laos, and Cambodia; took enemy prisoners, rescued downed pilots, conducted rescue operations to retrieve prisoners of war throughout Southeast Asia, and conducted clandestine agent team activities and psychological operations. The unit participated in most of the significant campaigns of the Vietnam War, including the Gulf of Tonkin incident which precipitated increased American involvement, Operation Steel Tiger, Operation Tiger Hound, the Tet Offensive, Operation Commando Hunt, the Cambodian Campaign, Operation Lam Son 719, and the Easter Offensive. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Laos
The Kingdom of Laos was the form of government in Laos from 1947 to 1975. Located in Southeast Asia at the heart of the Indochinese Peninsula, it was bordered by Burma and China to the northwest, North Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and southwest. The country was governed as a constitutional monarchy beginning with its independence on 22 October 1953. It survived until December 1975, when its last king, Sisavang Vatthana, surrendered the throne to the Pathet Lao during the civil war in Laos, who abolished the monarchy in favour of a Marxist–Leninist state called the Lao People's Democratic Republic, which has controlled Laos ever since. Given self-rule with the new Constitution in 1947 as part of the French Union and a federation with the rest of French Indochina, the 1953 Franco-Lao Treaty finally established a sovereign, independent Laos, but did not stipulate who would rule the country. In the years that followed, three grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam was supported by the Soviet Union and China, while South Vietnam was supported by the United States and other anti-communist nations. The conflict was the second of the Indochina wars and a proxy war of the Cold War between the Soviet Union and US. The Vietnam War was one of the postcolonial wars of national liberation, a theater in the Cold War, and a civil war, with civil warfare a defining feature from the outset. Direct United States in the Vietnam War, US military involvement escalated from 1965 until its withdrawal in 1973. The fighting spilled into the Laotian Civil War, Laotian and Cambodian Civil Wars, which ended with all three countries becoming Communism, communist in 1975. After the defeat of the French Union in the First Indoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Kittinger
Joseph William Kittinger II (July 27, 1928 – December 9, 2022) was an officer in the United States Air Force (USAF) who served from 1950 to 1978, and earned Command Pilot status before retiring with the rank of colonel. He held the world record for the highest skydive—102,800 feet (31.3 km)—from 1960 until 2012. Kittinger participated in the Project Manhigh and Project Excelsior high-altitude balloon flight projects from 1956 to 1960 and was the first man to fully witness the curvature of the Earth. A fighter pilot during the Vietnam War, Kittinger shot down a North Vietnamese MiG-21 jet fighter. He was later shot down as well, subsequently spending 11 months as a prisoner of war in a North Vietnamese prison before he was repatriated in 1973. In 1984, Kittinger became the first person to make a solo crossing of the Atlantic Ocean in a gas balloon. In 2012, Kittinger participated in the Red Bull Stratos project as capsule communicator at age 84, directing Fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejection Seat
In aircraft, an ejection seat or ejector seat is a system designed to rescue the aircraft pilot, pilot or other aircrew, crew of an aircraft (usually military) in an emergency. In most designs, the seat is propelled out of the aircraft by an explosive charge or rocket motor, carrying the pilot with it. The concept of an ejectable escape crew capsule has also been tried (see B-58 Hustler). Once clear of the aircraft, the ejection seat deploys a parachute. Ejection seats are common on certain types of military aircraft. History A bungee cord, bungee-assisted escape from an aircraft took place in 1910. In 1916, Everard Calthrop, an early inventor of parachutes, patented an ejector seat using compressed air. Compression springs installed under the seat were tested. The modern layout for an ejection seat was first introduced by Romanian inventor Anastase Dragomir in the late 1920s. The design featured a ''parachuted cell'' (a dischargeable chair from an aircraft or other vehicle) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
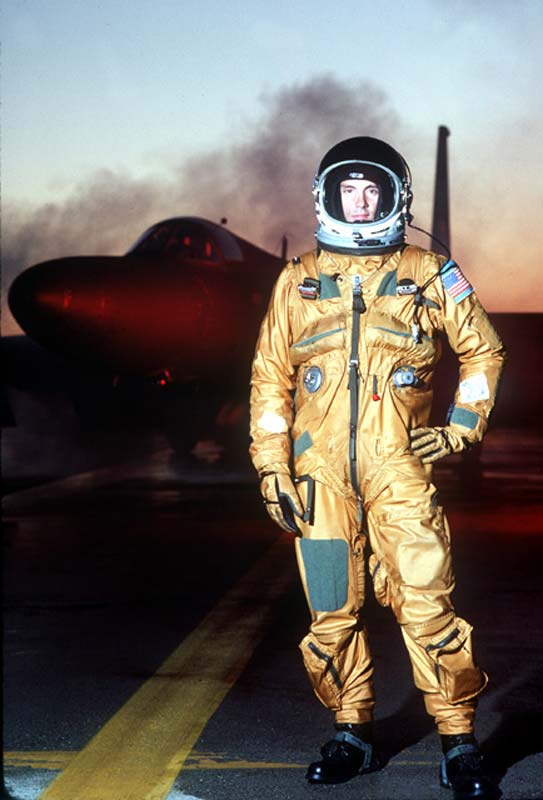
Pressure Suit
A pressure suit is a protective suit worn by high-altitude pilots who may fly at altitudes where the air pressure is too low for an unprotected person to survive, even when breathing pure oxygen at positive pressure. Such suits may be either full-pressure (e.g., a space suit) or partial-pressure (as used by aircrew). Partial-pressure suits work by providing mechanical counter-pressure to assist breathing at altitude. Background The region from sea level to around is known as the physiological-efficient zone. Oxygen levels are usually high enough for humans to function without supplemental oxygen and decompression sickness is rare. The physiological-deficient zone extends from to about . There is an increased risk of problems such as Hypoxia (medical), hypoxia, trapped-gas dysbarism (where gas trapped in the body expands), and evolved-gas dysbarism (where dissolved gases such as nitrogen may form in the tissues, i.e. decompression sickness). Above approximately oxygen-rich Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |