|
Gyurme Namgyal
Gyurme Namgyal (; ) (died 11 November 1750) was a ruling prince of Tibet of the Pholha family. He was the son and successor of Polhané Sönam Topgyé and ruled from 1747 to 1750 during the period of Tibet under Qing rule, Qing rule of Tibet. Gyurme Namgyal was murdered by the Manchu people, Manchu Ambans Fucin and Labdon in 1750. He was the last dynastic ruler of Tibet. After his death, in 1751, the Tibetan Ganden Phodrang government was taken over by the 7th Dalai Lama, Kelzang Gyatso. Thus began a new administrative order that would last for the next 150 years. Successor to the miwang Pholhané Gyurme Namgyal, also known as Dalai Batur, was the second son of the Tibetan ruling prince (miwang) Pholhané Sönam Topgyé who ruled from 1728 to 1747. The natural heir to the title was actually his eldest son Gyurme Yeshe Tseten, who had been given jurisdiction over Ngari Prefecture, Ngari (West Tibet) in 1729. Gyurme Yeshe Tseten had gathered good experience during the civil war in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Tibet
This article lists the rulers of Tibet from the beginning of legendary history. Included are regimes with their base in Central Tibet, that held authority over at least a substantial portion of the country. Pre-Imperial Yarlung dynasty * Nyatri Tsenpo * Mutri Tsenpo * Dingtri Tsenpo * Sotri Tsenpo * Mertri Tsenpo * Daktri Tsenpo * Siptri Tsenpo * Drigum Tsenpo * Pude Gunggyal * Esho Leg * Desho Leg * Tisho Leg * Gongru Leg * Drongzher Leg * Isho Leg * Zanam Zindé * Detrul Namzhungtsen * Senöl Namdé * Senöl Podé * Denöl Nam * Denöl Po * Degyal Po * Detring Tsen * Tore Longtsen * Tritsun Nam * Tridra Pungtsen * Tritog Jethogtsen * Lha Thothori * Trinyen Zungtsen * Drongnyen Deu * Tagri Nyenzig * Namri Songtsen Tibetan Empire * Songtsen Gampo 618–641 (son of Namri Songtsen) * Gungsong Gungtsen 641–646 (son) * Songtsen Gampo 646–649 (second time) * Mangsong Mangtsen 649–677 (son of Gungsong Gungtsen) * Tridu Songtsen 677–704 (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khangchenné
Khangchenné Sonam Gyalpo (; ) (died 5 August 1727) was the first important representative of the noble house Gashi () in Tibet. Between 1721 and 1727 he led the Tibetan cabinet (Kashag, ) that governed the country during the period of Qing rule of Tibet. He was eventually murdered by his peers in the cabinet, which triggered a bloody but brief civil war. The nobleman Polhané Sönam Topgyé came out as the victor and became the new ruling prince of Tibet under the Chinese protectorate. Rise to power Khangchenné (the one from Khangchen), often known by the title Dai-ching Batur in Tibetan sources, did not stem from any of the older noble houses of Tibet. He was able to make a career thanks to the Khoshut protector-king Lhabzang Khan who appointed him governor of West Tibet ( Ngari) in 1715. Simultaneously he was the chief minister of the ruler. It is possible that he reached this position since he was married to a daughter of Lhabzang Khan. The Dzungar people unexpectedly invad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luciano Petech
Luciano Petech (8 June 1914, Trieste – 29 September 2010, Rome) was an Italian scholar of Himalayan history and the early relations between Tibet, Nepal and Italy. He was Chair of History of Eastern Asia at the University of Rome from 1955 to 1984. He was a student of the Italian explorer, academic, and scholar Giuseppe Tucci. Luciano Petech was born in 1914 and retired in 1984. He learned several European languages, including Latin, as well as Asian languages such as Tibetan, Chinese, Japanese, Newari, Sanskrit, Arabic, Hindi and Urdu. Biography Petech began his teaching career in India at 25 years old, as a reader in Italian at the University of Allahabad from 1938 to 1946. His first recorded article is for the '' Calcutta Review'' in 1939. His subject was the dramas and stories of the great Italian author Luigi Pirandello, who had recently died two years after being awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature. He says “the people” in Italy had unfairly turned their backs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
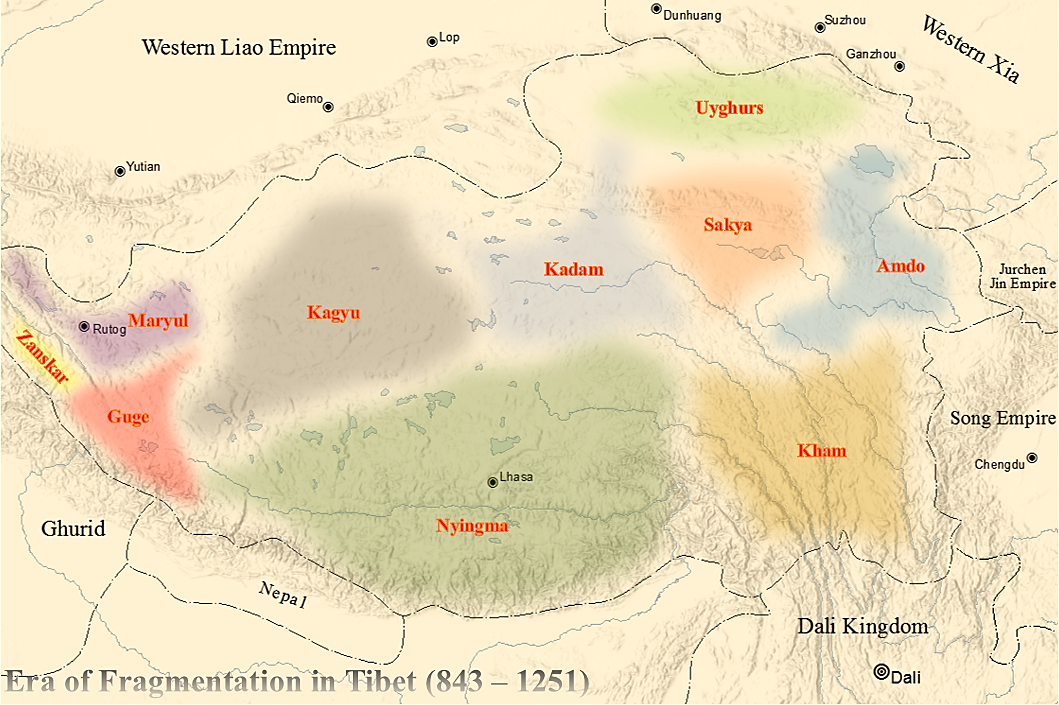
History Of Tibet
While the Tibetan plateau has been inhabited since pre-historic times, most of Tibet's history went unrecorded until the creation of Tibetan script in the 7th century. Tibetan texts refer to the kingdom of Zhangzhung (c. 500 BCE – 625 CE) as the precursor of later Tibetan kingdoms and the originators of the Bon religion. While mythical accounts of early rulers of the Yarlung dynasty exist, historical accounts begin with the introduction of Tibetan script from the unified Tibetan Empire in the 7th century. Following the dissolution of Tibetan Empire and a Era of Fragmentation, period of fragmentation in the 9th–10th centuries, a Buddhist revival in the 10th–12th centuries saw the development of three of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. After a period of control by the Mongol Empire and the Yuan dynasty, Tibet effectively became independent in the 14th century and was ruled by a succession of noble houses for the next 300 years. In the 16th century, the Dalai Lama t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lhasa Riot Of 1750
The Lhasa riot of 1750 or Lhasa uprising of 1750 took place in the Tibetan capital Lhasa, and lasted several days during the period of the Qing dynasty's patronage in Tibet. The uprising began on 11 November 1750 after the expected new regent of Tibet, Gyurme Namgyal, was assassinated by two Chinese diplomats, or ambans. As a result, both ''ambans'' were murdered, and 51 Qing soldiers and 77 Chinese citizens were killed in the uprising. A year later the leader of the rebellion, Lobsang Trashi, and fourteen other rebels were executed by Qing officials. Origins of the riot Pholhanas, the regent of Tibet, died in February 1747, during his time in office the country had enjoyed a relatively tranquil period, still, he had had discords with the Dalai Lama and news of them had reached Beijing after 1745. The ambans had mediated some of these conflicts, but the relations between them remained tense. In 1746 the Dalai Lama secretly sent a mission to Beijing to complain to the Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India and China since 1959.The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kashmir dispute is supported by the WP:TERTIARY, tertiary sources (a) through (e), reflecting WP:DUE, due weight in the coverage. Although "controlled" and "held" are also applied neutrally to the names of the disputants or to the regions administered by them, as evidenced in sources (h) through (i) below, "held" is also considered politicised usage, as is the term "occupied", (see (j) below). (a) (subscription required) Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent ... has been the subject of dispute between India and Pakistan since the partition of the Indian subcontinent in 1947. The northern and wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand'), also known as Northern Xinjiang or Beijiang, is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. Bound by the Altai Mountains to the north and the Tian Shan mountain range to the south, Dzungaria covers approximately , and borders Kazakhstan to the west and Mongolia to the east. In contexts prior to the mid-18th century Dzungar genocide, the term "Dzungaria" could cover a wider area, coterminous with the Oirat-led Dzungar Khanate. Although Dzungaria is geographically, historically, and ethnically distinct from the Tarim Basin or Southern Xinjiang (Nanjiang), the Manchu-led Qing dynasty integrated both areas into one province, Xinjiang. Dzungaria is Xinjiang's center of heavy industry, generates most of the region's GDP, and houses its political capital Ürümqi ( Oirat for 'beautiful pasture'). As such, Dzungaria continues to attract intraprovincial and interprovinci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese People
The Chinese people, or simply Chinese, are people or ethnic groups identified with Greater China, China, usually through ethnicity, nationality, citizenship, or other affiliation. Chinese people are known as Zhongguoren () or as Huaren () by speakers of standard Chinese, including those living in Greater China as well as overseas Chinese. Although both terms both refer to Chinese people, their usage depends on the person and context. The former term is commonly (but not exclusively) used to refer to the citizens of the People's Republic of China—especially mainland China. The term Huaren is used to refer to ethnic Chinese, and is more often used for those who reside overseas or are non-citizens of China. The Han Chinese are the largest ethnic group in China, comprising approximately 92% of its Mainland China, Mainland population. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ü-Tsang
Ü-Tsang (དབུས་གཙང་། Wylie; dbus gtsang) is one of the three Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo to the northeast and Kham to the east. Geographically Ü-Tsang covers the Yarlung Tsanpo drainage basin, the western districts surrounding and extending past Mount Kailash, and much of the Changtang plateau to the north. The Himalayas define Ü-Tsang's southern border. Ü-Tsang is the cultural heartland of the Tibetan people. It was formed by the merging of two earlier power centers of Ü (), controlled by the Gelug lineage of Tibetan Buddhism under the early Dalai Lamas, and Tsang (), which extended from Gyantse to the west and was controlled by the rival Sakya lineage. Military victories by the Khoshut Güshi Khan who had backed the 5th Dalai Lama consolidated power over the combined region. The region of Ngari in the northwest was incorporated into Ü-Tsang after the Tibet–Ladakh–Mughal War. The Yarlung dynasty had governed the Yarlung and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Tibet
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object. Central may also refer to: Directions and generalised locations * Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as Middle Africa * Central America, a region in the centre of America continent * Central Asia, a region in the centre of Eurasian continent * Central Australia, a region of the Australian continent * Central Belt, an area in the centre of Scotland * Central Europe, a region of the European continent * Central London, the centre of London * Central Region (other) * Central United States, a region of the United States of America Specific locations Countries * Central African Republic, a country in Africa States and provinces * Blue Nile (state) or Central, a state in Sudan * Central Department, Paraguay * Central Province (Kenya) * Central Province (Papua New Guinea) * Central Province (Solomon Islands) * Central Province, Sri Lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, personal name Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. He reigned officially from 1735 until his abdication in 1796, but retained ultimate power subsequently until his death in 1799, making him one of the longest-reigning monarchs in history as well as one of the longest-lived. The fourth and favourite son of the Yongzheng Emperor, Qianlong ascended the throne in 1735. A highly ambitious military leader, he led Ten Great Campaigns, a series of campaigns into Inner Asia, Burma, Nepal and Vietnam and suppressed rebellions in Jinchuan County, Jinchuan and Taiwan. During his lifetime, he was given the deified title Emperor Manjushri by the Qing's Tibetan subjects. Domestically, Qianlong was a major patron of the arts as well as a prolific writer. He sponsored the compilation of the ''Siku Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |